Johnnie Walker
 | |
| Type | Scotch whisky |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Diageo |
| Country of origin | Scotland |
| Introduced |
1820: Grocery store 1865: Scotch blending |
| Related products | Ballantine's, Buchanan's, Chivas Regal, Cutty Sark, Dewar's, Vat 69 |
| Website | johnniewalker.com |
Johnnie Walker is a brand of Scotch whisky now owned by Diageo that originated in the Scottish town of Kilmarnock, East Ayrshire. The brand was first established by grocer John Walker. It is the most widely distributed brand of blended Scotch whisky in the world, sold in almost every country, with annual sales of the equivalent of over 223.7 million 700 ml bottles in 2016 (156.6 million litres).[1]
History
When John Walker, born on 25 July 1805, lost his farmer father in 1819, the family sold the farm and their trustees invested the proceeds, £417, in an Italian warehouse, grocery, and wine and spirits shop on the High Street in Kilmarnock, Ayrshire, Scotland. Walker managed the grocery, wine and spirits segment as a teenager in 1820. The Excise Act of 1823 relaxed strict laws on distillation of whisky and reduced, by a considerable amount, the extremely heavy taxes on the distillation and sale of whisky.[2] By 1825, Walker, a teetotaller, was selling spirits, including rum, brandy, gin and whisky.[3]
In short order, he switched to dealing mainly in whisky. Since blending of grain and malt whiskies was still banned, he was selling both blended malt whiskies and grain whiskies.[4] They were sold as made-to-order whiskies, blended to meet specific customer requirements, because he did not have any brand of his own.[5] He began using his name on labels years later, selling a blended malt as Walker's Kilmarnock Whisky. John Walker died in 1857.[3]
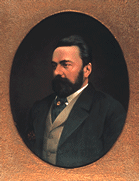
The brand became popular, but after Walker's death it was his son Alexander ‘Alec’ Walker and grandson Alexander Walker II who were largely responsible for establishing the whisky as a favoured brand. The Spirits Act of 1860 legalised the blending of grain whiskies with malt whiskies and ushered in the modern era of blended Scotch whisky.[6][3] Andrew Usher of Edinburgh, Scotland, was the first to capitalise on blended Scotch whisky, a more accessible whisky that was lighter and sweeter in character, making it much more marketable to a wider audience,[7] followed by the Walkers in due course.
Alexander Walker had introduced the brand's signature square bottle in 1860. This meant more bottles fitting the same space and fewer broken bottles. The other identifying characteristic of the Johnnie Walker bottle was – and still is – the label, which, since that year, is applied at an angle of 24 degrees upwards left to right and allows text to be made larger and more visible.[8][3] This also allowed consumers to identify it at a distance.[9] One major factor in his favour was the arrival of a railway in Kilmarnock, carrying goods to merchant ships travelling the world. Thanks to Alec's business acumen, sales of Walker's Kilmarnock reached 100,000 gallons (450,000 litres) per year by 1862.[3]
In 1865, Alec created Johnnie Walker's first commercial blend and called it Old Highland Whisky, before registering it as such in 1867.[3][10]
Under John Walker, whisky sales represented eight percent of the firm's income; by the time Alexander was ready to pass on the company to his own sons, that figure had increased to between 90 and 95 percent.[11][12]
In 1893, Cardhu distillery was purchased by the Walkers to reinforce the stocks of one of the Johnnie Walker blends' key malt whiskies.[3] This move took the Cardhu single malt out of the market and made it the exclusive preserve of the Walkers.[13] Cardhu's output was to become the heart of the Old Highland Whisky and, subsequent to the rebranding of 1909, the prime single malt in Johnnie Walker Red and Black Labels.[9]
From 1906 to 1909, John's grandsons George and Alexander II expanded the line and had three blended whiskies in the market, Old Highland at 5 years old, Special Old Highland at 9 years old, and Extra Special Old Highland at 12 years old. These three brands had the standard Johnnie Walker labels, the only difference being their colour, White, Red and Black respectively; they were commonly being referred to in public by the colour of their labels.[9] In 1909, as part of a rebranding that saw the introduction of the Striding Man, a mascot used to the present day that was created by cartoonist Tom Browne,[14] the company re-branded their blends to match the common colour names. The Old Highland was renamed Johnnie Walker White Label,[15] and made a 6 year old, the Special Old Highland became Johnnie Walker Red Label at 10 years old, and Extra Special Old Highland was renamed Johnnie Walker Black Label remaining 12 years old.[3]
Sensing an opportunity for their brands in terms of expansion of scale and variety, The Walker company became a shareholder in Coleburn Distillery in 1915, quickly followed by Clynelish Distillery Co. and Dailuaine- Talisker Co. in 1916.[3] This ensured a steady supply of the output from the Cardhu, Coleburn, Clynelish, Talisker and Dailuaine distilleries.[16] In 1923, John Walker & Sons bought Mortlach distillery, in furtherance of their strategy.[17] Most of their output was used in Johnnie Walker blends, whose burgeoning popularity required increasingly vast volumes of single malts.
Johnnie Walker White was dropped during World War I.[18] In 1932, Alexander II added Johnnie Walker Swing to the line, the name originating from the unusual shape of the bottle, which allowed it to rock back and forth.
The company joined Distillers Company in 1925. Distillers Company was acquired by Guinness in 1986, and Guinness merged with Grand Metropolitan to form Diageo in 1997. That year saw the introduction of the blended malt, Johnnie Walker Pure Malt, renamed as Johnnie Walker Green Label in 2004.[19]
When the brand's owners, Diageo, announced its decision in 2009 to close all operations in the town of Kilmarnock, it met with backlash from local people, local politics and then First Minister of Scotland, Alex Salmond. Despite petitions, public campaigns and a large-scale march around Kilmarnock, Diageo continued to forge ahead with the closure.[20][21] The Johnnie Walker plant in Kilmarnock closed its doors in March 2012.[22]
Blends
For most of its history Johnnie Walker only offered a few blends. Since the turn of the century, there has been a spate of special and limited bottlings.

- Red Label: A non age stated blend.[23] It has been the best selling Scotch whisky in the world since 1945.[24][25][26] Its primary use now is for making mixed drinks.[27][28]
- Black Label: Aged at least 12 years, it is one of the world's best-selling premium Scotch whiskies.[29]
- Double Black Label: Made available for general release in 2011 after a successful launch in travel retail.[30] The whisky was created taking Black Label as a blueprint, adding more peaty malt whiskies to it and maturing it in heavily charred old oak casks.[31]
- Green Label: First introduced in 1997 as Johnnie Walker Pure Malt 15 Year Old,[19] it was renamed Johnnie Walker Green Label in 2004. Green Label is a blended malt whisky, meaning it is made by mixing single malts with no grain whisky added.[32] All whiskies used are a minimum of 15 years old.[33][34][35] Diageo discontinued Green Label globally in 2012 (except for Taiwan, where demand for blended malts is very strong), as part of a reconstruction of the range that saw the introduction of Gold Label Reserve and Platinum Label. The brand was reintroduced in 2016 and is again globally available.[36]
- Gold Label: A blend of over 15 single malts, it was derived from Alexander Walker II's blending notes for a whisky to commemorate Johnnie Walker's centenary. Originally, Gold Label was bottled at 18 years and labelled "The Centenary blend".[37] In 2013, Gold Label was replaced by a no age statement blend, labelled "Gold Label Reserve".[38]
- Aged 18 Years: Originally introduced as Platinum Label, it was introduced to replace the original Gold Label in the Asian market, and sold alongside Gold Label Reserve. Though still available around the globe, the Platinum Label name was discontinued in mid-2017 and replaced by Johnnie Walker Aged 18 Years. The two are identical except for the label.[39]
- Blue Label: Johnnie Walker's premium blend with no age statement. Johnnie Walker Blue Label is blended to recreate the character and taste of some of the earliest whisky blends created in the 19th century.[40] Bottles are numbered serially and sold in a silk-lined box accompanied by a certificate of authenticity. It is one of the most expensive blended Scotch Whiskies on the market, with prices in the range of US$174–450.[41] Over 25 Limited Editions have been released till date.
- Johnnie Walker Swing: Supplied in a distinctive bottle whose irregular bottom allows it to rock back and forth. This type of bottle design was originally used aboard sailing ships. It was Alexander Walker II's last blend: it features a high proportion of Speyside malts, complemented by malts from the northern Highlands and Islay.
| Age | 1865–1905 | 1906–1908 | 1909–1920 | 1921–1931 | 1932–1991 | 1992–1996 | 1997–2010 | 2011— |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Old Highland | White Label | ||||||
| Not stated | Special O.H. | Red Label | ||||||
| 12 | Walker’s O.H. | Extra Sp. O.H. | Black Label | |||||
| Not stated | Double Black Label | |||||||
| Not stated | Swing | |||||||
| 15 | Green Label | |||||||
| Not stated ex 18> |
Gold Label Reserve | |||||||
| 18 | 18 Year Old (ex Platinum Label) | |||||||
| Not stated | Blue Label | |||||||
Marketing
Every type of Johnnie Walker scotch has had a label colour till 2017, except for the Swing label. The purpose is to supposedly denominate the different types of scotch and to position them to be used for different occasions. For example, Johnnie Walker Blue Label is rare and expensive, and so it is intended to be used for special occasions.
The Walkers created their primary marketing strategy in 1908 with advertisements featuring Browne's Striding Man, using the slogan, "Johnnie Walker: Born 1820, still going strong". Photographs replaced the drawings in the 1930s and the Striding Man was miniaturised to a coloured logo in 1939; it first appeared on the Johnnie Walker labels in 1960. In the late 1990s, the direction of the Striding Man was reversed as part of a "Keep Walking" campaign.[14] The Striding Man icon was most recently redrawn in 2015.[42]
In 2009, the advertising agency Bartle Bogle Hegarty (BBH) created a new short film, starring Robert Carlyle and directed by Jamie Rafn, titled The Man Who Walked Around the World, which outlined the history of the Johnnie Walker brand.[8][43][44]
Johnnie Walker also launched the international John Walker & Sons Voyager tour in order to market its higher variants in the Asia-Pacific, Europe and Caribbean markets. The Voyager tour was developed in order to promote the special edition Odyssey blend and pay tribute to the original trade routes and sea voyages by which Johnnie Walker was distributed throughout the world.
Accolades
Johnnie Walker spirits have received strong scores at international spirit ratings competitions and from liquor review bodies. The Green Label received a string of three double gold medals from the San Francisco World Spirits Competition between 2005 and 2007.[45] The Gold Label received double gold medals from the San Francisco competition in 2008 and 2009 and won a gold in 2010.[46] Spirits ratings aggregator proof66.com, which averages scores from the San Francisco Spirits Competition, Wine Enthusiast, and others, puts the Black, Blue, Gold and Green Labels in its highest performance category ("Tier 1" Spirits).[47] Johnnie Walker spirits have several times taken part in the Monde Selection's World Quality Selections and have received a Gold and Grand Gold Quality Award.[48] Johnnie Walker was voted India's Most Trusted Premium Whisky Brand according to the Brand Trust Report 2014, a study conducted by Trust Research Advisory.[49] Johnnie Walker Gold Label Reserve won the World's Best Blended -- Best Scotch Blended in World Whiskies Awards 2018.[50]
Sponsorships
Johnnie Walker is the official whisky of Formula One,[51] and are a sponsor of two F1 teams McLaren and Force India. Johnnie Walker sponsored the Johnnie Walker Classic, an Asia-Pacific golf tournament, up to 2009 and the Johnnie Walker Championship at Gleneagles, a golf tournament in Scotland up to 2013.[52] Diageo sold the Gleneagles Hotel and Golf Course, the site of the tournament, mid-2015 to focus on its core business.[53]
Cultural figures
Winston Churchill's favourite whisky was Johnnie Walker Red Label, which he mixed with water and drank throughout the day.[54]
Vanity Fair writer Christopher Hitchens was partial to Johnnie Walker Black Label, and referred to it as "Mr Walker's Amber Restorative".[55]
Johnnie Walker Blue Label was a favourite of the late US president Richard Nixon, who used to enjoy it with ginger ale and a wedge of lime.[56]
A number of singers and songwriters have referenced Johnnie Walker in their works, from Amanda Marshall to ZZ Top.[57] Heavy metal band Black Label Society was named after Johnnie Walker Black Label whisky, as Zakk Wylde was very fond of the drink.[58]
Gallery
 Johnnie Walker Red Label
Johnnie Walker Red Label Johnnie Walker Black Label
Johnnie Walker Black Label Johnnie Walker Double Black
Johnnie Walker Double Black Johnnie Walker Swing
Johnnie Walker Swing Johnnie Walker Green Label & Green Label 180 Cask
Johnnie Walker Green Label & Green Label 180 Cask Johnnie Walker Gold Label Reserve
Johnnie Walker Gold Label Reserve Johnnie Walker Platinum Label
Johnnie Walker Platinum Label Johnnie Walker Blue Label
Johnnie Walker Blue Label
References
- ↑ "Scotch Whisky Brand Champion 2017: Glenfiddich". thespiritsbusiness.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "History of Scotch Whisky". Scotch Whisky Association.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Johnnie Walker - History". www.thewhiskyexchange.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Inc., M. Shanken Communications,. "Walking Tall". Cigar Aficionado. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Scotch: The Story of Whisky S01E02. Per Mikkelsen.
- ↑ Micallef, Joseph V. Scotch Whisky, its History, Production and Appreciation (2015) Antioch Downs Press, Vancouver, Portland/www.AntiochDownsPress.com/ ISBN 978-0-9947571-1-1 Digital Edition: ISBN 978-0-9947571-0-4
- ↑ https://www.whiskyshop.com/brief-history-of-blended-whisky
- 1 2 The Man Who Walked Around the World. BBH New York. 2009. Retrieved 2017-06-30.
- 1 2 3 Inc., M. Shanken Communications,. "Walking Tall". Cigar Aficionado. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "The Johnnie Walker Story". John Walker and Sons. 2015. Retrieved 2017-06-30.
- ↑ MacDonogh, Giles (2005). "John Walker's legacy". Cigar Aficionado. Archived from the original on 2006-03-10.
- ↑ Maclean, Charles (2003). Scotch Whisky: A Liquid History. London, England: Cassell Illustrated. ISBN 1-84403-078-4.
- ↑ York, BBH New (5 December 2014). "Johnnie Walker: The Man Who Walked Around the World". Retrieved 16 December 2017 – via Vimeo.
- 1 2 "A Visual History of Johnnie Walker's Striding Man Logo". vinepair.com. 17 July 2017. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker White Label - Bot.~1900 : The Whisky Exchange". www.thewhiskyexchange.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "LUDICROUS COMMENTS ON SCOTCH WHISKY". noelonwhisky.blogspot.in. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Mortlach History - Mortlach Whisky - Malts". www.malts.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnny Walker – History". Specialty Drinks Limited. Retrieved 2014-12-12.
First World War; ... White Label is discontinued as the Johnnie Walker brand moves upmarket
- 1 2 "Expert Liquor Recommendations - Distiller". Distiller - The Liquor Expert. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Reports on 'end of Johnnie Walker' completely false: Diageo - Indian Express". archive.indianexpress.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker jobs plan rejected". BBC News. 9 September 2009. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
- ↑ Johnnie Walker whisky plant closes in Kilmarnock. BBC News. 23 March 2012. Retrieved 2012-08-07.
- ↑ "Whisky Notes: Johnnie Walker Red Label vs. Johnnie Walker Black Label". Ruben Luyten for Whisky Notes.
- ↑ whisky.com. "Johnnie Walker Blended Scotch Whisky". www.clubwhisky.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Red Label". John Walker and Sons.
- ↑ http://www.scotch-whisky.org.uk/media/12744/ scotchwhiskyregguidance2009.pdf
- ↑ "Whisky Notes: Johnnie Walker Red Label vs. Johnnie Walker Black Label: Johnnie Walker Red Label (40%, OB +/- 2013)". Ruben Luyten for Whisky Notes.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Red Label : The Whisky Exchange". www.thewhiskyexchange.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Johnnie Walker Colours
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Double Black : The Whisky Exchange". www.thewhiskyexchange.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Miller, Jared T. (2013-05-10). "Johnnie Walker adds Double Black to whisky line". Daily News. Retrieved 2013-05-27.
- ↑ Eats, Serious. "What Is the Difference Between Single Malt and Blended Whisky?". drinks.seriouseats.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Green Discontinued". www.scotch-tasting-bums.com. 2012-01-16. Archived from the original on 2012-10-04. Retrieved 2012-11-29.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Green Label 15 Year Old". The Whisky Exchange.
- ↑ Dominic, Roskrow. "Dominic Roskrow's Blog". The Whisky Tasting Club – UK.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Green Label returns - Scotch Whisky". scotchwhisky.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Gold Label The Centenary Blend 18 Year Old Blended Scotch Whisky (700ml) - Blended Scotch Whisky". www.nicks.com.au. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Gold Label 18 vs. Johnnie Walker Gold Label Reserve". drinkspirits.com. 1 November 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Platinum given new identity - Scotch Whisky". scotchwhisky.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Blue Scotland Scotch 750 ml". Wineanthology.com. Retrieved 2012-11-03.
- ↑ "Bottle King Largest New Jersey Retailer of Wine, Beer and Spirits". bottleking.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Bloom redraws Johnnie Walker's "Striding Man"". www.designweek.co.uk. Retrieved 10 January 2018.
- ↑ Robert Carlyle Italia (8 November 2013). "Robert Carlyle - Johnnie Walker - The Man Who Walked Around The World [SUB ITA]". Retrieved 16 December 2017 – via YouTube.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker : History & Trivia". wordpress.com. 30 July 2011. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Proof66.com Summary of Green Label Awards". Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ "Proof66.com Summary of Gold Label Awards". Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ "Proof66.com Website". Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ Marc Guison (2012-02-08). "Awards". Slideshare.net. Retrieved 2012-11-03.
- ↑ "India's Most Trusted Alcoholic Beverages 2014". Trust Research Advisory. Archived from the original on 2014-03-27.
- ↑ "World Whiskies Awards 2018 - Winners". www.worldwhiskiesawards.com. Retrieved 2018-10-05.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker becomes the Official Whisky Of Formula 1". formula1.com. 18 September 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ↑ europeantour.com. "Johnnie Walker Championship at Gleneagles plans for the future - European Tour". www.europeantour.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Tovey, Alan (1 July 2015). "Diageo sells golf's Gleneagles hotel as it focuses on core business". Retrieved 16 December 2017 – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- ↑ "How to drink like Winston Churchill". The Telegraph. 2015-01-28. Retrieved January 31, 2018.
- ↑ Brown, Craig (2012-03-21). "Christopher Hitchens's Diary". Vanity Fair. Retrieved 2012-11-03.
- ↑ Small, Melvin (2011). A Companion to Richard M. Nixon. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4443-3017-5.
- ↑ "Johnnie Walker Blue Label". www.tastersguide.com. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "Black Label Society - metalinside". www.metalinside.de. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
Further reading
- MacLean, Charles (2003). Scotch Whisky: A Liquid History. Cassell Illustrated. ISBN 1-84403-078-4.
- Molavi, Afshin. "Straight Up: How Johnnie Walker conquered the world". Foreign Policy. The Slate Group (September/October 2013). Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- Micallef, Joseph (2015). Scotch Whisky, its History, Production and Appreciation. Vancouver, Portland: Antioch Downs Press www.AntiochDownsPress.com. ISBN 978-0-9947571-1-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Johnnie Walker (whisky). |