Multiple-emitter transistor
A multiple-emitter transistor is a specialized bipolar transistor mostly used at the inputs of integrated circuit TTL NAND logic gates. Input signals are applied to the emitters. Collector current stops flowing only if all emitters are driven by the logical low voltage, thus performing a NAND logical operation using a single transistor. Multiple-emitter transistors replace diodes of DTL and allow reduction of switching time and power dissipation.[1][2]
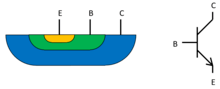
cross section and symbol of a simple NPN bipolar transistor

cross section and symbol of a multiple emitter NPN bipolar transistor
Logic gate use of multiple-emitter transistors was patented in 1961 in the UK and in the US in 1962.[4]
References
- ↑ Jacob Millman, Microelectronics: Digital and Analog Circuits and Systems, McGraw-Hill, 1979 ISBN 0-07-042327-X, pp.106-107
- ↑ Douglas J. Hamilton, William G Howard, Basic Integrated Circuit Engineering, McGraw Hill, 1975, ISBN 0-07-025763-9, pp. 457-467
- ↑ http://aries.ucsd.edu/NAJMABADI/CLASS/ECE65/06-W/NOTES/BJT1.pdf Bipolar-Junction(BJT) transistors
- ↑ B. A. Boulter, The Multiple Emitter Transistor In Low Power Logic Circuits in Edward Keonjian (ed) Micropower Electronics, Elsevier, 2013, ISBN 148315503X,p. 105 ff
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.