Mahoning River
| Mahoning River | |
|---|---|
 Mahoning river in Warren, Ohio | |
| Country | United States |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source |
Columbiana County, Ohio 367 m (1,204 ft) above sea level |
| River mouth |
Beaver River 232 m (761 ft) above sea level |
| Length | 182 km (113 mi)[1] |
| Discharge |
|
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 2,932 km2 (1,132 sq mi) |
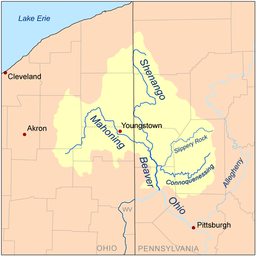
The Mahoning River is a river located in eastern Ohio and western Pennsylvania. Flowing primarily through several Ohio counties, it joins the Shenango River to form the Beaver River and is part of the Ohio River watershed.
Physical properties


The river is formed near Winona in Columbiana County, Ohio, and extends for a length of approximately 113 miles (182 km), with a watershed area of approximately 1,132 square miles (2,932 km²). It joins the Shenango River near New Castle, Pennsylvania to form the Beaver River. The river traverses five Ohio counties, Columbiana, Stark, Portage, Trumbull, and Mahoning, as well as Lawrence County, Pennsylvania. The watershed area also includes parts of Ashtabula and Geauga counties in Ohio.
The three main tributaries are Mosquito Creek, West Branch, and Eagle Creek, all in Ohio. There are 15 dams on the river course. The river has a course of 97.1 miles (156.3 km) in Ohio, with the remainder in Pennsylvania.
The river supports more than 72 species of fish and 15 species of freshwater mussels.
The river is roughly divided into two sections. The “upper elevation” extends roughly from Winona to Leavittsburg and is generally rural in nature. The mainstem (lower elevation) extends roughly from Leavittsburg to the river’s mouth near New Castle, Pennsylvania; it is heavily populated and is heavily industrialized. The mainstem area has a population of over 500,000 and has a long history of steel making, coke production, and other industries.
Environmental concerns
The industrial nature of the mainstem area has caused considerable pollution in the river. Much of the pollution has left the ecosystem via the natural river flow. But analysts estimate that 750,000 cubic yards (573,416 m³) of river bed and shoreline sediment, over a 30 mile (48.2 km) stretch of the mainstem from Leavittsburg to the Pennsylvania border, is so heavily polluted that it will need to be remediated. Approximately 45% of this material is located in the vicinity of the Girard Dam near Girard, Ohio, which has acted as a trap for much of the contaminated sediment.
Petroleum hydrocarbons, benzo(a)pyrene (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), and mercury have all been found in quantities several times the maximum safe levels. Since 1988, the Ohio Department of Health has maintained an advisory against swimming or wading in the river between Leavittsburg and the Pennsylvania border, and also advises against eating fish caught there. The Corps of Engineers estimates that the remediation will take up to 15 years to complete and cost in excess of US$100 million. If approved, the dredging project will probably begin in the late 2010s.
Cities and towns along its course include:
Floods
The Mahoning river is susceptible to frequent flooding during high rain events. One such event started when 3 days of torrential rain fell in July 2003,[2] resulting in such high volume that the river changed its course in Leavittsburg, Ohio, flooding and destroying nearly 100 homes.
The gallery of photos below shows some of the flooded areas in Leavittsburg.
- July 2003 flood
 Packard Park lower section
Packard Park lower section Packard Park ball diamonds flooded
Packard Park ball diamonds flooded Packard Park crosswalk
Packard Park crosswalk Packard Park seagulls escaping the flood
Packard Park seagulls escaping the flood Summit Street bridge almost overrun
Summit Street bridge almost overrun Summit Street old power plant dam engulfed
Summit Street old power plant dam engulfed Summit Street closeup of dam engulfed
Summit Street closeup of dam engulfed Riverwalk to nowhere
Riverwalk to nowhere
See also
References
- 1 2
- ↑ "Mahoning River Watershed Action Plan" (PDF). Youngstown State University.
External links
Coordinates: 41°02′58″N 80°34′18″W / 41.04932°N 80.57167°W