Orang laut
 An Orang Laut family living in a boat, circa 1914–1921. | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
|
Andaman Archipelago: Malay Peninsula: Riau Archipelago: | |
| Languages | |
| Loncong language, Malay language | |
| Religion | |
| Islam, Animism | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Orang Kuala, Orang Seletar, Sama-Bajau, Moken, Urak Lawoi’ people |
The Orang Laut are an ethnic group living around Singapore, peninsular Malaysia and the Riau Islands. It also may refer to any Malay origin people living on coastal islands, including those of Andaman Sea islands of India and those in Thailand and Burma, commonly known as Moken.
Etymology
The Malay term orang laut literally means "sea peoples". The Orang laut live and travel in their boats on the sea.[1] Another Malay term for them, Orang Selat (literally "Straits people" ), was brought into European languages as Celates.
Distribution
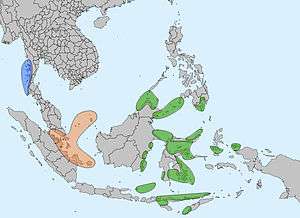
Broadly speaking, the term encompasses the numerous tribes and groups inhabiting the islands and estuaries in the Riau-Lingga Archipelagos, the Pulau Tujuh Islands, the Batam Archipelago, and the coasts and offshore islands of eastern Sumatra, southern Malaysia Peninsula and Singapore.[3]
History

Historically, the orang laut played major roles in Srivijaya, the Sultanate of Malacca, and the Sultanate of Johor. They patrolled the adjacent sea areas, repelling real pirates, directing traders to their employers' ports and maintaining those ports' dominance in the area.[4] The earliest description of orang laut may have been by the 14th century Chinese traveller Wang Dayuan who described the inhabitants of temasek (present day Singapore) in his work Daoyi Zhilüe.[5]
Popular culture

In the story "The Disturber of Traffic" by Rudyard Kipling, a character called Fenwick misrenders the Orang laut as "Orange-Lord" and the narrator character corrects him that they are the "Orang-Laut".
See also
References
- ↑ Adriaan J. Barnouw (February 1946). "Cross Currents of Culture in Indonesia". The Far Eastern Quarterly. The Far Eastern Quarterly, Vol. 5, No. 2. 5 (2): 143&ndash, 151. doi:10.2307/2049739. JSTOR 2049739.
- ↑ David E. Sopher (1965). "The Sea Nomads: A Study Based on the Literature of the Maritime Boat People of Southeast Asia". Memoirs of the National Museum. 5: 389&ndash, 403. doi:10.2307/2051635.
- ↑ "The Malay Peninsula and Archipelago 1511–1722" The Encyclopedia of World History 2001;
- ↑ Mary Somers Heidhues. Southeast Asia: A Concise History. London: Hudson and Thames, 2000. Page 27
- ↑ Paul Wheatley (1961). The Golden Khersonese: Studies in the Historical Geography of the Malay Peninsula before A.D. 1500. Kuala Lumpur: University of Malaya Press. pp. 82–83. OCLC 504030596.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Orang Laut. |
