References
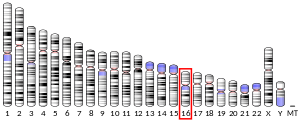
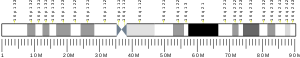
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000131149 - Ensembl, May 2017
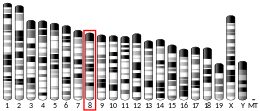
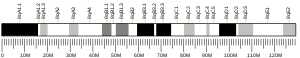
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031822 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Tanaka A, Nomura N (Nov 1996). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. V. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0161-KIAA0200) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1". DNA Res. 3 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1093/dnares/3.1.17. PMID 8724849.
- ↑ Chiang PW, Wang S, Smithivas P, Song WJ, Ramamoorthy S, Hillman J, Puett S, Van Keuren ML, Crombez E, Kumar A, Glover TW, Miller DE, Tsai CH, Blackburn CC, Chen XN, Sun Z, Cheng JF, Korenberg JR, Kurnit DM (Sep 1996). "Identification and analysis of the human and murine putative chromatin structure regulator SUPT6H and Supt6h". Genomics. 34 (3): 328–33. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0294. PMID 8786132.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: KIAA0182 KIAA0182".
Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
- Hakimi MA, Dong Y, Lane WS, et al. (2003). "A candidate X-linked mental retardation gene is a component of a new family of histone deacetylase-containing complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (9): 7234–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208992200. PMID 12493763.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.