Porphobilinogen
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
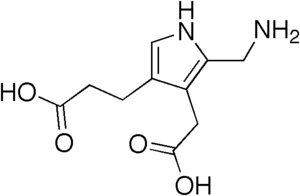
| IUPAC name
3-[5-(Aminomethyl)-4-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.970 |
| EC Number | 207-666-3 |
| MeSH | Porphobilinogen |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 226.229 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Porphobilinogen (PBG) is a pyrrole-containing intermediate in the biosynthesis of porphyrins (such as hemes).[1] It is generated from aminolevulinate (ALA) by the enzyme ALA dehydratase. PBG is then converted into hydroxymethyl bilane by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase, also known as hydroxymethylbilane synthase.
Acute intermittent porphyria causes an increase in urinary porphobilinogen.[2]
References
- ↑ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221.
- ↑ Aarsand, AK; Petersen PH; Sandberg S (April 2006). "Estimation and application of biological variation of urinary delta-aminolevulinic acid and porphobilinogen in healthy individuals and in patients with acute intermittent porphyria". Clinical Chemistry. 52 (4): 650–656. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.060772. PMID 16595824.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.