KIAA0430
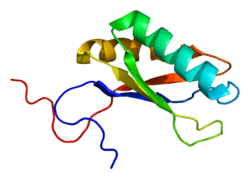
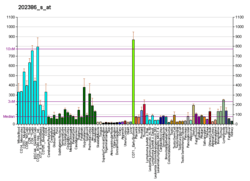
Limkain-b1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIAA0430 gene.[5][6][7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 ENSG00000277140 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166783, ENSG00000277140 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000060657 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Ishikawa K, Nagase T, Nakajima D, Seki N, Ohira M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (Feb 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VIII. 78 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 4 (5): 307–13. doi:10.1093/dnares/4.5.307. PMID 9455477.
- ↑ Loftus BJ, Kim UJ, Sneddon VP, Kalush F, Brandon R, Fuhrmann J, Mason T, Crosby ML, Barnstead M, Cronin L, Deslattes Mays A, Cao Y, Xu RX, Kang HL, Mitchell S, Eichler EE, Harris PC, Venter JC, Adams MD (Nov 1999). "Genome duplications and other features in 12 Mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q". Genomics. 60 (3): 295–308. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5927. PMID 10493829.
- ↑ Dunster K, Lai FP, Sentry JW (Jun 2005). "Limkain b1, a novel human autoantigen localized to a subset of ABCD3 and PXF marked peroxisomes". Clin Exp Immunol. 140 (3): 556–63. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02774.x. PMC 1809386. PMID 15932519.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: KIAA0430 KIAA0430".
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Brandenberger R, Wei H, Zhang S, et al. (2005). "Transcriptome characterization elucidates signaling networks that control human ES cell growth and differentiation". Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (6): 707–16. doi:10.1038/nbt971. PMID 15146197.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Martin J, Han C, Gordon LA, et al. (2005). "The sequence and analysis of duplication-rich human chromosome 16". Nature. 432 (7020): 988–94. doi:10.1038/nature03187. PMID 15616553.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.