Ayrshire
| Ayrshire | |
|---|---|
| Historic county | |
 | |
| Country | Scotland |
| County town | Ayr |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,129 sq mi (2,924 km2) |
| Ranked 7th of 34 | |
| Chapman code | AYR |
Ayrshire (Scottish Gaelic: Siorrachd Inbhir Àir, pronounced [ˈʃirˠəxk iɲiˈɾʲaːɾʲ]) is a historic county and registration county in south-west Scotland, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. Its principal towns include Ayr, Kilmarnock and Irvine. Like the other counties of Scotland, it currently has no administrative function, instead being sub-divided into the council areas of North Ayrshire, South Ayrshire and East Ayrshire. It has a population of approximately 366,800.
The electoral and valuation area named Ayrshire covers the three council areas of South Ayrshire, East Ayrshire and North Ayrshire, therefore including the Isle of Arran, Great Cumbrae and Little Cumbrae. These three islands are part of the County of Bute and are sometimes included when the term Ayrshire is applied to the region. The same area is known as Ayrshire and Arran in other contexts.
Geography
_-_geograph.org.uk_-_554287.jpg)
Ayrshire is one of the most agriculturally fertile regions of Scotland. Potatoes are grown in fields near the coast, using seaweed-based fertiliser, and in addition the region produces pork products, other root vegetables, and cattle (see below); and summer berries such as strawberries are grown abundantly.
Ayrshire shares with Dumfries and Galloway some rugged hills country known as the Galloway Hills. These hill lie to the west of the A713 (Ayr to Castle Douglas road) and they run south from the Loch Doon area almost to the Solway Firth. To the east of this route through the hills lie the Carsphairn and Scaur Hills which lie to the south east of Dalmellington and south of New Cumnock. Glen Afton runs deep into these hills.
Glasgow Prestwick International Airport, serving Glasgow and the West of Scotland more generally, is located more than 30 miles away from Glasgow in Ayrshire. The name Glasgow was added on in front of Prestwick as per American military airport naming conventions, as the airport was in the past oft-used as a stopover by US military personnel on their way to and from military bases in Germany. Moreover, it has a niche in rock history as the only place in Britain visited by Elvis Presley, on his way home from Army service in Germany in 1960.
History
The area that today forms Ayrshire was part of the area south of the Antonine Wall which was briefly occupied by the Romans during the reign of Emperor Antoninus Pius (see: Roman Britain#Occupation and retreat from southern Scotland). It was inhabited by the Damnonii, who are presumed to have been Britons. Later, it formed part of the British Kingdom of Strathclyde, which was incorporated into the Kingdom of Scotland during the 11th century. In 1263, the Scots successfully drove off the Norwegian leidang-army in a skirmish known as the Battle of Largs.
A notable historic building in Ayrshire is Turnberry Castle, which dates from the 13th century or earlier, and which may have been the birthplace of Robert the Bruce.
The historic shire or sheriffdom of Ayr was divided into three districts or bailieries which later made up the county of Ayrshire. The three districts were:
- Carrick in the south. It was situated between the Doon and the wild district of Galloway in the adjoining Stewartries, an area that was little else than a vast tract of hills and mosses.[1]
- Kyle in the centre, which included the royal burgh of Ayr, occupied the central district between the River Irvine in the north, and the River Doon in the south and south-west, an area that is quite hilly inland. It was subdivided into "Kyle Stewart",[2] (sometimes called "Stewart Kyle"[1] or "Walter's Kyle"[3]) and "King's Kyle," the former embracing the country between the Irvine and the River Ayr; and the latter, the triangular portion between the Ayr and the Doon, which is honoured as the birthplace and youthful home of Robert Burns.[1]
- Cunninghame in the north which included the royal burgh of Irvine was that part of the county which lay north of the Irvine water, and was in an area that is generally level and fertile.[1]
The area used to be heavily industrialised, with steel making, coal mining and in Kilmarnock numerous examples of production-line manufacturing, most famously Johnnie Walker whisky. In more recent history, Digital Equipment had a large manufacturing plant near Ayr from about 1976 until the company was taken over by Compaq in 1998. Some supplier companies grew up to service this site and the more distant IBM plant at Greenock in Renfrewshire. Scotland's aviation industry has long been based in and around Prestwick and its international airport, and although aircraft manufacture ceased at the former British Aerospace plant in 1998, a significant number of aviation companies are still based on the Prestwick site. However, unemployment in the region (excluding the more rural South Ayrshire) is above the national average.
Throughout the 17th century, huge numbers of people from Ayrshire moved to Ulster, the northern province in Ireland, as part of the Plantation of Ulster, many of them with surnames such as Burns, Hamilton, Morrow, Stewart, Flanagan, Kennedy and Cunningham. Today, the Ulster Scots dialect is largely an offshoot of the version of Lowland Scots spoken in Ayrshire. The Ulster Scots dialect is still widely spoken throughout County Antrim and in parts of County Down and County Londonderry, as well as still being widely spoken in West Tyrone and parts of County Donegal (chiefly East Donegal and Inishowen).
Local government
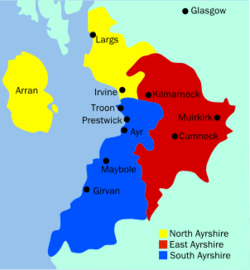
The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 established a uniform system of county councils in Scotland and realigned the boundaries of many of Scotland's counties. Subsequently, Ayr county council was created in 1890. In 1930 the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929 was implemented. This re-designated the Burghs into large burghs and small burghs. This new categorisation influenced the level of autonomy that the Burghs enjoyed from the county council. The act also abolished the parish as a unit of local government in Scotland. In Ayrshire in excess of 30 parishes were consolidated into ten district councils. The District Councils were Ayr, Cumnock, Dalmellington, Girvan, Irvine, Kilbirnie, Kilmarnock, Maybole, Newmilns and Saltcoats.
In May 1975 the county council was abolished and its functions were transferred to Strathclyde Regional Council. The county area was divided between four new districts within the two-tier Strathclyde region: Cumnock and Doon Valley, Cunninghame, Kilmarnock and Loudoun and Kyle and Carrick. The Cunninghame district included the Isle of Arran, Great Cumbrae and Little Cumbrae, which had until then been administered as part of the County of Bute.
In 1996 the two-tier system of regions and districts was abolished and Ayrshire was divided between the unitary council areas of East Ayrshire (covering the area of the former Kilmarnock & Loudoun District and Cumnock & Doon Valley District), North Ayrshire (covering the area of the former Cunninghame District Council) and South Ayrshire (covering the area of the former Kyle and Carrick District).
Parliamentary constituencies
There was an Ayrshire constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1708 to 1801 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 until 1868, when the constituency was divided into Ayrshire North and Ayrshire South.
During the whole of the 1708 to 1868 period, and until 1950, the burghs of Ayr and Irvine were parliamentary burghs, represented as components of Ayr Burghs. In 1832 Kilmarnock became a parliamentary burgh, to be represented as a component of Kilmarnock Burghs until 1918. Ayr Burghs and Kilmarnock Burghs were districts of burghs, and quite different in character from later Ayr and Kilmarnock constituencies.
From 1918 to 1983 Ayrshire and Buteshire were treated as if a single area for purposes of parliamentary representation, with their combined area being divided into different constituencies at different times. Scottish local government counties were abolished in 1975, in favour of regions and districts, but the next reform of constituency boundaries was not until 1983.
Constituencies covering Ayrshire may be listed by periods as below, but the story is somewhat more complicated than the lists may imply: until 1918, Ayr Burghs and Kilmarnock Burghs included burghs lying outside both Ayrshire and Buteshire; a particular constituency name may represent different boundaries in different periods; in 1974, there were boundary changes without the creation of any new constituency names.
| Period | Constituencies |
|---|---|
| 1708 to 1832 | Ayrshire and Ayr Burghs |
| 1832 to 1868 | Ayrshire, Kilmarnock Burghs and Ayr Burghs |
| 1868 to 1918 | North Ayrshire, Kilmarnock Burghs, Ayr Burghs and South Ayrshire |
| 1918 to 1950 | Bute and Northern Ayrshire, Kilmarnock, Ayr Burghs and South Ayrshire |
| 1950 to 1983 | Bute and Northern Ayrshire, Central Ayrshire, Kilmarnock, Ayr and South Ayrshire |
Towns and villages in Ayrshire
- Alloway
- Ardrossan
- Annbank
- Auchentiber
- Auchinleck
- Ayr
- Ballantrae
- Barrhill
- Barr
- Beith
- Bellsbank
- Catrine
- Coylton
- Crosshill
- Crosshouse
- Cumnock
- Dailly
- Dalmellington
- Dalry
- Dalrymple
- Darvel
- Drongan
- Dreghorn
- Drybridge
- Dundonald
- Dunlop
- Dunure
- Fairlie
- Fenwick
- Galston
- Gatehead
- Girvan
- Glengarnock
- Hansel
- Hurlford
- Irvine
- Kilbirnie
- Kilmarnock
- Kilmaurs
- Kilwinning
- Kirkmichael
- Kirkoswald
- Knockentiber
- Largs
- Lendalfoot
- Logan
- Lugton
- Lugar
- Mauchline
- Maidens
- Maybole
- Monkton
- Mossblown
- Minishant
- Muirkirk
- New Cumnock
- Newmilns
- Ochiltree
- Old Dailly
- Pinmore
- Pinwherry
- Prestwick
- Saltcoats
- Seamill
- Skelmorlie
- Sorn
- Springside
- Stair
- Stevenston
- Stewarton
- Straiton
- Symington
- Tarbolton
- Troon
- Turnberry
- West Kilbride
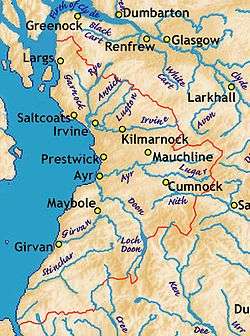
Rivers in Ayrshire
The main rivers flowing to the Clyde coast are, from north to south, the following:
Places of interest
- Auchenharvie Castle
- Barony and Castle of Giffen
- Cleeves Cove
- Clyde Muirshiel Regional Park
- Corsehill
- Dalgarven Mill – Museum of Ayrshire Country Life and Costume
- Dean Castle - Kilmarnock]]
- Eglinton Country Park
- Laigh Milton viaduct
- Thurgartstone
- Ayr Seafront Playpark
- Burns National Heritage Park
- The Low Green, Ayr
- Turnberry (golf course)
People from Ayrshire
- Hew Ainslie (1792–1878), poet[4]
- Sir Thomas Brisbane (1773–1860), Scottish soldier and colonial administrator, after whom the city of Brisbane is named.
- John Boyd Orr (1880–1971), Nobel Peace Prize winner
- George Douglas Brown (1869–1902), novelist, best known for The House with the Green Shutters
- Robert the Bruce (1274–1329), possibly at Turnberry Castle.
- Robert Burns (1759–1796), poet, in Alloway;
- Kenneth Campbell (1917–1941), RAF pilot, posthumous recipient of the Victoria Cross, born in Ardrossan.
- James McCosh Clark (1833–1898), Mayor of Auckland
- Robert Craufurd (1764–1812), British Major-General;
- Thomas Craig (1855–1900), professor of mathematics, editor, and author.[4]
- John Dunlop (1840–1921), Scottish inventor of the pneumatic tire, in Dreghorn.
- Robert Dunsmuir (1825-1889) Coal baron and industrial capitalist on Vancouver Island, Canada
- Andrew Fisher (1862–1928), 5th Prime Minister of Australia 1908-1909, 1910–1913, 1914–1915;
- Sir Alexander Fleming (1881–1955), inventor/discoverer of penicillin, in Darvel;
- John Galt (1779–1839), author.
- Drew Galloway (1985-), professional wrestler on WWE's NXT brand as Drew McIntyre.
- Air Chief Marshal Angus Houston, current Australian Chief of Defence Force Emigrated to Australia in 1968
- George Houston (artist) (1869–1947), landscape painter of Scottish locales;[5]
- Tom Hunter, entrepreneur and philanthropist
- The MacDonald Brothers, recording artists and contestants on The X Factor
- John McAdam (1756–1836), engineer, responsible for a system of road design;
- James McCosh (1811–1894), philosopher of the Scottish School of Common Sense and president of what would become Princeton University.[4]
- Jai McDowall (1986-), winner of Britain's Got Talent in 2011
- William McIlvanney, writer.
- Sir Thomas McKillop, (1943-) CEO of AstraZeneca, born in Dreghorn
- James Henry McLean (1806–1886), born in Ayrshire, physician and United States Congressman from Missouri.[4]
- Colin Mochrie (born 1957) Scottish /Canadian improvisational comedian and actor (best known for being in Whose Line Is It Anyway?)
- William Murdoch (1754–1839), Inventor of gas lighting and Engineer
- Simon Neil (1979-), James Johnston, and Ben Johnston of Biffy Clyro
- Neil Oliver, Archaeologist, Historian & Author
- Alexander Peden (1626 – 1686), leading figure in the Covenanter movement
- Bill Shankly (1913–1981), football manager
- Robert Simson (1687–1768), mathematician and professor of mathematics for 50 years
- Nicola Sturgeon (1970-), First Minister of Scotland (SNP) Born in Irvine
- Sam Torrance (1953-), professional golfer born in Largs
- Viper (1991-), Professional wrestler best known for her work in WWE and ICW
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Douglas, William Scott (1874). In Ayrshire; a descriptive picture of the County of Ayr, with relative notes on interesting local subjects, chiefly derived during a recent personal tour. Kilmarnock M'Kie & Drennan. p. 2.
- ↑

- ↑ Murray, David (1924). Early burgh organization in Scotland: as illustrated in the history of Glasgow and of some neighbouring burghs. 2. Maclehose, Jackson & Co.
- 1 2 3 4 Who Was Who in America, Historical Volume, 1607-1896. Chicago: Marquis Who's Who. 1963.
- ↑ Euan Robson, George Houston: Nature's Limner (Atelier Books: Edinburgh, 1997).
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Ayrshire. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ayrshire. |