Oganesson
| General properties | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
| |||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | 294 (most stable isotope) (unconfirmed: 295) | |||||||||||||||||
| Oganesson in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 118 | |||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 18 | |||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||
| Element category | unknown chemical properties, but probably a noble gas | |||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p6 (predicted)[2][3] | |||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8 (predicted) | |||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid (predicted)[2] | |||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 350±30 K (80±30 °C, 170±50 °F) (extrapolated)[2] | |||||||||||||||||
| Density when liquid (at m.p.) | 4.9–5.1 g/cm3 (predicted)[4] | |||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 439 K, 6.8 MPa (extrapolated)[5] | |||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 23.5 kJ/mol (extrapolated)[5] | |||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 19.4 kJ/mol (extrapolated)[5] | |||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states |
−1,[3] 0, +1,[6] +2,[7] +4,[7] +6[3] | |||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | ||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 157 pm (predicted)[10] | |||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure |
face-centered cubic (fcc) (extrapolated)[11] | |||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 54144-19-3 | |||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Yuri Oganessian | |||||||||||||||||
| Prediction | Niels Bohr (1922) | |||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Joint Institute for Nuclear Research and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (2002) | |||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of oganesson | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
Oganesson is a synthetic chemical element with symbol Og and atomic number 118. It was first synthesized in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia by a joint team of Russian and American scientists. In December 2015, it was recognized as one of four new elements by the Joint Working Party of the international scientific bodies IUPAC and IUPAP. It was formally named on 28 November 2016.[15][16] The name is in line with the tradition of honoring a scientist, in this case the nuclear physicist Yuri Oganessian, who has played a leading role in the discovery of the heaviest elements in the periodic table. It is one of only two elements named after a living person at the time of naming, the other being seaborgium.[17]
Oganesson has the highest atomic number and highest atomic mass of all known elements. The radioactive oganesson atom is very unstable, and since 2005, only five (possibly six) atoms of the nuclide 294Og have been detected.[18] Although this allowed very little experimental characterization of its properties and possible compounds, theoretical calculations have resulted in many predictions, including some surprising ones. For example, although oganesson is a member of group 18 – the first synthetic element to be so – it may be significantly reactive, unlike all the other elements of that group (the noble gases).[2] It was formerly thought to be a gas under normal conditions but is now predicted to be a solid due to relativistic effects.[2] On the periodic table of the elements it is a p-block element and the last one of the 7th period.
History
Early speculation
The Danish physicist Niels Bohr was the first to seriously consider the possibility of an element with an atomic number as high as 118, noting in 1922 that such an element would take its place in the periodic table below radon as the seventh noble gas.[19] Following this, Aristid von Grosse wrote an article in 1965 predicting the likely properties of element 118. These were remarkably early predictions, given that it was not yet known how to produce elements artificially in 1922, and that the existence of the island of stability had not yet been theorized in 1965. It was 80 years from Bohr's prediction before oganesson was successfully synthesised, although its chemical properties have not been investigated to determine if it behaves as the heavier congener of radon.[9]
Unconfirmed discovery claims
In late 1998, Polish physicist Robert Smolańczuk published calculations on the fusion of atomic nuclei towards the synthesis of superheavy atoms, including oganesson.[20] His calculations suggested that it might be possible to make oganesson by fusing lead with krypton under carefully controlled conditions, and that the fusion probability (cross-section) of that reaction would be close to the lead–chromium reaction that had produced element 106, seaborgium. This contradicted predictions that the cross-sections for reactions with lead or bismuth targets would go down exponentially as the atomic number of the resulting elements increased.[20]
In 1999, researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory made use of these predictions and announced the discovery of livermorium and oganesson, in a paper published in Physical Review Letters,[21] and very soon after the results were reported in Science.[22] The researchers reported that they had performed the reaction
- 86
36Kr
+ 208
82Pb
→ 293
118Og
+
n
.
The following year, they published a retraction after researchers at other laboratories were unable to duplicate the results and the Berkeley lab could not duplicate them either.[23] In June 2002, the director of the lab announced that the original claim of the discovery of these two elements had been based on data fabricated by principal author Victor Ninov.[24][25] Newer experimental results and theoretical predictions have confirmed the exponential decrease in cross-sections with lead and bismuth targets as the atomic number of the resulting nuclide increases.[26]
Discovery reports
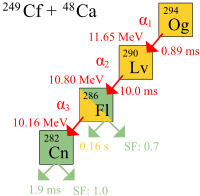
The first genuine decay of atoms of oganesson was observed in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia, by a joint team of Russian and American scientists. Headed by Yuri Oganessian, a Russian nuclear physicist of Armenian ethnicity, the team included American scientists of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, California.[27] The discovery was not announced immediately, because the decay energy of 294Og matched that of 212mPo, a common impurity produced in fusion reactions aimed at producing superheavy elements, and thus announcement was delayed until after a 2005 confirmatory experiment aimed at producing more oganesson atoms.[28] On 9 October 2006, the researchers announced[13] that they had indirectly detected a total of three (possibly four) nuclei of oganesson-294 (one or two in 2002[29] and two more in 2005) produced via collisions of californium-249 atoms and calcium-48 ions.[30][31][32][33][34]
In 2011, IUPAC evaluated the 2006 results of the Dubna–Livermore collaboration and concluded: "The three events reported for the Z = 118 isotope have very good internal redundancy but with no anchor to known nuclei do not satisfy the criteria for discovery".[35]
Because of the very small fusion reaction probability (the fusion cross section is ~0.3–0.6 pb or (3–6)×10−41 m2) the experiment took four months and involved a beam dose of 2.5×1019 calcium ions that had to be shot at the californium target to produce the first recorded event believed to be the synthesis of oganesson.[36] Nevertheless, researchers were highly confident that the results were not a false positive, since the chance that the detections were random events was estimated to be less than one part in 100000.[37]
In the experiments, the alpha-decay of three atoms of oganesson was observed. A fourth decay by direct spontaneous fission was also proposed. A half-life of 0.89 ms was calculated: 294
Og decays into 290
Lv by alpha decay. Since there were only three nuclei, the half-life derived from observed lifetimes has a large uncertainty: 0.89+1.07
−0.31 ms.[13]
- 294
118Og
→ 290
116Lv
+ 4
2He
The identification of the 294
Og nuclei was verified by separately creating the putative daughter nucleus 290
Lv directly by means of a bombardment of 245
Cm with 48
Ca ions,
- 245
96Cm
+ 48
20Ca
→ 290
116Lv
+ 3
n
,
and checking that the 290
Lv decay matched the decay chain of the 294
Og nuclei.[13] The daughter nucleus 290
Lv is very unstable, decaying with a lifetime of 14 milliseconds into 286
Fl, which may experience either spontaneous fission or alpha decay into 282
Cn, which will undergo spontaneous fission.[13]
In a quantum-tunneling model, the alpha decay half-life of 294
Og was predicted to be 0.66+0.23
−0.18 ms[38] with the experimental Q-value published in 2004.[39] Calculation with theoretical Q-values from the macroscopic-microscopic model of Muntian–Hofman–Patyk–Sobiczewski gives somewhat lower but comparable results.[40]
Confirmation
In December 2015, the Joint Working Party of international scientific bodies International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) recognized the element's discovery and assigned the priority of the discovery to the Dubna–Livermore collaboration.[41] This was on account of two 2009 and 2010 confirmations of the properties of the granddaughter of 294Og, 286Fl, at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, as well as the observation of another consistent decay chain of 294Og by the Dubna group in 2012. The goal of that experiment had been the synthesis of 294Ts via the reaction 249Bk(48Ca,3n), but the short half-life of 249Bk resulted in a significant quantity of the target having decayed to 249Cf, resulting in the synthesis of oganesson instead of tennessine.[42]
From 1 October 2015 to 6 April 2016, the Dubna team performed a similar experiment with 48Ca projectiles aimed at a mixed-isotope californium target containing 249Cf, 250Cf, and 251Cf, with the aim of producing the heavier oganesson isotopes 295Og and 296Og. Two beam energies at 252 MeV and 258 MeV were used. Only one atom was seen at the lower beam energy, whose decay chain fitted the previously known one of 294Og (terminating with spontaneous fission of 286Fl), and none were seen at the higher beam energy. The experiment was then halted, as the glue from the sector frames covered the target and blocked evaporation residues from escaping to the detectors. The Dubna team planned to repeat this experiment in 2017.[43] One atom of the isotope 295Og may have been seen in a 2011 experiment at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt, Germany aimed at the synthesis of element 120 in the reaction 248Cm+54Cr, but uncertainties in the data meant that the observed chain cannot be definitely assigned to 299120 and 295Og: the data indicates a longer half-life of 295Og of 181 milliseconds than that of 294Og, which is 0.7 milliseconds.[12]
Naming

Using Mendeleev's nomenclature for unnamed and undiscovered elements, oganesson is sometimes known as eka-radon (until the 1960s as eka-emanation, emanation being the old name for radon).[11] In 1979, IUPAC assigned the systematic placeholder name ununoctium to the undiscovered element, with the corresponding symbol of Uuo,[44] and recommended that it be used until after confirmed discovery of the element.[45] Although widely used in the chemical community on all levels, from chemistry classrooms to advanced textbooks, the recommendations were mostly ignored among scientists in the field, who called it "element 118", with the symbol of E118, (118), or even simply 118.[3]
Before the retraction in 2002, the researchers from Berkeley had intended to name the element ghiorsium (Gh), after Albert Ghiorso (a leading member of the research team).[46]
The Russian discoverers reported their synthesis in 2006. According to IUPAC recommendations, the discoverers of a new element have the right to suggest a name.[47] In 2007, the head of the Russian institute stated the team were considering two names for the new element: flyorium, in honor of Georgy Flyorov, the founder of the research laboratory in Dubna; and moskovium, in recognition of the Moscow Oblast where Dubna is located.[48] He also stated that although the element was discovered as an American collaboration, who provided the californium target, the element should rightly be named in honor of Russia since the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions at JINR was the only facility in the world which could achieve this result.[49] These names were later proposed for element 114 (flerovium) and element 116 (moscovium).[50] However, the final name proposed for element 116 was instead livermorium,[51] and the name moscovium was later proposed and accepted for element 115 instead.[17]
Traditionally, the names of all noble gases end in "-on", with the exception of helium, which was not known to be a noble gas when discovered. The IUPAC guidelines valid at the moment of the discovery approval however required all new elements be named with the ending "-ium", even if they turned out to be halogens (traditionally ending in "-ine") or noble gases (traditionally ending in "-on").[52] While the provisional name ununoctium followed this convention, a new IUPAC recommendation published in 2016 recommended using the "-on" ending for new group 18 elements, regardless of whether they turn out to have the chemical properties of a noble gas.[53]
| Wikinews has related news: IUPAC proposes four new chemical element names |
In June 2016 IUPAC announced that the discoverers planned to give the element the name oganesson (symbol: Og), in honour of the Russian nuclear physicist Yuri Oganessian, a pioneer in superheavy element research for sixty years reaching back to the field's foundation: his team and his proposed techniques had led directly to the synthesis of elements 106 through 118.[54] The name became official on 28 November 2016.[17] Oganessian later commented on the naming:[55]
For me, it is an honour. The discovery of element 118 was by scientists at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Russia and at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the US, and it was my colleagues who proposed the name oganesson. My children and grandchildren have been living in the US for decades, but my daughter wrote to me to say that she did not sleep the night she heard because she was crying.[55]
— Yuri Oganessian
The naming ceremony for moscovium, tennessine, and oganesson was held on 2 March 2017 at the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow.[56]
Characteristics
Nuclear stability and isotopes
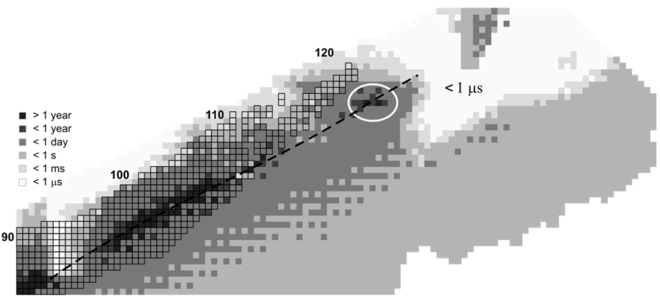
The stability of nuclei quickly decreases with the increase in atomic number after curium, element 96, whose half-life is four orders of magnitude longer than that of any subsequent element. All isotopes with an atomic number above 101 undergo radioactive decay with half-lives of less than 30 hours. No elements with atomic numbers above 82 (after lead) have stable isotopes.[57] This is because of the ever-increasing Coulomb repulsion of protons, so that the strong nuclear force cannot hold the nucleus together against spontaneous fission for long. Calculations suggest that in the absence of other stabilizing factors, elements with more than 103 protons should not exist. However, researchers in the 1960s suggested that the closed nuclear shells around 114 protons and 184 neutrons should counteract this instability, creating an "island of stability" where nuclides could have half-lives reaching thousands or millions of years. While scientists have still not reached the island, the mere existence of the superheavy elements (including oganesson) confirms that this stabilizing effect is real, and in general the known superheavy nuclides become exponentially longer-lived as they approach the predicted location of the island.[58][59] Oganesson is radioactive and has a half-life that appears to be less than a millisecond. Nonetheless, this is still longer than some predicted values,[38][60] thus giving further support to the idea of this "island of stability".[61]
Calculations using a quantum-tunneling model predict the existence of several neutron-rich isotopes of oganesson with alpha-decay half-lives close to 1 ms.[62][63]
Theoretical calculations done on the synthetic pathways for, and the half-life of, other isotopes have shown that some could be slightly more stable than the synthesized isotope 294Og, most likely 293Og, 295Og, 296Og, 297Og, 298Og, 300Og and 302Og.[38][64] Of these, 297Og might provide the best chances for obtaining longer-lived nuclei,[38][64] and thus might become the focus of future work with this element. Some isotopes with many more neutrons, such as some located around 313Og, could also provide longer-lived nuclei.[65] Since these heavier isotopes greatly facilitate future chemical studies of oganesson, due to their expected longer half-lives, the Dubna team plans to conduct an experiment through the second half of 2017 with a heavier target containing a mix of the isotopes 249Cf, 250Cf, and 251Cf with 48Ca projectiles, aimed at the synthesis of the new isotopes 295Og and 296Og; a repeat of this reaction in 2020 at the JINR is planned to produce 297Og. The production of 293Og and its daughter 289Lv in this reaction is also possible. The isotopes 295Og and 296Og may also be produced in the fusion of 248Cm with 50Ti projectiles, a reaction planned at the JINR and at RIKEN in 2017–2018.[43][66][67]
Calculated atomic and physical properties
Oganesson is a member of group 18, the zero-valence elements. The members of this group are usually inert to most common chemical reactions (for example, combustion) because the outer valence shell is completely filled with eight electrons. This produces a stable, minimum energy configuration in which the outer electrons are tightly bound.[68] It is thought that similarly, oganesson has a closed outer valence shell in which its valence electrons are arranged in a 7s27p6 configuration.[2]
Consequently, some expect oganesson to have similar physical and chemical properties to other members of its group, most closely resembling the noble gas above it in the periodic table, radon.[69] Following the periodic trend, oganesson would be expected to be slightly more reactive than radon. However, theoretical calculations have shown that it could be significantly more reactive.[7] In addition to being far more reactive than radon, oganesson may be even more reactive than the elements flerovium and copernicium, which are heavier homologs of the more chemically active elements lead and mercury respectively.[2] The reason for the possible enhancement of the chemical activity of oganesson relative to radon is an energetic destabilization and a radial expansion of the last occupied 7p-subshell.[2] More precisely, considerable spin–orbit interactions between the 7p electrons and the inert 7s electrons effectively lead to a second valence shell closing at flerovium, and a significant decrease in stabilization of the closed shell of oganesson.[2] It has also been calculated that oganesson, unlike the other noble gases, binds an electron with release of energy, or in other words, it exhibits positive electron affinity,[70][71] due to the relativistically stabilized 8s energy level and the destabilized 7p3/2 level,[72] whereas copernicium and flerovium are predicted to have no electron affinity.[73][74] Nevertheless, quantum electrodynamic corrections have been shown to be quite significant in reducing this affinity by decreasing the binding in the anion Og− by 9%, thus confirming the importance of these corrections in superheavy elements.[70]
Oganesson is expected to have an extremely broad polarizability, almost double that of radon.[2] By extrapolating from the other noble gases, it is expected that oganesson has a boiling point between 320 and 380 K.[2] This is very different from the previously estimated values of 263 K[75] or 247 K.[76] Even given the large uncertainties of the calculations, it seems highly unlikely that oganesson would be a gas under standard conditions,[2] and as the liquid range of the other gases is very narrow, between 2 and 9 kelvins, this element should be solid at standard conditions. If oganesson forms a gas under standard conditions nevertheless, it would be one of the densest gaseous substances at standard conditions, even if it is monatomic like the other noble gases.
Because of its tremendous polarizability, oganesson is expected to have an anomalously low ionization energy (similar to that of lead which is 70% of that of radon[6] and significantly smaller than that of flerovium)[77] and a standard state condensed phase.[2] Even the shell structure in the nucleus and electron cloud of oganesson is strongly impacted by relativistic effects: the valence and core electron subshells in oganesson are expected to be "smeared out" in a homogeneous Fermi gas of electrons, unlike those of the "less relativistic" radon and xenon (although there is some incipient delocalisation in radon), due to the very strong spin-orbit splitting of the 7p orbital in oganesson.[78] A similar effect for nucleons, particularly neutrons, is incipient in the closed-neutron-shell nucleus 302Og and is strongly in force at the hypothetical superheavy closed-shell nucleus 472164, with 164 protons and 308 neutrons.[78]
Predicted compounds
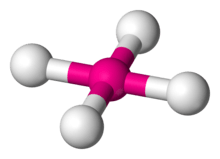
4 has a square planar molecular geometry.
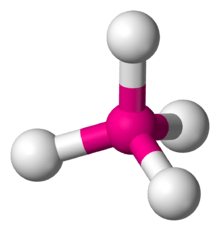
4 is predicted to have a tetrahedral molecular geometry.
The only confirmed isotope of oganesson, 294Og, has much too short a half-life to be chemically investigated experimentally. As such, no compounds of oganesson have been synthesized yet.[28] Nevertheless, calculations on theoretical compounds have been performed since 1964.[11] It is expected that if the ionization energy of the element is high enough, it will be difficult to oxidize and therefore, the most common oxidation state would be 0 (as for the noble gases);[79] nevertheless, this appears not to be the case.[9]
Calculations on the diatomic molecule Og
2 showed a bonding interaction roughly equivalent to that calculated for Hg
2, and a dissociation energy of 6 kJ/mol, roughly 4 times of that of Rn
2.[2] Most strikingly, it was calculated to have a bond length shorter than in Rn
2 by 0.16 Å, which would be indicative of a significant bonding interaction.[2] On the other hand, the compound OgH+ exhibits a dissociation energy (in other words proton affinity of oganesson) that is smaller than that of RnH+.[2]
The bonding between oganesson and hydrogen in OgH is predicted to be very weak and can be regarded as a pure van der Waals interaction rather than a true chemical bond.[6] On the other hand, with highly electronegative elements, oganesson seems to form more stable compounds than for example copernicium or flerovium.[6] The stable oxidation states +2 and +4 have been predicted to exist in the fluorides OgF
2 and OgF
4.[80] The +6 state would be less stable due to the strong binding of the 7p1/2 subshell.[9] This is a result of the same spin-orbit interactions that make oganesson unusually reactive. For example, it was shown that the reaction of oganesson with F
2 to form the compound OgF
2 would release an energy of 106 kcal/mol of which about 46 kcal/mol come from these interactions.[6] For comparison, the spin-orbit interaction for the similar molecule RnF
2 is about 10 kcal/mol out of a formation energy of 49 kcal/mol.[6] The same interaction stabilizes the tetrahedral Td configuration for OgF
4, as distinct from the square planar D4h one of XeF
4, which RnF
4 is also expected to have.[80] The Og–F bond will most probably be ionic rather than covalent, rendering the oganesson fluorides non-volatile.[7][81] OgF2 is predicted to be partially ionic due to oganesson's high electropositivity.[82] Unlike the other noble gases (except possibly xenon and radon),[83][84] oganesson is predicted to be sufficiently electropositive[82] to form an Og–Cl bond with chlorine.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Ritter, Malcolm (9 June 2016). "Periodic table elements named for Moscow, Japan, Tennessee". Associated Press. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Nash, Clinton S. (2005). "Atomic and Molecular Properties of Elements 112, 114, and 118". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 109 (15): 3493–3500. Bibcode:2005JPCA..109.3493N. doi:10.1021/jp050736o. PMID 16833687.
- 1 2 3 4 Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 1-4020-3555-1.
- ↑ Bonchev, Danail; Kamenska, Verginia (1981). "Predicting the Properties of the 113–120 Transactinide Elements". Journal of Physical Chemistry. American Chemical Society. 85 (9): 1177–1186. doi:10.1021/j150609a021.
- 1 2 3 Eichler, R.; Eichler, B., Thermochemical Properties of the Elements Rn, 112, 114, and 118 (PDF), Paul Scherrer Institut, retrieved 2010-10-23
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Han, Young-Kyu; Bae, Cheolbeom; Son, Sang-Kil; Lee, Yoon Sup (2000). "Spin–orbit effects on the transactinide p-block element monohydrides MH (M=element 113–118)". Journal of Chemical Physics. 112 (6): 2684. Bibcode:2000JChPh.112.2684H. doi:10.1063/1.480842.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kaldor, Uzi; Wilson, Stephen (2003). Theoretical Chemistry and Physics of Heavy and Superheavy Elements. Springer. p. 105. ISBN 140201371X. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
- ↑ Pershina, Valeria. "Theoretical Chemistry of the Heaviest Elements". In Schädel, Matthias; Shaughnessy, Dawn. The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements (2nd ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 154. ISBN 9783642374661.
- 1 2 3 4 Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ↑ Chemical Data. Ununoctium - Uuo, Royal Chemical Society
- 1 2 3 Grosse, A. V. (1965). "Some physical and chemical properties of element 118 (Eka-Em) and element 86 (Em)". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. Elsevier Science Ltd. 27 (3): 509–19. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(65)80255-X.
- 1 2 Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; Maurer, J.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Barth, W.; Burkhard, H. G.; Dahl, L.; Eberhardt, K.; Grzywacz, R.; Hamilton, J. H.; Henderson, R. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharov, I.; Lang, R.; Lommel, B.; Miernik, K.; Miller, D.; Moody, K. J.; Morita, K.; Nishio, K.; Popeko, A. G.; Roberto, J. B.; Runke, J.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Saro, S.; Schneidenberger, C.; Schött, H. J.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Thörle-Pospiech, P.; Tinschert, K.; Trautmann, N.; Uusitalo, J.; Yeremin, A. V. (2016). "Remarks on the Fission Barriers of SHN and Search for Element 120". In Peninozhkevich, Yu. E.; Sobolev, Yu. G. Exotic Nuclei: EXON-2016 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Exotic Nuclei. Exotic Nuclei. pp. 155–164. ISBN 9789813226555.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Utyonkov, V. K.; Lobanov, Yu. V.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Polyakov, A. N.; Sagaidak, R. N.; Shirokovsky, I. V.; Tsyganov, Yu. S.; et al. (2006-10-09). "Synthesis of the isotopes of elements 118 and 116 in the 249Cf and 245Cm+48Ca fusion reactions". Physical Review C. 74 (4): 044602. Bibcode:2006PhRvC..74d4602O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.74.044602. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yuri Ts.; Rykaczewski, Krzysztof P. (August 2015). "A beachhead on the island of stability". Physics Today. 68 (8): 32–38. Bibcode:2015PhT....68h..32O. doi:10.1063/PT.3.2880. Retrieved 2017-06-14.
- ↑ Staff (30 November 2016). "IUPAC Announces the Names of the Elements 113, 115, 117, and 118". IUPAC. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- ↑ St. Fleur, Nicholas (1 December 2016). "Four New Names Officially Added to the Periodic Table of Elements". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- 1 2 3 "IUPAC Is Naming The Four New Elements Nihonium, Moscovium, Tennessine, And Oganesson". IUPAC. 2016-06-08. Retrieved 2016-06-08.
- ↑ "The Top 6 Physics Stories of 2006". Discover Magazine. 7 January 2007. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Leach, Mark R. "The INTERNET Database of Periodic Tables". Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- 1 2 Smolanczuk, R. (1999). "Production mechanism of superheavy nuclei in cold fusion reactions". Physical Review C. 59 (5): 2634–2639. Bibcode:1999PhRvC..59.2634S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.59.2634.
- ↑ Ninov, Viktor (1999). "Observation of Superheavy Nuclei Produced in the Reaction of 86Kr with 208Pb". Physical Review Letters. 83 (6): 1104–1107. Bibcode:1999PhRvL..83.1104N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.1104.
- ↑ Service, R. F. (1999). "Berkeley Crew Bags Element 118". Science. 284 (5421): 1751. doi:10.1126/science.284.5421.1751.
- ↑ Public Affairs Department (21 July 2001). "Results of element 118 experiment retracted". Berkeley Lab. Archived from the original on 29 January 2008. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Dalton, R. (2002). "Misconduct: The stars who fell to Earth". Nature. 420 (6917): 728–729. Bibcode:2002Natur.420..728D. doi:10.1038/420728a. PMID 12490902.
- ↑ Element 118 disappears two years after it was discovered. Physicsworld.com. Retrieved on 2 April 2012.
- ↑ Zagrebaev, Valeriy; Karpov, Alexander; Greiner, Walter (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?" (PDF). Journal of Physics. IOP Publishing Ltd. 420: 012001. arXiv:1207.5700. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. T.; et al. (2002). "Results from the first 249
Cf+48
Ca experiment" (PDF). JINR Communication. JINR, Dubna. - 1 2 Moody, Ken. "Synthesis of Superheavy Elements". In Schädel, Matthias; Shaughnessy, Dawn. The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements (2nd ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 24–8. ISBN 9783642374661.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. T.; et al. (2002). "Element 118: results from the first 249
Cf
+ 48
Ca
experiment". Communication of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. - ↑ "Livermore scientists team with Russia to discover element 118". Livermore press release. 3 December 2006. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. T. (2006). "Synthesis and decay properties of superheavy elements". Pure Appl. Chem. 78 (5): 889–904. doi:10.1351/pac200678050889.
- ↑ Sanderson, K. (2006). "Heaviest element made – again". Nature News. Nature. doi:10.1038/news061016-4.
- ↑ Schewe, P. & Stein, B. (17 October 2006). "Elements 116 and 118 Are Discovered". Physics News Update. American Institute of Physics. Archived from the original on 1 January 2012. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Weiss, R. (17 October 2006). "Scientists Announce Creation of Atomic Element, the Heaviest Yet". Washington Post. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Barber, Robert C.; Karol, Paul J.; Nakahara, Hiromichi; Vardaci, Emanuele; Vogt, Erich W. (2011). "Discovery of the elements with atomic numbers greater than or equal to 113 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 83 (7): 1. doi:10.1351/PAC-REP-10-05-01.
- ↑ "Ununoctium". WebElements Periodic Table. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- ↑ Jacoby, Mitch (17 October 2006). "Element 118 Detected, With Confidence". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
I would say we're very confident.
- 1 2 3 4 Chowdhury, Roy P.; Samanta, C.; Basu, D. N. (2006). "α decay half-lives of new superheavy elements". Phys. Rev. C. 73: 014612. arXiv:nucl-th/0507054. Bibcode:2006PhRvC..73a4612C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.73.014612.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Utyonkov, V.; Lobanov, Yu.; Abdullin, F.; Polyakov, A.; Shirokovsky, I.; Tsyganov, Yu.; Gulbekian, G.; Bogomolov, S.; Gikal, B. N.; et al. (2004). "Measurements of cross sections and decay properties of the isotopes of elements 112, 114, and 116 produced in the fusion reactions 233,238U, 242Pu, and 248Cm+48Ca" (PDF). Physical Review C. 70 (6): 064609. Bibcode:2004PhRvC..70f4609O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.70.064609.
- ↑ Samanta, C.; Chowdhury, R. P.; Basu, D.N. (2007). "Predictions of alpha decay half-lives of heavy and superheavy elements". Nucl. Phys. A. 789: 142–154. arXiv:nucl-th/0703086. Bibcode:2007NuPhA.789..142S. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2007.04.001.
- ↑ Discovery and Assignment of Elements with Atomic Numbers 113, 115, 117 and 118. IUPAC (30 December 2015)
- ↑ Karol, Paul J.; Barber, Robert C.; Sherrill, Bradley M.; Vardaci, Emanuele; Yamazaki, Toshimitsu (29 December 2015). "Discovery of the element with atomic number Z = 118 completing the 7th row of the periodic table (IUPAC Technical Report)" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. 88 (1–2): 155–160. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0501. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- 1 2 Voinov, A. A.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Brewer, N. T.; Dmitriev, S. N.; Grzywacz, R. K.; Hamilton, J. H.; Itkis, M. G.; Miernik, K.; Polyakov, A. N.; Roberto, J. B.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Sabelnikov, A. V.; Sagaidak, R. N.; Shriokovsky, I. V.; Shumeiko, M. V.; Stoyer, M. A.; Subbotin, V. G.; Sukhov, A. M.; Tsyganov, Yu. S.; Utyonkov, V. K.; Vostokin, G. K. (2016). "Results from the Recent Study of the 249–251Cf + 48Ca Reactions". In Peninozhkevich, Yu. E.; Sobolev, Yu. G. Exotic Nuclei: EXON-2016 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Exotic Nuclei. Exotic Nuclei. pp. 219–223. ISBN 9789813226555.
- ↑ Chatt, J. (1979). "Recommendations for the Naming of Elements of Atomic Numbers Greater than 100". Pure Appl. Chem. 51 (2): 381–384. doi:10.1351/pac197951020381.
- ↑ Wieser, M.E. (2006). "Atomic weights of the elements 2005 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure Appl. Chem. 78 (11): 2051–2066. doi:10.1351/pac200678112051.
- ↑ "Discovery of New Elements Makes Front Page News". Berkeley Lab Research Review Summer 1999. 1999. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Koppenol, W. H. (2002). "Naming of new elements (IUPAC Recommendations 2002)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (5): 787. doi:10.1351/pac200274050787.
- ↑ "New chemical elements discovered in Russia`s Science City". 12 February 2007. Retrieved 9 February 2008.
- ↑ Yemel'yanova, Asya (17 December 2006). "118-й элемент назовут по-русски (118th element will be named in Russian)" (in Russian). vesti.ru. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ "Российские физики предложат назвать 116 химический элемент московием (Russian Physicians Will Suggest to Name Element 116 Moscovium)" (in Russian). rian.ru. 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ↑ "News: Start of the Name Approval Process for the Elements of Atomic Number 114 and 116". International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2011.
- ↑ Koppenol, W. H. (2002). "Naming of new elements (IUPAC Recommendations 2002)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (5): 787–791. doi:10.1351/pac200274050787.
- ↑ Koppenol, Willem H.; Corish, John; García-Martínez, Javier; Meija, Juris; Reedijk, Jan (2016). "How to name new chemical elements (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 88 (4). doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0802.
- ↑ "What it takes to make a new element". Chemistry World. Retrieved 2016-12-03.
- 1 2 Gray, Richard (11 April 2017). "Mr Element 118: The only living person on the periodic table". New Scientist. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ↑ Fedorova, Vera (3 March 2017). "At the inauguration ceremony of the new elements of the Periodic table of D.I. Mendeleev". jinr.ru. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ↑ de Marcillac, P.; Coron, N.; Dambier, G.; et al. (2003). "Experimental detection of α-particles from the radioactive decay of natural bismuth". Nature. 422 (6934): 876–878. Bibcode:2003Natur.422..876D. doi:10.1038/nature01541. PMID 12712201.
- ↑ Considine, G. D.; Kulik, Peter H. (2002). Van Nostrand's scientific encyclopedia (9th ed.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-33230-5. OCLC 223349096.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Sobiczewski, A.; Ter-Akopian, G. M. (9 January 2017). "Superheavy nuclei: from predictions to discovery". Physica Scripta. 92 (2): 023003–1–21. Bibcode:2017PhyS...92b3003O. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/aa53c1.
- ↑ Oganessian, Yu. T. (2007). "Heaviest nuclei from 48Ca-induced reactions". Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics. 34 (4): R165–R242. Bibcode:2007JPhG...34..165O. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/34/4/R01.
- ↑ "New Element Isolated Only Briefly". The Daily Californian. 18 October 2006. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ Chowdhury, Roy P.; Samanta, C.; Basu, D. N. (2008). "Search for long lived heaviest nuclei beyond the valley of stability". Physical Review C. 77 (4): 044603. arXiv:0802.3837. Bibcode:2008PhRvC..77d4603C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.77.044603.
- ↑ Chowdhury, R. P.; Samanta, C.; Basu, D.N. (2008). "Nuclear half-lives for α -radioactivity of elements with 100 ≤ Z ≤ 130". Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables. 94 (6): 781–806. arXiv:0802.4161. Bibcode:2008ADNDT..94..781C. doi:10.1016/j.adt.2008.01.003.
- 1 2 Royer, G.; Zbiri, K.; Bonilla, C. (2004). "Entrance channels and alpha decay half-lives of the heaviest elements". Nuclear Physics A. 730 (3–4): 355–376. arXiv:nucl-th/0410048. Bibcode:2004NuPhA.730..355R. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.010.
- ↑ Duarte, S. B.; Tavares, O. A. P.; Gonçalves, M.; Rodríguez, O.; Guzmán, F.; Barbosa, T. N.; García, F.; Dimarco, A. (2004). "Half-life predictions for decay modes of superheavy nuclei" (PDF). Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics. 30 (10): 1487–1494. Bibcode:2004JPhG...30.1487D. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/30/10/014.
- ↑ Sychev, Vladimir (8 February 2017). "Юрий Оганесян: мы хотим узнать, где кончается таблица Менделеева" [Yuri Oganessian: we want to know where the Mendeleev table ends]. RIA Novosti (in Russian). Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ↑ Roberto, J. B. (31 March 2015). "Actinide Targets for Super-Heavy Element Research" (PDF). cyclotron.tamu.edu. Texas A & M University. Retrieved 28 April 2017.
- ↑ Bader, Richard F.W. "An Introduction to the Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules". McMaster University. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ↑ "Ununoctium (Uuo) – Chemical properties, Health and Environmental effects". Lenntech. Archived from the original on 16 January 2008. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- 1 2 Goidenko, Igor; Labzowsky, Leonti; Eliav, Ephraim; Kaldor, Uzi; Pyykkö, Pekka (2003). "QED corrections to the binding energy of the eka-radon (Z=118) negative ion". Physical Review A. 67 (2): 020102(R). Bibcode:2003PhRvA..67b0102G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.67.020102.
- ↑ Eliav, Ephraim; Kaldor, Uzi; Ishikawa, Y.; Pyykkö, P. (1996). "Element 118: The First Rare Gas with an Electron Affinity". Physical Review Letters. 77 (27): 5350–5352. Bibcode:1996PhRvL..77.5350E. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.5350. PMID 10062781.
- ↑ Landau, Arie; Eliav, Ephraim; Ishikawa, Yasuyuki; Kador, Uzi (25 May 2001). "Benchmark calculations of electron affinities of the alkali atoms sodium to eka-francium (element 119)" (PDF). Journal of Chemical Physics. 115 (6): 2389–92. Bibcode:2001JChPh.115.2389L. doi:10.1063/1.1386413. Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- ↑ Borschevsky, Anastasia; Pershina, Valeria; Kaldor, Uzi; Eliav, Ephraim. "Fully relativistic ab initio studies of superheavy elements" (PDF). www.kernchemie.uni-mainz.de. Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ↑ Borschevsky, Anastasia; Pershina, Valeria; Eliav, Ephraim; Kaldor, Uzi (27 August 2009). "Electron affinity of element 114, with comparison to Sn and Pb". Chemical Physics Letters. 480: 49–51. Bibcode:2009CPL...480...49B. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2009.08.059.
- ↑ Seaborg, Glenn Theodore (1994). Modern Alchemy. World Scientific. p. 172. ISBN 981-02-1440-5.
- ↑ Takahashi, N. (2002). "Boiling points of the superheavy elements 117 and 118". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 251 (2): 299–301. doi:10.1023/A:1014880730282.
- ↑ Nash, Clinton S.; Bursten, Bruce E. (1999). "Spin-Orbit Effects, VSEPR Theory, and the Electronic Structures of Heavy and Superheavy Group IVA Hydrides and Group VIIIA Tetrafluorides. A Partial Role Reversal for Elements 114 and 118". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 1999 (3): 402–410. Bibcode:1999JPCA..103..402N. doi:10.1021/jp982735k.
- 1 2 Jerabek, Paul; Schuetrumpf, Bastian; Schwerdtfeger, Peter; Nazarewicz, Witold (2018). "Electron and Nucleon Localization Functions of Oganesson: Approaching the Thomas-Fermi Limit". Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 (5): 053001. arXiv:1707.08710. Bibcode:2018PhRvL.120e3001J. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.053001.
- ↑ "Ununoctium: Binary Compounds". WebElements Periodic Table. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- 1 2 Han, Young-Kyu; Lee, Yoon Sup (1999). "Structures of RgFn (Rg = Xe, Rn, and Element 118. n = 2, 4.) Calculated by Two-component Spin-Orbit Methods. A Spin-Orbit Induced Isomer of (118)F4". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 103 (8): 1104–1108. Bibcode:1999JPCA..103.1104H. doi:10.1021/jp983665k.
- ↑ Pitzer, Kenneth S. (1975). "Fluorides of radon and element 118". Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications (18): 760–761. doi:10.1039/C3975000760b.
- 1 2 Seaborg, Glenn Theodore (c. 2006). "transuranium element (chemical element)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ↑ 张青莲 (November 1991). 《无机化学丛书》第一卷:稀有气体、氢、碱金属 (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press. pp. P72. ISBN 7-03-002238-6.
- ↑ Proserpio, Davide M.; Hoffmann, Roald; Janda, Kenneth C. (1991). "The xenon-chlorine conundrum: van der Waals complex or linear molecule?". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 113 (19): 7184. doi:10.1021/ja00019a014.
Further reading
- Scerri, Eric (2007). The Periodic Table, Its Story and Its Significance. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530573-9.
External links
- Element 118: experiments on discovery, archive of discoverers' official web page
- It's Elemental: Oganesson
- Oganesson at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- On the Claims for Discovery of Elements 110, 111, 112, 114, 116, and 118 (IUPAC Technical Report)
- "Element 118, Heaviest Ever, Reported for 1,000th of a Second", NYTimes.com.
- WebElements: Oganesson