Proposed secession of Republika Srpska
_-_colored.svg.png)
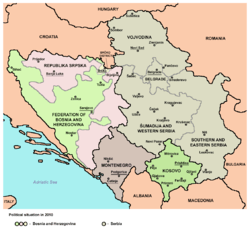
The Dayton Agreement ended the Bosnian War and created the federal republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), made up of two entities, the Bosniak and Croat-inhabited Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (FBiH), and the Serb-inhabited Republika Srpska (RS). In the first years after the war, the Bosnian Serbs were viewed of as "anti-Dayton", however, since 2000, they are staunch supporters of the Dayton Agreement and preservation of RS. Bosniaks, overall, view RS as illegitimate and would see it abolished.[1] There has been statements in RS regarding a theoretical future independence referendum from BiH in case of abolition.[2] The 2006 Montenegrin independence referendum and Kosovo's declaration of independence in 2008 have raised the issue of RS's referendum and possibility of unification with Serbia.[3] In 2015, RS government SNSD stated it would call an independence referendum in 2018 if RS's autonomy is not preserved, following a crisis in the country regarding judicial and police matters.
Background
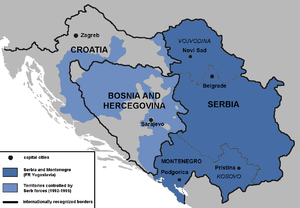
During the Yugoslav Wars, the aim of Republika Srpska (RS), a Serb-controlled territory in the SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, was the unification with the rest of the "Serb lands" — Republika Srpska Krajina (RSK, in Croatia), Republic of Serbia and Republic of Montenegro (into FR Yugoslavia).[4] The "United Serb Republic" was a project of unification of the two self-proclaimed Serb states, RS and RSK, with the intent of it later being annexed by the "mother-state of Serbia".[5]
The Serb and Croat political leadership agreed on a partition of BiH with the 1991 Karađorđevo agreement and the 1992 Graz agreement, leading the way to a tripartite division of the country.[6] The Serb-Croat negotiations also resulted in the Croat forces turning against the Bosnian Army in the Croat–Bosniak War (1992–94).[7] The failed Graz agreement would see the establishment of a small Bosniak buffer state.[8] The Dayton Agreement (November–December 1995) ended the war and created the federal republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), made up of two entities, the Bosniak and Croat-inhabited Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (FBiH), and the Serb-inhabited Republika Srpska (RS). As noted by international relations expert Niels van Willigen: "Whereas the Bosnian Croats and Bosnian Serbs could identify themselves with Croatia or Serbia respectively, the absence of a Bosniak state made the Bosniaks firmly committed to Bosnia as a single political entity."[9]
History
Post-war
On 12 September 1996, Biljana Plavšić called for the secession of RS and unification with FRY; as it contravened the Dayton Agreement, the OSCE forced her to publicy retract the statement.[10] Propaganda texts appeared in 1996 calling for a Bosniak state.[11]
2000s
In the first years after the war, the Bosnian Serbs were viewed of as "anti-Dayton", however, since 2000, they are staunch supporters of the Dayton Agreement and preservation of RS.[12] Meanwhile, the Bosniak Party for Bosnia and Herzegovina has called for the abolition of RS.[12]
An international policy of partitioning Kosovo and unification of Republika Srpska with Serbia and Montenegro was seen as offering "long-term security and stability for the region", according to Aleksandar Jokic (2003).[13]
On 15 June 2006, a demonstration was held in Banja Luka in which it was demanded that in case Kosovo becomes independent, RS must hold an independence referendum. In 2007, the "Plebiscit of Republika Srpska" demanding an independence referendum was handed over to the National Assembly. In 2007, Bosniak and Bosnian Croat members of the Presidency called for the abolishment of the entities.[14] In 2007, American scholar Walid Phares (later Trump adviser) argued that Republika Srpska should be given the same rights as Kosovo.[15]

Since Kosovo's declaration of independence Bosnian Serb nationalists have called for Milorad Dodik to fulfill his promises and call a referendum. Dodik has since said he will only call a referendum if Srpska's autonomy is threatened.[16] Despite this, Bosnian Serb lawmakers passed a resolution on 21 February 2008 calling for an independence referendum if a majority of the UN members, especially members of the European Union (EU), recognise Kosovo's declaration of independence.[17] After the resolution was passed the U.S. cut aid to the Alliance of Independent Social Democrats (SNSD) and the resolution was condemned by the EU.[18] The Peace Implementation Council (PIC) overseeing Bosnia and Herzegovina said the country's entities have no right to secede.[19] The High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, Miroslav Lajčák, said RS has "absolutely no right" to secede and that he would use his Bonn Powers "if there are threats to peace and stability" or the Dayton peace agreement,[20] "Republika Srpska does not have the right to secede from BiH, at the same time no one can unilaterally abolish Republika Srpska."[21] In an interview, Dodik said if most countries recognise Kosovo's self-proclaimed independence, this would legitimise the right to secession and added "we do not see a single reason why we should not be granted the right to self-determination, the right envisaged in international conventions."[22] Serbian President Boris Tadić said that Serbia does not support a breakup of Bosnia and that, as a guarantor of the Dayton Accords that brought peace to Bosnia, supports Bosnia’s territorial integrity.[23]
2010s

According to a poll of Bosnian Serbs taken by the Brussels-based Gallup Balkan Monitor in November 2010, 88% would support a referendum being called on Republika Srpska's independence from Bosnia and Herzegovina.[24]
In 2011, RS planned for a referendum on leaving Bosnian state federal institutions (supra-entity), which was thwarted by the EU.[25]
In 2012, Dodik said that Republika Srpska one day would be independent.[26] In 2013, there were discussions on the matter.[27] Steven Meyer, former CIA director and expert on the Balkans, said in 2013 and 2014 that he believes that Republika Srpska will become independent in time, that Bosnia and Herzegovina is a made-up state only existing on paper, and that the people should decide for itself.[28]
The largest Serb party in Bosnia and Herzegovina, SNSD, adopted a resolution in April 2015 in which it is stated that unless RS is able to strengthen its autonomy, the RS assembly would call on a referendum to break from the FBiH in 2018;[29] although this referendum on the state court and prosecution "would not weaken the state judiciary", it "would destabilise the country" says Bosnian legal experts.[30] SDA, the largest party in BiH, adopted a resolution in May 2015 in which the country would be reorganized into five regions – the removal of RS.[31] Milorad Dodik warned in November 2015 that if the Constitutional Court was not reformed, it would break up the country.[32]
In January 2016, Dodik claimed that American lobbyists asked for a billion dollars in return for independence in 10 to 15 years.[33] American analysts of Mic claim that RS will become independent by 2025.[34] BMI Research said, in the Republika Srpska: How Likely Is Independence? analysis, that "Bosnia's Serbian entity, Republika Srpska (RS), is unlikely to achieve formal independence over the next five years, owing to widespread opposition on the part of the EU and US, which do not wish to see a redrawing of Balkan borders. RS could conceivably declare independence regardless, but it would risk being diplomatically and economically isolated."[35] In February, the RS court referendum was indefinitely postponed.[36] US Balkan analyst Daniel Serwer said in May 2015 that RS would never become independent.[37] On 31 May 2016, Dodik stated that never before has RS had the danger of disappearing as now.[38]
In December 2016, High Representative Valentin Inzko threatened that 'separatism', a RS independence referendum, would force international 'intervention'.[39] He also stated that the international community would never recognize an independent RS, and also that he had the powers to replace RS President Dodik, but that those 'times have passed. Today we need domestic solutions and responsibility'.[40]
In May 2017 Steven Meyer, while speaking on the situation in Macedonia and Kosovo and the possible creation of Greater Albania, also stated that Bosnia and Herzegovina was "far from a united country",[41] and in July said that "It remains a country in name only; a fiction that is real only in the minds of outdated, mostly mid-level American—and some European—diplomats."[42]
In June[43] and again in September 2017 RS President Dodik stated that plans of the 2018 independence referendum had been dropped.[44]
In November 2017 Presidency member Bakir Izetbegović threatened with war if Republika Srpska opts for independence, and at the same time controversially said that Bosnia and Herzegovina should recognize the independence of Kosovo.[45] On 22 November 2017 a discussion was held on the matter on the TV show Globalno of RTV BN.[46]
Polls
| Date | Source | Samples | For | Against |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15–21 June 2007 | 1,699 (992 RS, 707 FBiH) | 51% (83% Serbs live in RS, 2.5% in FBiH)[47] | 46% | |
| November 2010 | Gallup Balkan Monitor[24] | (Bosnian Serbs) | 88% (83% Serbs live in RS)[47] | |
| 17–20 July 2015 | Centar za društvena istraživanja i analize[48] | 1,414 (RS - 83% Serbs live in RS)[47] | 53,54% | 15,34% |
See also
References
- ↑ Joanne McEvoy; Brendan O'Leary (2 May 2013). Power Sharing in Deeply Divided Places. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 267. ISBN 0-8122-4501-6.
- ↑ Adis Merdzanovic (1 August 2015). Democracy by Decree: Prospects and Limits of Imposed Consociational Democracy in Bosnia and Herzegovina. ibidem. pp. 328–. ISBN 978-3-8382-6792-0.
- ↑ Trbovich 2008.
- ↑ Bernard A. Cook (27 January 2014). Europe Since 1945: An Encyclopedia. Taylor & Francis. pp. 331–. ISBN 978-1-135-17939-7.
- ↑ Međimorec, Miroslav (2002). "The Medak Pocket". National Security and the Future. Zagreb: St. George Association. 3 (3–4): 29–30.
- ↑ Reneo Lukic; Allen Lynch (1996). Europe from the Balkans to the Urals: The Disintegration of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union. SIPRI. p. 209–211. ISBN 978-0-19-829200-5.
- ↑ Laura Silber (1 January 1997). Yugoslavia: Death of a Nation. Penguin Books. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-14-026263-6.
- ↑ Blaine, Harden (1992-05-08). "Warring Factions Agree on Plan to Divide up Former Yugoslavia". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2009-08-11.
- ↑ Niels van Willigen (18 July 2013). Peacebuilding and International Administration: The Cases of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo. Routledge. pp. 52–. ISBN 978-1-134-11725-3.
- ↑ Robert Bideleux; Ian Jeffries (24 January 2007). The Balkans: A Post-Communist History. Routledge. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-1-134-58328-7.
- ↑ FBIS Daily Report: East Europe. The Service. 1996. p. 20.
- 1 2 Bose 2002.
- ↑ Aleksandar Jokic (26 February 2003). Lessons of Kosovo: The Dangers of Humanitarian Intervention. Broadview Press. pp. 180–. ISBN 978-1-55111-545-0.
- ↑ "Bosnian Presidency members call for abolition of entities". Balkan Insight. 2007.
- ↑ "Trump adviser advocated for Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina". Telegraf. November 2016.
- ↑ "Bosnia's Dodik Calms Secession Fears". Balkan Insight (Bosnia). Balkan Insight Reporting Network. 2008-02-20. Archived from the original on 2008-02-26. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serbs threaten secession over Kosovo". New York City: Reuters. 2008-02-22. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ↑ "U.S. cuts aid to main Bosnian Serb party". PR-inside. 2008-03-04. Archived from the original on February 10, 2012. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- ↑ "Bosnia Serb PM Dismisses US Aid Cuts". Balkan Insight (Bosnia). Balkan Insight Reporting Network. 2008-03-05. Archived from the original on 2008-03-07. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- ↑ "Major powers reject Bosnian Serb secession calls". Agence France-Presse (Paris). 2008-02-27. Archived from the original on 2008-03-03. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- ↑ "Existence of Bosnia and Herzegovina cannot be questioned". EUSR / OHR. 2008-01-30. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ "Dodik insists RS has right to self-determination". B92. 2008-03-09. Archived from the original on 2008-04-13. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- ↑ "Policy of peace Serbia's goal – Tadić". B92. 2008.
- 1 2 "Za nezavisnu RS 88 odsto građana -- poll". Gallup Balkan Monitor. 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Bosnia: What Does Republika Srpska Want?". Crisis Group. 2011. Archived from the original on 2016-05-20.
- ↑ "Dodik: Republika Srpska Will Be Independent". Balkan Insight. 2012.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serb Leaders Still Talking Secession". Institute for War and Peace Reporting. 2013.
- ↑ "Meyer: Srpska bi mogla postati dio Srbije". Bljesak. ; "BIH je izmisljena drzava". Hercegovina.
- ↑ "Biggest Serb party in Bosnia threatens 2018 secession". Reuters. 25 April 2015.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serb Referendum 'Can't Destroy State Judiciary'". Balkan Insight. 1 February 2016.
- ↑ "Dodik: Sramna rezolucija, SDA trazi ukidanje Republike Srpske". Srbija Danas. 27 May 2015.
- ↑ "Serb Leader Warns Bosnia Could Break Up". Balkan Insight. 2 December 2015.
- ↑ "ДОДИК ОТКРИВА: Американци су ми тражили милијарду долара за независност Републике Српске!". Pravda. 12 January 2016.
- ↑ "Republika Srpska nezavisna do 2025. godine?!". Telegraf.
- ↑ "Republika Srpska: How Likely Is Independence?". BMI Research.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serb leader puts controversial referendum on hold". Balkan Insight. 9 February 2016.
- ↑ "U.S. analyst tells Dodik "RS will never be independent"". B92. 17 May 2016.
- ↑ "Dodik: Republika Srpska nije nikada bila u opasnosti da nestane kao sada". Kurir.
- ↑ "Incko preti umesto da miri". Novosti.
- ↑ "Incko: Imam ovlašćenja da smenim Dodika, ali..." B92.
- ↑ "Ex CIA chief on Balkans Steven Meyer: Border changes may happen in Kosovo and Macedonia". Oculus News. May 2017.
- ↑ "Steven E. Meyer: Where is the Leadership in the Balkans?". Nedeljnik. July 2017.
- ↑ "Bosnia's Serb Republic leader: No breakaway vote next year". Politico. June 2017.
- ↑ "Dodik Drops Plans For Holding 2018 Republika Srpska Independence Referendum". Beta. September 2017.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serbs Threaten Walkout Over Izetbegovic Statement". Balkan Insight. 14 November 2017.
- ↑ "Da li je moguća nezavisnost RS?". RTV BN.
- 1 2 3 "Census of population, households and dwellings in Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2013: Final results" (PDF). Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina. June 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ↑ "Anketa: Više od polovine ispitanika za samostalnost RS, vole Dodika, a vjeruju crkvi". Nezavisne. 2015.
Further reading
- Bose, Sumantra (2002). Bosnia After Dayton: Nationalist Partition and International Intervention. Oxford University Press. pp. 26–. ISBN 978-0-19-515848-9.
- Rajko Kuzmanović; Dragoljub Mirjanić (2005). The Republic of Srpska - Tenth Years of the Dayton Peace Agreement. Academy of Sciences and Arts of the Republika Srpska. ISBN 978-99938-631-9-9.
- Trbovich, Ana S. (2008). A Legal Geography of Yugoslavia's Disintegration. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 381–. ISBN 978-0-19-533343-5.
External links
- "Is War About to Break Out in the Balkans?". Foreign Policy.
- "Is Republika Srpska About to Be the Next Crimea?".
- "The False Threat of Secession in Bosnia". Balkan Insight.