Lilotomab
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Mouse |
| Target | CD37 |
| Clinical data | |
| Synonyms | Tetulomab, HH1 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
Lilotomab (formerly tetulomab, HH1)[1] is a murine monoclonal antibody against CD37,[2] a glycoprotein which is expressed on the surface of mature human B cells.[3] It was generated at the Norwegian Radium Hospital.[3]
As of 2016 it was under development by the Norwegian company Nordic Nanovector ASA as a radioimmunotherapeutic in which lilotomab is conjugated to the beta radiation-emitting isotope lutetium-177 by means of a linker called satetraxetan, a derivative of DOTA.[2] This compound is called 177Lu-HH1 or lutetium (177Lu) lilotomab satetraxetan (trade name Betalutin).[1] As of 2016, a phase 1/2 clinical trial in people with non-Hodgkin lymphoma was underway.[4]
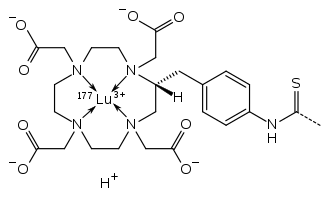
The satetraxetan structure chelating lutetium-177[5]
References
- 1 2 "Lutetium (177lu) lilotomab satetraxetan". Adis Insight. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Recommended INN List 74" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 29 (3). 2015.
- 1 2 Robak T, Robak P (2014). "Anti-CD37 antibodies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14 (5): 651–61. doi:10.1517/14712598.2014.890182. PMID 24555705.
- ↑ "EudraCT Number: 2011-000033-36". EU Clinical Trials Registry.
Treatment of lymphoma with targeted internal radiation therapy (Betalutin)
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Proposed INN: List 112" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 28 (4): 515. 2014.
Further reading
- Repetto-Llamazares, A. H.; Larsen, R. H.; Mollatt, C; Lassmann, M; Dahle, J (2013). "Biodistribution and dosimetry of (177)Lu-tetulomab, a new radioimmunoconjugate for treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma". Current Radiopharmaceuticals. 6 (1): 20–7. PMC 3624777. PMID 23256748.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.