Gubbi Gubbi people
 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| South East Queensland |
The Gubbi Gubbi, also written Kabi Kabi, people are an Indigenous Australian people native to southeastern Queensland. They are now classified as one of several Murri language groups in Queensland.
Ethnonym
The Gubbi Gubbi's ethnonym is formed from the reduplication of kabi, their most common word for "no",[1] a generic denominator of several tribes speaking similar dialects to the Gubbi Gubbi.[2]
Language
Gubbi Gubbi refers to a number of dialects and is classified as one of the Waka–Kabic languages. One variety of the language was first described by the Reverend William Ridley on the basis of notes taken from an interview with James Davis in 1855. Davis lived among the Ginginbara clan and called it Dippil,[3]
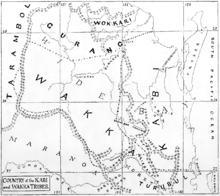
Country
Norman Tindale situated the Gubbi Gubbi as an inland tribe of the Wide Bay–Burnett area, whose lands extended over 3,700 square miles (9,600 km2) and lay west of Maryborough. The northern borders ran as far as Childers and Hervey Bay. On the south, they approached the headwaters of the Mary River and Cooroy. Westwards, they reached as far as the Coast Ranges and Kilkivan.[4] Gubbi Gubbi country is currently located between Pumicestone Road, near Caboolture in the south, through to Childers in the north. Their habitat was originally rain forest, with cleared areas created by regular firing of the scrub.[4]
John Mathew's description of the Kabi group he knew describes their land as embracing,
the Manumbar Run in the south-west corner of the Burnett District, the country watered by the Amamoor and Koondangoor creeks, tributaries of the Mary River, and the Imbil Station.[1]
Social organization
The Gubbi Gubbi were divided into several clans or bora:
| Clan name | Meaning | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Dauwa-bora | Noise of hacking people | North of Mount Bopple |
| Gunda-bora | Cabbage Palm people | Mount Bopple |
| Gigar-bora | Sweet people | Widgee |
| Kaiya-bora | Bite people | near Widgee |
| Kunyam-bora | Pine tree people | South of Mount Bopple |
| Kuli-bora | Native bee people | South Burnett |
| Baiyam-bora | Pipe people | Yabba Creek[5] |
History of contact
Some Gubbi Gubbi died in the mass poisoning of upwards of 60 Aborigines on the Kilcoy run in 1842.[6] A further 50-60 are said to have been killed by food laced with arsenic at Whiteside Station in April 1847.[7] As colonial entrepreneurs pushed into their territory to establish pastoral stations, they together with the Butchulla set up a fierce resistance: from 1847 to 1853, 28 squatters and their shepherds were killed.[8] In June 1849 two youths, the Pegg brothers, were speared on the property while herding sheep. Gregory Blaxland, the 7th son of the eponymous explorer Gregory Blaxland took vengeance, heading a vigilante posse of some 50 squatters and station hands and, at Bingera, ambushed a group of 100 sleeping myalls of the "Gin gin tribe" who are usually identified now as the Gubbi Gubbi.[9] They had feasted on stolen sheep. Marksmen picked off many, even those fleeing by diving into the Burnett River. The slaughter was extensive, and the bones of many of the dead were uncovered on the site many decades later.[10][11][12] Blaxland was in turn killed in a payback action sometime in July–August 1850. His death was revenged in a further large-scaled massacre of tribes in the area.[lower-alpha 1]
The escaped convict James Davis, in addition to dwelling with several other tribes, is said to have lived for a time with the Gubbi Gubbi.[14] John Mathew, a clergyman turned anthropologist, also spent 5 years with them at Manumbar and mastered their language. He described their society in a 1910 monograph, Two Representative Tribes of Queensland.[15][16] The Kabi he grew up with numbered no more than a score by the early 1880s.[17]
Culture and people

The Gubbigubbi were one of the two host tribes for the great bunya nut festivals every three years, which attracted many people from distant areas to the area of the Blackall Range.[18]
The Queensland lungfish was native to Gubbi Gubbi waters and the species fell under a taboo among them, forbidding its consumption. It was known in their language as "dala".[19]
Notable Gubbi Gubbi people
- Arthur Beetson, Queensland Rugby League legend and former Australian captain
- Bianca Beetson, a contemporary artist
- Naomi Wenitong, a Hip hop performer formerly from the duo Shakaya and currently associated with The Last Kinection
Native title
The descendants of the Gubbi Gubbi made a application for native title on 31 May 2013.[20]
Alternative names
- Kabi
- Cabbee
- Karbi
- Karabi
- Carbycarbery
- Kabbi, Kahby, Carby
- Gabigabi
- Dippil (generic descriptor also for adjacent several tribes speaking similar languages)
- Dipple
- Maiba (river chestnut people)
- Dundu:ra
- Doondoora, Dundubara, Doondooburra. (Hervey Bay people)
- Dowarburra. (horde north of Kilkivan).[4]
Some words
Notes
- ↑ A force was organized among all these settlers and their employees, and they set out on their mission of revenge guided by the friendly gin already referred to. The fugitive blacks were tracked down the Burnett River, where they had foregathered at a place now called Paddy's Island, not far from the mouth of the river. It was estimated by the white party that there were about a thousand blacks congregated here when the attack was made, and the result was the blacks suffered severely. The avenging whites were determined to end the antagonistic blacks' attitude towards their settlements. It is not known how many blacks were killed in this fight, but they must have numbered hundreds; but it is also known that a large number escaped into the Wongarra scrub on the south side of the river. This attack really broke the power of the blacks in this region. They continued to be hostile often in individual cases, but were never afterwards a serious menace.[13]
Citations
- 1 2 Mathew 1887, p. 152.
- ↑ Tindale 1974.
- ↑ Steele 1984, p. 160.
- 1 2 3 Tindale 1974, p. 172.
- ↑ Tindale 1974, p. 21.
- ↑ Greer 2014, p. 134.
- ↑ Bottoms 2013, p. 21.
- ↑ Bottoms 2013, p. 25.
- ↑ Maynard & Haskins 2016, p. 99.
- ↑ Reid 2006, p. 16.
- ↑ Bottoms 2013, pp. 25–26.
- ↑ Laurie 1952, pp. 709–717.
- ↑ Laurie 1952, p. 713.
- ↑ Osbaldiston 2017, p. 109.
- ↑ Mathews 2007, p. 10.
- ↑ Prentis 1998, pp. 62–63.
- ↑ Mathew 1887, p. 153.
- ↑ Tindale 1974, p. 124.
- ↑ Kind 2016, p. 85.
- ↑ NNTT 2013.
- ↑ Mathew 1887, p. 196.
- ↑ Mathew 1887, p. 156.
Sources
- Bottoms, Timothy (2013). Conspiracy of Silence: Queensland's Frontier Killing Times. Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-743-31382-4.
- Deming, Willoughby (2015). Understanding the Religions of the World: An Introduction. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-77055-9.
- Greer, Germaine (2014). White Beech: The Rainforest Years. A&C Black. ISBN 978-1-408-84671-1.
- Kind, Peter K. (2016). "The Natural History of the Australian Lungfish Neoceratodus forsteri (Krefft, 1870)". In Jorgensen, Jorden Morup; Joss, Jean. The Biology of Lungfishes. CRC Press. pp. 61–96. ISBN 978-1-439-84861-6.
- Laurie, Arthur (27 November 1952). "Early Gin Gin and the Blaxland Tragedy" (PDF). Historical Society of Queensland: 709–717.
- Mathew, John (1887). "Mary River and Bunya Bunya Country" (PDF). In Curr, Edward Micklethwaite. The Australian race: its origin, languages, customs, place of landing in Australia and the routes by which it spread itself over the continent. Volume 3. Melbourne: J. Ferres. pp. 152–209.
- Mathew, John (1910). Two Representative Tribes of Queensland (PDF). T. Fisher Unwin.
- Mathews, Robert Hamilton (2007). Thomas, Martin Edward, ed. Culture in Translation: The Anthropological Legacy of R. H. Mathews. Australian National University Press. ISBN 978-1-921-31324-0.
- Maynard, John; Haskins, Victoria Katharine (2016). Living with the Locals: Early Europeans' Experience of Indigenous Life. National Library of Australia. ISBN 978-0-642-27895-1.
- Osbaldiston, Nick (2017). Towards a Sociology of the Coast: Our Past, Present and Future Relationship to the Shore. Springer. ISBN 978-1-137-48680-6.
- Prentis, Malcolm D. (1998). "Research and friendship: John Mathew and his Aboriginal informants". Aboriginal History. Australian National University. 22: 62–93. JSTOR 24046160.
- "QC2013/003 - Kabi Kabi First Nation". National Native Title Tribunal. 31 May 2013.
- Reid, Gordon (2006). "That Unhappy Race": Queensland and the Aboriginal Problem, 1838-1901. australian scholarly publishing. ISBN 978-1-740-97104-1.
- Steele, John Gladstone (1984). Aboriginal Pathways: in Southeast Queensland and the Richmond River. University of Queensland Press. ISBN 978-0-702-25742-1.
- Tindale, Norman (1974). Aboriginal Tribes of Australia, Kabikabi (QLD). Australian National University Press.
External links
- http://www.gubbigubbi.com
- https://web.archive.org/web/20140517232411/http://www.triballink.com.au/index.php/gubbigubbi
- http://library.sunshinecoast.qld.gov.au/sitePage.cfm?code=maroochy-region
- Bibliography of Gubbi Gubbi people and language resources, at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies