Health in the United Kingdom
Health in the United Kingdom refers to the overall health of the population of the United Kingdom. Smoking, alcohol consumption and obesity in the United Kingdom are all above the OECD average.[1]
Health status
Life expectancy

In 2013 Life expectancy at birth for women was 83 years and for men 79 years.[2] Life expectancy in the UK is rising more slowly than in other comparable nations. Austerity may be a cause.[3] Underfunding of the NHS and Social care are blamed.[4] In 2018 life expectancy in the UK stopped increasing for the first time since 1982 when recording started.[5]
Infant mortality
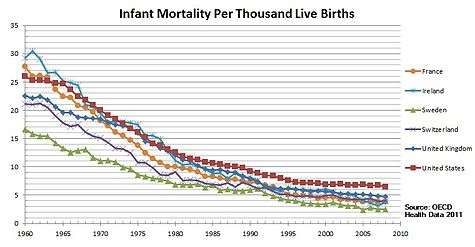
Infant mortality rates have been decreasing since the early 1900s, partially due to general improvements in healthcare and more recently because of improvements in midwifery and neonatal intensive care.[6]
Obesity
The rising rates of childhood obesity were described as a "national emergency" by Health Secretary Jeremy Hunt in February 2016.[7] 28.1% of adults in the United Kingdom were recognised as clinically obese with a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30 in 2014.[8]
Smoking rates
In 1974, 45% of the British population smoked. The smoking rate was down to 30% by the early-1990s, 21% by 2010, and 19.3% by 2013, the lowest level for eighty years.[9] In 2015, smoking rates in England had fallen to 16.9%.[10]
Cancer
There were 361,216 cancer diagnoses in 2014 in the United Kingdom.[11] Three quarters of cancers were related to smoking and drinking.[12]
Mental health
In 2014, the Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey reported that 17% of those surveyed in England met the criteria for a common mental disorder. About 37% of those were accessing mental health treatment. Those more severely affected were more likely to be accessing services.[13] In 2017 a survey found that 65% of Britons have experienced a mental health problem, with 26% having had a panic attack and 42% said they had suffered from depression.[14]
Benefit cuts and sanctions "are having a toxic impact on mental health" according to the UK Council for Psychotherapy. Rates of severe anxiety and depression among unemployed people increased from 10.1% in June 2013 to 15.2% in March 2017. In the general population the increase was from 3.4% to 4.1%.[15]
Suicide
6,045; 5,608 and 5,675 people aged 15 and over died by suicide in from 2009-2011 respectively.[16][17]
Drug-related deaths
HIV/AIDS
In 2015, the prevalence of HIV in the United Kingdom was estimated at 101,200 (0.16% of the population), 13% of whom are unaware of their infection.[18][19][20][21] Prevalence is highest amongst gay/bisexual men in London with an estimated 1 in 7 living with HIV.[19]
An estimated 101,200 people are living with HIV in the UK. Of those, 69% are men and 31% were women.[19] Just under half of those living with HIV are gay or bisexual men.[19] 1 in 7 gay or bisexual men in London are living with HIV, compared to 1 in 25 in the rest of the UK and less than 1 in 500 for the general population.[19]
6,095 people were newly diagnosed during 2015, a trend which has remained relatively constant since 2010.[22] An estimated 39% of diagnoses were late (likely to have been living with the virus for over three years).[19]
Disability
In 2014 more than 11 million British people (excluding Northern Ireland) were reported to have a long term impairment or disability. The incidence rises with age. About 6% of children, 16% of working age adults and 45% of pensioners are reported as having a disability.[23]
Vaccination
In the United Kingdom, the purchase and distribution of vaccines is managed centrally, and recommended vaccines are provided for free by the NHS.[24] In the UK, no laws require vaccination of schoolchildren.[24]
Health dynamics
Socioeconomics
The Black Report, published reluctantly by the Thatcher government in 1980, highlighted the relationship between socioeconomic status and health outcomes. It demonstrated greater inequality of mortality between occupational classes I and V both in 1970-72 and 1959-63 than in 1949-53.[25]
See also
- Healthcare in the United Kingdom
- Category:Health disasters in the United Kingdom
- Category:Diseases and disorders in the United Kingdom
- Category:Drugs in the United Kingdom
- Category:Public health in the United Kingdom
References
- ↑ "Health at a Glance 2015 How does the United Kingdom compare?" (PDF). OECD. 2015. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ↑ "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland". World Health Organisation. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ↑ UK among worst for life expectancy rises BBC
- ↑ UK life expectancy growth falls faster than other leading nations The Guardian
- ↑ Life expectancy progress in UK 'stops for first time' BBC
- ↑ "Childhood mortality in England and Wales: 2015". Office for National Statistics. 20 April 2017. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ↑ Sparrow, Andrew (7 February 2016). "Childhood obesity is a national emergency, says Jeremy Hunt". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 February 2016.
- ↑ "Prevalence of obesity, ages 18+, 2010-2014". World Health Organisation. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- ↑ "Ministers aim to halve number of people smoking by 2020". BBC News. 1 February 2010. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ↑ "Smoking rates in England fall to lowest on record". 20 September 2016 – via www.bbc.co.uk.
- ↑ "Cancer Is More Common Than Marriage Or Having A First Baby In The UK". International Business Times. 10 July 2017. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ "Revealed for the first time: the cancer map of Britain". Daily Telegraph. 11 July 2005. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ "Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey: Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing, England, 2014". NHS Digital. 29 September 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ↑ Two thirds of adults experience mental health problems such as anxiety or depression, survey finds. The Independent. Published 8 May 2017. Retrieved 26 January 2018.
- ↑ "Government welfare cuts blamed for 50% surge in mental health issues among unemployed". Independent. 17 July 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ↑ "UK suicide rate rises 'significantly' in 2011". BBC News. 22 January 2013. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ↑ "Suicide rates in the United Kingdom, 2006 to 2010" (PDF). Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ↑ "HIV and AIDS in the United Kingdom (UK)". AVERT. 2015-07-21. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "HIV in the UK" (PDF). UK Government. Public Health England. 2016-12-01. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ Trust, Terrence Higgins. "HIV in the UK | Terrence Higgins Trust". www.tht.org.uk. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "UK HIV Statistics | National AIDS Trust - NAT". www.nat.org.uk. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "HIV diagnoses, late diagnoses and numbers accessing treatment and care" (PDF). UK Government. Public Health England. October 2016. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "Disability facts and figures". Department for Work and Pensions - Office for Disability Issues. 2014-01-16. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- 1 2 Freed GL (2005). "Vaccine policies across the pond: looking at the U.K. and U.S. systems". Health Affairs. 24 (3): 755–7. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.24.3.755. PMID 15886170.
- ↑ Black Report. London: HMSO. 1980. Retrieved 24 August 2017.