Mecklenburg (1945–1952)
| Land Mecklenburg Land Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (1945–1947) | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
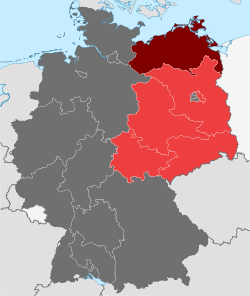 | ||||||
| Capital | Rostock | |||||
| President of the State Administration | ||||||
| • | 1945–1946 | Wilhelm Höcker | ||||
| Minister-President | ||||||
| • | 1946–1951 | Wilhelm Höcker | ||||
| • | 1951 | Kurt Bürger | ||||
| • | 1951–1952 | Bernhard Quandt | ||||
| Legislature | Landtag | |||||
| Historical era | Post-World War II Cold War | |||||
| • | Established | 9 July 1945 | ||||
| • | Declaration as state | 16 January 1947 | ||||
| • | State of East Germany |
7 October 1949 | ||||
| • | Disestablished | 25 July 1952 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | 1946 | 23,402 km2 (9,036 sq mi) | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | 1946 | 2,100,000 | ||||
| Density | 89.7 /km2 (232.4 /sq mi) | |||||
| Today part of | ||||||
The State of Mecklenburg (German: Land Mecklenburg) was a subdivision of the Soviet occupation zone (until 1949) and state of East Germany (from 1949) which corresponds widely to the present-day German state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The state was originally formed as administrative division State of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Land Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (SMAD) in July 1945. It consisted of the 1934-established Mecklenburg (a merger by the NSDAP-Gauleiter Friedrich Hildebrandt of the free states of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz) and parts of the former Prussian provinces of Pommern (Western Pomerania to the Oder–Neisse line) and Hanover (Amt Neuhaus). The city of Świnoujście was handed over in October 1945 to Poland (became part of Szczecin Voivodeship). In November 1945, a transfer of small territories along the Inner German border to the former Province of Schleswig-Holstein was carried out (Barber–Lyashchenko Agreement). About 2.1 million people were estimated to live in Mecklenburg in 1946.[1] From 1947, the term Vorpommern was excluded from the official name as the SMAD feared that this would support revisionist actions against the Polish parts (in particular Farther Pomerania). Compared to the administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, it comprised the Gaue Mecklenburg and parts of Pomerania and Eastern Hanover.
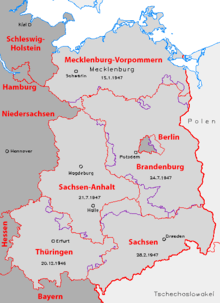
Due to the post-war situation in Germany, the SMAD appointed state administrations in all subdivisions of their occupation zone in July 1945. Wilhelm Höcker became the president of the state administration in Mecklenburg and was elected later to the Minister-President. The first election for the Landtag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern was held on 20 October 1946, on the same day the elections for the Landtage of the other divisions in the SBZ had been ruled out. The Soviet-backed SED (which became the ruling party of the GDR from 1949 onwards) received 49.5% of the votes, CDU 34.1%, LDPD 12.5% and VdgB 3.9%.[2] In February 1947, the state-constitution was adopted.[3] However, all resolutions by the parliament were made subject to approval of the SMAD.
After the foundation of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in October 1949, a second election for the Landtag was held in October 1950. The only party was the National Front, an alliance of political parties and mass organisations controlled by the SED, which received 99.9% of the votes. Following this election, it became the first and only time that four members of the Landtag were send to the Chamber of States of the GDR. As the ruling communists aimed to build a quasi-unitary state, the state was dissolved by a change of the Constitution of East Germany in July 1952. All of the five Länder were replaced by 14 newly formed Bezirke. In case of Brandenburg, the territory was transferred to the Bezirke Neubrandenburg, Rostock and Schwerin. The abolishment of the Chamber of States in 1958 and two ratifications of the constitution in 1968 and 1974 finally eliminate all kinds of federalism in the GDR until the peaceful revolution in 1989. After the first free elections in the GDR, the five Länder were re-established with some smaller geographical adjustments in August 1990 to accede to the Federal Republic of Germany.
References
- ↑ "Deutschland 2020 - Die demographische Zukunft der Nation" (PDF). Berlin Institut. May 2005. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ↑ "Landtagswahlen Mecklenburg-Vorpommern". wahlen-in-deutschland.de. 24 September 2016. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ↑ "Verfassung des Landes Mecklenburg". verfassungen.de. 16 January 1947. Retrieved 8 June 2017.

.svg.png)