Labdane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
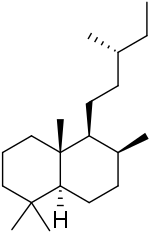
| IUPAC name
(4aR,5S,6S,8aS)-1,1,4a,6-Tetramethyl-5-[(3R)-3-methylpentyl]decalin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H38 | |
| Molar mass | 278.52 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Labdane is a natural bicyclic diterpene. It forms the structural core for a wide variety of natural products collectively known as labdanes or labdane diterpenes. The labdanes were so named because the first members of the class were originally obtained from labdanum, a resin derived from the gum rockrose.[1][2]
A variety of biological activities have been determined for labdane diterpenes including antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, and anti-inflammatory activities.[3]
Example labdane derivatives
- Forskolin
- Stemodene
- Isocupressic acid - is an abortifacient component of Cupressus macrocarpa.[4]
- Sclareol
- Medigenin
See also
References
- ↑ Cocker, J. D.; Halsall, T. G.; Bowers, A. (1956). "The chemistry of gum labdanum. I. Some acidic constituents". Journal of the Chemical Society: 4259–62.
- ↑ Cocker, J. D.; Halsall, T. G. (1956). "The chemistry of gum labdanum. II. The structure of labdanolic acid". Journal of the Chemical Society: 4262–71.
- ↑ Atta-Ur-Rahman (ed.). Studies in Natural Product Chemistry : Bioactive Natural Products, Part F. ISBN 978-0-08-044001-9.
- ↑ Parton, K; Gardner, D; Williamson, N.B (1996). "Isocupressic acid, an abortifacient component of Cupressus macrocarpa". New Zealand Veterinary Journal. 44 (3): 109. doi:10.1080/00480169.1996.35946. PMID 16031906.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.