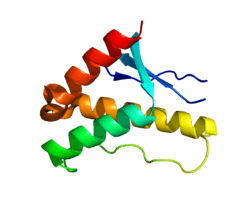
SNX17
Sorting nexin-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX17 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phox (PX) domain, which is a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking. This protein does not contain a coiled coil region, like some family members, but contains a B41 domain. This protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin, and may function in the intracellular trafficking of P-selectin.[7]
Interactions
SNX17 has been shown to interact with Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8[5]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000115234 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029146 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 Stockinger W, Sailler B, Strasser V, Recheis B, Fasching D, Kahr L, Schneider WJ, Nimpf J (Aug 2002). "The PX-domain protein SNX17 interacts with members of the LDL receptor family and modulates endocytosis of the LDL receptor". EMBO J. 21 (16): 4259–67. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf435. PMC 126172. PMID 12169628.
- ↑ Knauth P, Schlüter T, Czubayko M, Kirsch C, Florian V, Schreckenberger S, Hahn H, Bohnensack R (Mar 2005). "Functions of sorting nexin 17 domains and recognition motif for P-selectin trafficking". J. Mol. Biol. 347 (4): 813–25. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.004. PMID 15769472.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: SNX17 sorting nexin 17".
Further reading
- Nomura N, Nagase T, Miyajima N, Sazuka T, Tanaka A, Sato S, Seki N, Kawarabayasi Y, Ishikawa K, Tabata S (1994). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. II. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0041-KIAA0080) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1". DNA Res. 1 (5): 223–9. doi:10.1093/dnares/1.5.223. PMID 7584044.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Hoja MR, Wahlestedt C, Höög C (2000). "A visual intracellular classification strategy for uncharacterized human proteins". Exp. Cell Res. 259 (1): 239–46. doi:10.1006/excr.2000.4948. PMID 10942595.
- Florian V, Schlüter T, Bohnensack R (2001). "A new member of the sorting nexin family interacts with the C-terminus of P-selectin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281 (4): 1045–50. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4467. PMID 11237770.
- Teasdale RD, Loci D, Houghton F, Karlsson L, Gleeson PA (2001). "A large family of endosome-localized proteins related to sorting nexin 1". Biochem. J. 358 (Pt 1): 7–16. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580007. PMC 1222026. PMID 11485546.
- Gevaert K, Goethals M, Martens L, Van Damme J, Staes A, Thomas GR, Vandekerckhove J (2003). "Exploring proteomes and analyzing protein processing by mass spectrometric identification of sorted N-terminal peptides". Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (5): 566–9. doi:10.1038/nbt810. PMID 12665801.
- Burden JJ, Sun XM, García AB, Soutar AK (2004). "Sorting motifs in the intracellular domain of the low density lipoprotein receptor interact with a novel domain of sorting nexin-17". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (16): 16237–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313689200. PMID 14739284.
- Williams R, Schlüter T, Roberts MS, Knauth P, Bohnensack R, Cutler DF (2004). "Sorting nexin 17 accelerates internalization yet retards degradation of P-selectin". Mol. Biol. Cell. 15 (7): 3095–105. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-02-0143. PMC 452567. PMID 15121882.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, Mougin C, Groizeleau C, Hamburger A, Meil A, Wojcik J, Legrain P, Gauthier JM (2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- van Kerkhof P, Lee J, McCormick L, Tetrault E, Lu W, Schoenfish M, Oorschot V, Strous GJ, Klumperman J, Bu G (2005). "Sorting nexin 17 facilitates LRP recycling in the early endosome". EMBO J. 24 (16): 2851–61. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600756. PMC 1187941. PMID 16052210.
- Czubayko M, Knauth P, Schlüter T, Florian V, Bohnensack R (2006). "Sorting nexin 17, a non-self-assembling and a PtdIns(3)P high class affinity protein, interacts with the cerebral cavernous malformation related protein KRIT1". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 345 (3): 1264–72. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.04.129. PMID 16712798.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.