J. B. Hunt
 | |
| Public | |
| Traded as |
NASDAQ: JBHT NASDAQ-100 component DJTA component S&P 500 component |
| Founded | August 10, 1961 |
| Founder |
Johnelle Hunt (Co-Founder) Johnnie Bryan Hunt (Co-Founder) |
| Headquarters | Lowell, Arkansas, U.S. |
Key people |
Kirk Thompson (Chairman of the Board) John N. Roberts, III (President & CEO) David G. Mee (Executive VP & CFO) |
| Revenue |
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
Number of employees | 124,681 (2017) |
| Website | JBHunt.com |
|
Footnotes / references [1] | |
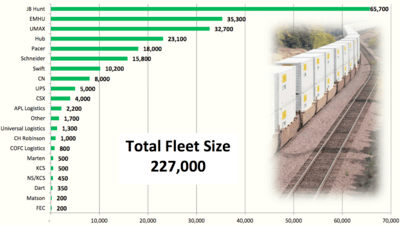
J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc. is a trucking and transportation company that was founded by Johnnie Bryan Hunt, and based in the Northwest Arkansas city of Lowell. J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc. was incorporated in Arkansas on August 10, 1961 and started with five trucks and seven refrigerated trailers to support the rice hull business. By 1983, J.B. Hunt had grown into the 80th largest trucking firm in the US and earned $63 million in revenue. At that time J.B. Hunt was operating 550 tractors, 1,049 trailers, and had roughly 1,050 employees. Today the company has grown into one of the largest transportation companies in the US with annual revenues of about $7 billion. J.B. Hunt primarily operates large semi-trailer trucks, and provides transportation services throughout the continental US, Canada and Mexico. The company currently employs over 124,000 and operates more than 12,000 trucks. Over 100,000 trailers and containers can be found in the company's fleet.[2]
J.B. Hunt's major competitors in the US are Swift Transportation, Schneider National, Werner Enterprises, and Hub Group.
In 1989, J.B. Hunt Transport began partnering with railroads to offer intermodal service. Today, about two-thirds of the company's revenues and profits come from intermodal. The company also launched a specialized trucking service division along with a flatbed operation, which was later sold.
Dedicated Contract Services (DCS): Started in 1992, DCS operations typically provide customized services that are governed by long-term contracts and currently include dry-van, flatbed, temperature-controlled, dump trailers and local inner-city operations

Intermodal (JBI): The JBI segment began operations in 1989 with a partnership with the former Santa Fe Railway (now the BNSF Railway Company). Essentially, JBI draws on the intermodal (also known as "container on flatcar") services of rail carriers for the underlying linehaul movement of its equipment and performs the pickups and deliveries ("drayage") for customers at the origin and destination rail terminal locations. May directly provide the drayage service at either the origin or destination rail ramp using company-controlled tractors, or they purchase these services from third parties.
Integrated Capacity Solutions (ICS): This segment includes full truckload, dry-van freight using company-controlled tractors operating over roads and highways. ICS also features a suite of specialty transportation services including Less than Truck Load (LTL), Refrigerated, and Flatbed. ICS reported record revenue in 2016 of over $800 million.
Truckload: This segment includes full truckload, dry-van freight using company-controlled tractors operating over roads and highways.
See also
References
- ↑ "US SEC: Form 10-K J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc". U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Retrieved March 2, 2018.
- ↑ "NASDAQ". https://www.google.com/finance?cid=275712. NASDAQ. Retrieved 29 June 2014. External link in
|website=(help)
External links
- Business data for J.B. Hunt: Google Finance
- Yahoo! Finance
- Reuters
- SEC filings