Inter-Korean House of Freedom
The House of freedom, on the South Korean side of the boundary (the building behind the blue cabins), as seen from Phanmun Pavilion on the North Korean side of the boundary | |
| Korean name | |
|---|---|
| Hangul | 자유의집 |
| Revised Romanization | Jyoueujip |
|
Maps of the Panmunjom Truce Village 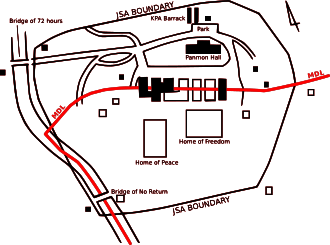 Key[1] | |
| Red | Military Demarcation Line |
| Solid black | Buildings under North Korean administration |
| Outlined | Buildings under joint U.N./South Korean administration |
The Inter-Korean House of Freedom is a four-story building located in the southern part of Panmunjom, which is a building corresponding to the North Korean Building Panmungak. It is located 130 meters southwest of the Peace House in the south of Panmunjom. The house of freedom was rebuilt on 9 July 1998 after demolition of the old house of freedom.
Summary
The Panmunjom Inter-Korean House of freedom is a four-story Top and two-story underground building built to serve as a liaison between North and South Korea. Originally built on September 30, 1965, it was a two-story building on the left and right, centered on an octagonal building. The south building facing the Panmunjeom Military Demarcation Line (MDL) is the house of liberty, and the north building is the Panmungak.[2]
Usages
The house of freedom is one of the main inter-Korean meeting places along with the House of Peace. On 30 April 2018, U.S President Donald Trump suggested that the house of freedom would be reasonable place to discuss about denuclearization and peace treaty on Korean Peninsula during the Trump–Kim summit.[3] It is the first public announcement by the US president's preferred meeting location of the historic summit between USA and North Korea. [4] Trump said on his Twitter posting, "Although many countries are being considered as a place for talks for Trump-Kim meeting, the House of Peace / Freedom in the DMZ border region of South and North Korea (in Panmunjom) is more representative than the third country "Is it an important and sustainable place for the future? [5] There has been some negative image about Panmunjom and Peace House, but after the successful 2018 inter-Korean summit, the vision of Panmunjom and the House of Peace/House of Freedom has improved positively by the world-wide press.[6] The North Korea–United States summit is the first to be held after more than 65 years since the Korean War in 1950, and former US presidents have already visited the DMZ. [7] According to diplomatic information obtained by CNN, North Korea's supreme leader Kim Jong-un agreed to meet US president Donald Trump in a Inter-Korean Peace House/House of Freedom on the Korean Demilitarized Zone.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "The Truce Village of Panmunjom - The New York Times". Nytimes.com. 2017-11-14. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ↑ tourdmz.com. "국제문화서비스클럽 - 외국인 판문점 관광". tourdmz.com.
- ↑ Pengelly, Martin; Smith, David (30 April 2018). "Trump suggests meeting Kim on border as South Korean leader touts Nobel". the Guardian.
- ↑ CNN, Maegan Vazquez and Kevin Liptak,. "Trump 'just asking' if Korean border would be best suited for Kim meeting".
- ↑ "Trump, Hoping for 'Great Celebration,' Wants to Hold North Korea Talks in DMZ".
- ↑ Seok-Hyun, Hong (7 May 2018). "Opinion - Former South Korea special envoy: Why I'm hopeful about North Korea" – via www.washingtonpost.com.
- ↑ Press, Associated. "Trump floats Korean DMZ as location for summit with Kim Jong Un". latimes.com.
- ↑ CNN, Will Ripley, Ralph Ellis and Ben Westcott,. "Kim agrees to meet Trump at DMZ, source says".