Peptide nucleic acid
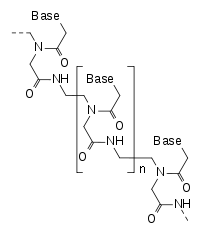
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificially synthesized polymer similar to DNA or RNA.[1] It was invented by Peter E. Nielsen (Univ. Copenhagen), Michael Egholm (Univ. Copenhagen), Rolf H. Berg (Risø National Lab), and Ole Buchardt (Univ. Copenhagen) in 1991.
Synthetic peptide nucleic acid oligomers have been used in recent years in molecular biology procedures, diagnostic assays, and antisense therapies. Due to their higher binding strength it is not necessary to design long PNA oligomers for use in these roles, which usually require oligonucleotide probes of 20–25 bases. The main concern of the length of the PNA-oligomers is to guarantee the specificity. PNA oligomers also show greater specificity in binding to complementary DNAs, with a PNA/DNA base mismatch being more destabilizing than a similar mismatch in a DNA/DNA duplex. This binding strength and specificity also applies to PNA/RNA duplexes. PNAs are not easily recognized by either nucleases or proteases, making them resistant to degradation by enzymes. PNAs are also stable over a wide pH range. Though an unmodified PNA cannot readily cross cell membranes to enter the cytosol, covalently coupling a cell penetrating peptide to a PNA can improve cytosolic delivery.
PNA is not known to occur naturally but N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine (AEG), the backbone of PNA, are possibly an early form of genetic molecules for life on earth and produced by cyanobacteria.[2]
Structure
DNA and RNA have a deoxyribose and ribose sugar backbone, respectively, whereas PNA's backbone is composed of repeating N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine units linked by peptide bonds. The various purine and pyrimidine bases are linked to the backbone by a methylene bridge (-CH
2-) and a carbonyl group (-(C=O)-). PNAs are depicted like peptides, with the N-terminus at the first (left) position and the C-terminus at the last (right) position.[3]
Binding
Since the backbone of PNA contains no charged phosphate groups, the binding between PNA/DNA strands is stronger than between DNA/DNA strands due to the lack of electrostatic repulsion. Unfortunately, this also causes it to be rather hydrophobic, which makes it difficult to deliver to body cells in solution without being flushed out of the body first. Early experiments with homopyrimidine strands (strands consisting of only one repeated pyrimidine base) have shown that the Tm ("melting" temperature) of a 6-base thymine PNA/adenine DNA double helix was 31 °C in comparison to an equivalent 6-base DNA/DNA duplex that denatures at a temperature less than 10 °C. Mixed base PNA molecules are true mimics of DNA molecules in terms of base-pair recognition. PNA/PNA binding is stronger than PNA/DNA binding.
PNA translation from other nucleic acids
Several labs have reported sequence-specific polymerization of peptide nucleic acids from DNA or RNA templates.[4][5][6] Liu and coworkers used these polymerization methods to evolve functional PNAs with the ability to fold into three-dimensional structures, similar to proteins, aptamers and ribozymes.[7]
Delivery
In 2015 Jain et. al. described a trans-acting DNA-based amphiphatic delivery system for convenient delivery of poly A tailed uncharged nucleic acids (UNA) such as PNAs and morpholinos, so that several UNA’s can be easily screened ex vivo.[8]
PNA world hypothesis
It has been hypothesized that the earliest life on Earth may have used PNA as a genetic material due to its extreme robustness, simpler formation, and possible spontaneous polymerization at 100 °C[9] (while water at standard pressure boils at this temperature, water at high pressure—as in deep ocean—boils at higher temperatures). If this is so, life evolved to a DNA/RNA-based system only at a later stage.[10][11] Evidence for this PNA world hypothesis is however far from conclusive.[12]
Applications
Applications include alteration of gene expression - both as inhibitor and promoter in different cases, antigene and antisense therapeutic agent, anticancer agent, antiviral, antibacterial and antiparasitic agent, molecular tools and probes of biosensor, detection of DNA sequences, and nanotechnology.[13]
See also
References
- ↑ Nielsen PE, Egholm M, Berg RH, Buchardt O (December 1991). "Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide". Science. 254 (5037): 1497–500. Bibcode:1991Sci...254.1497N. doi:10.1126/science.1962210. PMID 1962210.
- ↑ Cyanobacteria Produce N-(2-Aminoethyl)Glycine, a Backbone for Peptide Nucleic Acids Which May Have Been the First Genetic Molecules for Life on Earth
- ↑ Egholm M, Buchardt O, Christensen L, Behrens C, Freier SM, Driver DA, Berg RH, Kim SK, Nordén B, Nielsen PE (1993). "PNA Hybridizes to Complementary Oligonucleotides Obeying the Watson-Crick Hydrogen Bonding Rules". Nature. 365 (6446): 566–8. Bibcode:1993Natur.365..566E. doi:10.1038/365566a0. PMID 7692304.
- ↑ Brudno, Yevgeny; Birnbaum, Michael E; Kleiner, Ralph E; Liu, David R. "An in vitro translation, selection and amplification system for peptide nucleic acids". Nature Chemical Biology. 6 (2): 148–155. doi:10.1038/nchembio.280. PMC 2808706. PMID 20081830.
- ↑ Kleiner, Ralph E.; Brudno, Yevgeny; Birnbaum, Michael E.; Liu, David R. (2008-03-15). "DNA-Templated Polymerization of Side-Chain-Functionalized Peptide Nucleic Acid Aldehydes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (14): 4646–4659. doi:10.1021/ja0753997. PMC 2748799. PMID 18341334.
- ↑ Ura, Yasuyuki; Beierle, John M.; Leman, Luke J.; Orgel, Leslie E.; Ghadiri, M. Reza (2009-07-03). "Self-Assembling Sequence-Adaptive Peptide Nucleic Acids". Science. 325 (5936): 73–77. Bibcode:2009Sci...325...73U. doi:10.1126/science.1174577. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 19520909.
- ↑ Brudno, Yevgeny; Birnbaum, Michael E; Kleiner, Ralph E; Liu, David R. "An in vitro translation, selection and amplification system for peptide nucleic acids". Nature Chemical Biology. 6 (2): 148–155. doi:10.1038/nchembio.280. PMC 2808706. PMID 20081830.
- ↑ Jain, H. V.; Verthelyi, D.; Beaucage, S. L. (2015). "Amphipathic trans-acting phosphorothioate DNA elements mediate the delivery of uncharged nucleic acid sequences in mammalian cells". RSC Advances. 5 (80): 65245–65254. doi:10.1039/C5RA12038A. ISSN 2046-2069.
- ↑ Wittung P; Nielsen PE; Buchardt Ole; Egholm M & Nordén B (1994). "DNA-like Double Helix formed by Peptide Nucleic Acid". Nature. 368 (6471): 561–3. Bibcode:1994Natur.368..561W. doi:10.1038/368561a0. PMID 8139692.
- ↑ Nelson KE, Levy M, Miller SL (2000). "Peptide nucleic acids rather than RNA may have been the first genetic molecule". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97 (8): 3868–71. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.3868N. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.8.3868. PMC 18108. PMID 10760258.
- ↑ Alberts, Johnson, Lewis, Raff, Roberts, and Walter (March 2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Routledge. ISBN 0-8153-3218-1.
- ↑ Zimmer C (January 2009). "On the Origin of Life on Earth". Science. 323 (5911): 198–9. doi:10.1126/science.323.5911.198. PMID 19131603.
- ↑ Anstaett P, Gasser G (2014). "Peptide nucleic acid - an opportunity for bio-nanotechnology". Chimia. 68 (4): 264–8. doi:10.2533/chimia.2014.264. PMID 24983612.
Further reading
- Peter E. Nielsen (December 2008). "Triple Helix: Designing a New Molecule of Life". Scientific American.
- Krämer, Roland; Mokhir, Andriy (2012). "Chapter 12. Metal Complex Derivatives of Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNA)". In Astrid Sigel, Helmut Sigel and Roland K. O. Sigel. Interplay between Metal Ions and Nucleic Acids. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. 10. Springer. pp. 319–340. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2172-2_12.
- Shakeel, Shabih; et al. (June 2006). "Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA): A Review". Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology.
- An overview of the PNA molecule
- Kaihatsu K, Janowski BA, Corey DR (June 2004). "Recognition of chromosomal DNA by PNAs". Chem. Biol. 11 (6): 749–58. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2003.09.014. PMID 15217608.
- Ng PS, Bergstrom DE (2005). "Alternative Nucleic Acid Analogues for Programmable Assembly: Hybridization of LNA to PNA". Nano Lett. 5 (1): 107–111. Bibcode:2005NanoL...5..107N. doi:10.1021/nl048246f. PMID 15792422.
- Paulasova P, Pellestor F (2004). "The peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): a new generation of probes for genetic and cytogenetic analyses". Ann. Genet. 47 (4): 349–58. doi:10.1016/j.anngen.2004.07.001. PMID 15581832.
- A New Game of Life
- Nielsen PE, Egholm M (1999). "An Introduction to Peptide Nucleic Acid" (PDF). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 1 (2): 89–104.