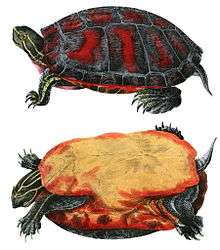
Nicaraguan slider
| Nicaraguan slider | |
|---|---|
| Trachemys emolli | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Genus: | Trachemys |
| Species: | T. emolli |
| Binomial name | |
| Trachemys emolli (Legler, 1990)[1] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The Nicaraguan slider (Trachemys emolli )[1] is a species of turtle in the family Emydidae. The species is endemic to Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Formerly it was considered a subspecies of Trachemys scripta, but was elevated to its own species level.[1]
Etymology
The specific name, emolli, is in honor of American herpetologist Edward Moll (E. Moll).[3]
Geographic range
The Nicaraguan slider is native to Nicaragua and Costa Rica, and is found in places such as Lake Nicaragua, Lake Managua, and the lakes and streams that connect them.[4]
Characteristics
The Nicaraguan slider has a carapace with many circular markings on it, and in the middle of each marking, there is a dark spot. The main color of the carapace and the turtle's skin is olive green to dark brown. It also has yellow markings on it as well. The supratemporal markings can be orange, pink, or yellow. Males averagely grow to 8–12 in (20–30 cm) straight carapace length, and females can averagely grow to 15 in (38 cm) or larger.[4]
Biology
The Nicaraguan slider likes its water to be around mid-70s to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (24 to 27 degrees Celsius). As far as basking goes, it likes its basking area to be in the high 80s to mid-90s degrees Fahrenheit (30 to 35 degrees Celsius).[4]
Diet
In the wild, the juvenile Nicaraguan slider eats the following: tadpoles, crustaceans, fish, insects and insect larvae.[4]
Breeding
The nesting season of T. emolli ranges from about the month of December to May. Females are can lay several clutches per season with up to thirty-five eggs per clutch. The hatchlings emerge about 69 to 123 days after the eggs have been deposited.[4]
Subspecies
- No subspecies.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Rhodin 2010, p. 000.103
- ↑ Fritz, Uwe; Havaš, Peter. (2007). "Checklist of Chelonians of the World" (PDF). Vertebrate Zoology. 57 (2): 204–205. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-12-17. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Trachemys emolli, p. 83).
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Trachemys emolli / Nicaraguan Slider Care Sheet". B and H Turtle Site. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- Bibliography
- Rhodin, Anders G.J.; van Dijk, Peter Paul; Iverson, John B.; Shaffer, H. Bradley (2010-12-14). "Turtles of the World 2010 Update: Annotated Checklist of Taxonomy, Synonymy, Distribution and Conservation Status" (PDF). Archived from the original (pdf) on 2010-12-15. Retrieved 2010-12-15.
Further reading
- Legler, John M. (1990). "The Genus Pseudemys in Mesoamerica: Taxonomy, Distribution, and Origins". pp. 82-105. In: Gibbons, J. Whitfield (editor) (1990). Life History and Ecology of the Slider Turtle. Washington, District of Columbia: Smithsonian Institution Press. 368 pp. ISBN 978-0874744682. (Pseudemys scripta emolli, new species, p. 91).
| Wikispecies has information related to Trachemys emolli |