Loyalty Islands
| Native name: Îles Loyauté | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: 21°04′S 167°21′E / 21.067°S 167.350°E |
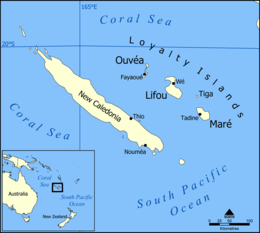
| Major islands | Lifou, Maré, Tiga, Ouvéa, Mouli, Faiava |
| Area | 1,981 km2 (765 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 138 m (453 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Overseas territory |
|
| Largest settlement | Wé |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 18,297[1] (2014) |
| Pop. density | 9.2 /km2 (23.8 /sq mi) |
| Languages | Loyalty Islands languages: Drehu, Iaai, Nengone |
| Ethnic groups | Predominantly Kanak and Tavu'avua' |
The Loyalty Islands (French: Îles Loyauté) are an archipelago in the Pacific. They are part of the French territory of New Caledonia, whose mainland is 100 kilometres (62 mi) away. They form the Loyalty Islands Province (province des îles Loyauté), one of the three provinces of New Caledonia. It has 18,000 people living on almost 2,000 square km. The native inhabitants are the Kanak people and the Tavu'avua' people.
The first Western contact on record is attributed to British Captain William Raven of the whaler Britannia, who in 1793 was on his way from Norfolk Island to Batavia, now called Jakarta. It is very likely, however, that the discovery and name goes back to the London ship Loyalty on a Pacific Ocean trading voyage from 1789 to 1790.
Geography
The archipelago consists of six inhabited islands: Lifou Island, Maré Island, Tiga Island, Ouvéa Island, Mouli Island, and Faiava Island, as well as several smaller uninhabited islands and islets. Their combined land area is 1,981 km2 (765 sq mi). The highest elevation is at 138 m (453 ft) above sea level on Maré Island.
Loyalty Islands Province is divided into three communes (municipalities):
- Lifou (comprises Lifou Island, Tiga Island, and several islets)
- Maré (comprises Maré Island and Dudun Island)
- Ouvéa (comprises Ouvéa Island, Mouli Island, Faiava Island, and several nearby islands and islets)
- Walpole Island is geographically part of the Loyalty Islands, but administratively part of the commune of Île des Pins, South Province.
The people of the Loyalty Islands are of mixed Melanesian and Polynesian ancestry, with a small European minority. They numbered 17,436 at the 2009 census, a 7.9% reduction from the 22,080 as at the preceding 2004 census. However, in 2014, the population grew to 18,297, an increase of 4.9%. Several thousand more Loyalty Islanders live in Nouméa, the capital, and in the mining areas of New Caledonia's main island. The chief export of the Loyalty Islands is copra. The islands are part of the New Caledonia rain forests ecoregion.
Provincial congress
Of 14 seats in the province's congress, the nationalist Caledonian Union holds four, the anti-independence Rally for Caledonia in the Republic holds two, and the National Union for Independence-Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front, Socialist Kanak Liberation, Renewed Caledonian Union and Union of Pro-Independence Co-operation Committees each have two.
See also
References
- ↑ "Population Structure and Trends". Institute de la Statistique et des études économiques Nouvelle-Calédonie (in French). Institute de la Statistique et des études économiques Nouvelle-Calédonie. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- Dunbabin, Thomas: William Raven, RN, and his 'Britannia', 1792–95; in: The Mariner's mirror, Vol. 46, No. 4 (Nov.); London [u.a.] 1960 (S. 297-303)
- Dunmore, John: Who's who in Pacific navigation; Carlton, Vic. 1992
- Henze, Dietmar: Enzyklopädie der Entdecker und Erforscher der Erde, Bd. 4; Graz 2000
- Jones, A. G. E.: Ships employed in the South Seas trade Vol. 1: 1775 - 1861; Canberra 1986 & Vol. 2: 1775 - 1859; Burwood, Vic. [1992]
- Parsons, Vivienne (1967). "Raven, William (1756–1814)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Canberra: Australian National University.
- Riesenberg, Saul H.: Six Pacific island discoveries; in: The American Neptune, Vol. 34; Salem, Mass. 1974 (S. 249-57)
- Sharp, Andrew: The discovery of the Pacific Islands; Oxford 1960