Ghalib
| Mirza Ghalib Damir-ul-Mulk | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Native name |
مِرزا اسَدُاللہ بیگ خان Mirza Asadullah Baig Khan |
| Born |
27 December 1797 Darya ganj, Akbarabad Agra, Mughal Empire |
| Died |
15 February 1869 (aged 71) Gali Qasim Jaan, Ballimaran, Chandni Chowk, (now Ghalib ki Haveli, Delhi, India) |
| Pen name | Ghalib |
| Occupation | Poet |
| Nationality | Indian |
| Period | Mughal era, British Raj |
| Genre | Ghazal, Qasida, Rubai, Qat'aa |
| Subject | |
| Parents |
|
Ghalib (Urdu: غاؔلِب, Hindi: ग़ालिब), born Mirza Asadullah Baig Khan (Urdu: مِرزااسَدُاللہ بیگ خان, Hindi: मिर्ज़ा असदुल्लाह् बेग ख़ान), 27 December 1797 – 15 February 1869),[1] was a prominent[2] Urdu and Persian-language poet during the last years of the Mughal Empire. He used his pen-names of Ghalib (Urdu: غالِب, ġhālib means "dominant") and Asad (Urdu: اسَد, Asad means "lion"). His honorific was Dabir-ul-Mulk, Najm-ud-Daula. During his lifetime the Mughals were eclipsed and displaced by the British and finally deposed following the defeat of the Indian rebellion of 1857, events that he described.[3] Most notably, he wrote several ghazals during his life, which have since been interpreted and sung in many different ways by different people. Ghalib, the last great poet of the Mughal Era, is considered to be one of the most famous and influential poets of the Urdu language. Today Ghalib remains popular not only in India and Pakistan but also among the Hindustani diaspora around the world.[4]
Personal life
Background

Mirza Ghalib was born in Kala Mahal, Agra[5] into a family descended from Aibak Turks who moved to Samarkand(in modern-day Uzbekistan) after the downfall of the Seljuk kings. His paternal grandfather, Mirza Qoqan Baig, was a Saljuq Turk who had immigrated to India from Samarkand during the reign of Ahmad Shah (1748–54). He worked at Lahore, Delhi and Jaipur, was awarded the subdistrict of Pahasu (Bulandshahr, UP) and finally settled in Agra, UP, India. He had four sons and three daughters. Mirza Abdullah Baig and Mirza Nasrullah Baig were two of his sons.
Mirza Abdullah Baig (Ghalib's father) married Izzat-ut-Nisa Begum, an ethnic Kashmiri,[6] and then lived at the house of his father-in-law. He was employed first by the Nawab of Lucknow and then the Nizam of Hyderabad, Deccan. He died in a battle in 1803 in Alwar and was buried at Rajgarh (Alwar, Rajasthan).[7] Then Ghalib was a little over 5 years of age. He was raised first by his Uncle Mirza Nasrullah Baig Khan.
At the age of thirteen, Ghalib married Umrao Begum, daughter of Nawab Ilahi Bakhsh (brother of the Nawab of Ferozepur Jhirka). He soon moved to Delhi, along with his younger brother, Mirza Yousuf , who had developed schizophrenia at a young age and later died in Delhi during the chaos of 1857.[7]
In accordance with upper class Muslim tradition, he had an arranged marriage at the age of 13, but none of his seven children survived beyond infancy. After his marriage he settled in Delhi. In one of his letters he describes his marriage as the second imprisonment after the initial confinement that was life itself. The idea that life is one continuous painful struggle which can end only when life itself ends, is a recurring theme in his poetry. One of his couplets puts it in a nutshell:[8]
- قید حیات و بند غم ، اصل میں دونوں ایک ہیں
- موت سے پہلے آدمی غم سے نجات پائے کیوں؟
Transliteration in Hindi
- क़ैद-ए-हयात-ओ-बंद-ए-ग़म, अस्ल में दोनों एक हैं
- मौत से पहले आदमी ग़म से निजात पाए क्यूँ?
Translation in English
- The prison of life and the bondage of grief are one and the same
- Before the onset of death, why should man expect to be free of grief?
Mirza Ghalib's view of world as he sees world is like a playground where everyone is busy in some mundane activity and merrymaking rather than something of greater value as he wrote:
- بازیچہ اطفال ہے دنیا میرے آگے
- ہوتا ہے شب و روز تماشا میرے آگے
Transliteration in Hindi
- बाज़ीचा-ए-अत्फ़ाल है दुनिया मेरे आगे
- होता है शबो-रोज़ तमाशा मेरे आगे।
Translation in English
- Just like a child's play this world appears to me
- Every single night and day, this spectacle I see
At the age of thirty he had seven children, none of whom survived (this pain has found its echo in some of Ghalib's ghazals). There are conflicting reports regarding his relationship with his wife. She was considered to be pious, conservative and God-fearing.[9]
Ghalib was proud of his reputation as a rake. He was once imprisoned for gambling and subsequently relished the affair with pride. In the Mughal court circles, he even acquired a reputation as a "ladies' man".[10]:41 Once, when someone praised the poetry of the pious Sheikh Sahbai in his presence, Ghalib immediately retorted:
How can Sahbai be a poet? He has never tasted wine, nor has he ever gambled; he has not been beaten with slippers by lovers, nor has he ever seen the inside of a jail.[10]:41
| ؎ | اگ رہا ہے در و دیوار سے سبزہ غاؔلب |
| ہم بیاباں میں ہیں اور گھر میں بہار آئی ہے |
He died in Delhi on 15 February 1869. The house where he lived in Gali Qasim Jaan, Ballimaran, Chandni Chowk, in Old Delhi known as the Ghalib ki Haveli has now been turned into 'Ghalib Memorial' and houses a permanent Ghalib exhibition.
Mughal Titles
In 1850, Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar II bestowed upon Mirza Ghalib the title of "Dabir-ul-Mulk". The Emperor also added to it the additional title of "Najm-ud-daula".[1] The conferment of these titles was symbolic of Mirza Ghalib's incorporation into the nobility of Delhi. He also received the title of 'Mirza Nosha' from the Emperor, thus adding Mirza as his first name. He was also an important courtier of the royal court of the Emperor. As the Emperor was himself a poet, Mirza Ghalib was appointed as his poet tutor in 1854. He was also appointed as tutor of Prince Fakhr-ud Din Mirza, eldest son of Bahadur Shah II,(d. 10 July 1856). He was also appointed by the Emperor as the royal historian of Mughal Court.[1]
Being a member of declining Mughal nobility and old landed aristocracy, he never worked for a livelihood, lived on either royal patronage of Mughal Emperors, credit or the generosity of his friends. His fame came to him posthumously. He had himself remarked during his lifetime that he would be recognized by later generations. After the decline of the Mughal Empire and the rise of the British Raj, despite his many attempts, Ghalib could never get the full pension restored.[1]
Literary career
Ghalib started composing poetry at the age of 11. His first language was Urdu, but Persian and Turkish were also spoken at home. He received an education in Persian and Arabic at a young age. When Ghalib was in his early teens, a newly converted Muslim tourist from Iran (Abdus Samad, originally named Hormuzd, a Zoroastrian) came to Agra. He stayed at Ghalib's home for two years and taught him Persian, Arabic, philosophy, and logic.[11]

Although Ghalib himself was far prouder of his poetic achievements in Persian,[12] he is today more famous for his Urdu ghazals. Numerous elucidations of Ghalib's ghazal compilations have been written by Urdu scholars. The first such elucidation or Sharh was written by Ali Haider Nazm Tabatabai of Hyderabad during the rule of the last Nizam of Hyderabad. Before Ghalib, the ghazal was primarily an expression of anguished love; but Ghalib expressed philosophy, the travails and mysteries of life and wrote ghazals on many other subjects, vastly expanding the scope of the ghazal.
In keeping with the conventions of the classical ghazal, in most of Ghalib's verses, the identity and the gender of the beloved is indeterminate. The critic/poet/writer Shamsur Rahman Faruqui explains[13] that the convention of having the "idea" of a lover or beloved instead of an actual lover/beloved freed the poet-protagonist-lover from the demands of realism. Love poetry in Urdu from the last quarter of the seventeenth century onwards consists mostly of "poems about love" and not "love poems" in the Western sense of the term.
The first complete English translation of Ghalib's ghazals was Love Sonnets of Ghalib, written by Sarfaraz K. Niazi[14] and published by Rupa & Co in India and Ferozsons in Pakistan. It contains complete Roman transliteration, explication and an extensive lexicon.[15]
Letters

Mirza Ghalib was a gifted letter writer.[16] Not only Urdu poetry but prose is indebted to Mirza Ghalib. His letters gave foundation to easy and popular Urdu. Before Ghalib, letter writing in Urdu was highly ornamental. He made his letters "talk" by using words and sentences as if he were conversing with the reader. According to him Sau kos se ba-zaban-e-qalam baatein kiya karo aur hijr mein visaal ke maze liya karo (from a hundred of miles talk with the tongue of the pen and enjoy the joy of meeting even when you are separated). His letters were very informal; sometimes he would just write the name of the person and start the letter. He was very humorous and wrote very interesting letters. In one letter he wrote, "Main koshish karta hoon ke koi aisi baat likhoon jo padhe khush ho jaaye'" (I want to write lines such that whoever reads them would enjoy them). Some scholars say that Ghalib would have the same place in Urdu literature on the basis of his letters only. They have been translated into English by Ralph Russell in The Oxford Ghalib.
Ghalib was a chronicler of a turbulent period. One by one, Ghalib saw the bazaars – Khas Bazaar, Urdu Bazaar, Kharam-ka Bazaar, disappear, and whole mohallas (localities) and katras (lanes) vanish. The havelis (mansions) of his friends were razed to the ground. Ghalib wrote that Delhi had become a desert. Water was scarce. Delhi was "a military camp". It was the end of the feudal elite to which Ghalib had belonged. He wrote:
"An ocean of blood churns around me
Alas! Were this all!
The future will show
What more remains for me to see."[17]
Pen name
His original Takhallus (pen-name) was Asad, drawn from his given name, Asadullah Khan. At some point early in his poetic career he also decided to adopt the pen-name of Ghalib (meaning all conquering, superior, most excellent). At some places in his poetry Ghalib also used the pen name of Asad Ullah Khan.
Mirza Ghalib and Sir Syed Ahmed Khan
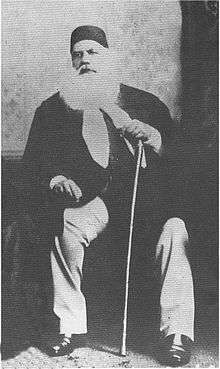
1855, Sir Syed Ahmed Khan finished his scholarly, well researched and illustrated edition of Abul Fazl's Ai’n-e Akbari. Having finished the work to his satisfaction, and believing that Mirza Asadullah Khan Ghalib was a person who would appreciate his labours, Syed Ahmad approached the great Ghalib to write a taqriz (in the convention of the times, a laudatory foreword) for it. Ghalib obliged, but what he produced was a short Persian poem castigating the Ai’n-e Akbari and, by implication, the imperial, sumptuous, literate and learned Mughal culture of which it was a product.[18] The least that could be said against it was that the book had little value even as an antique document. Ghalib practically reprimanded Syed Ahmad Khan for wasting his talents and time on dead things.[19] Worse, he highly praised the "sahibs of England" who at that time held all the keys to all the a’ins in this world.[20]
This poem is often referred to but had never been translated into English. Shamsur Rahman Faruqi wrote an English translation.[18] The translation is accurate if lacking the felicity of the original:
| “ | Good news my friends, this ancient book's door
Is now open, because of the Syed's grace and fortune, 1 The eye began to see, the arm found strength That which was wrapped in ancient clothes, now put on a new dress. 2 And this idea of his, to establish its text and edit the A’in Puts to shame his exalted capability and potential, 3 He put his heart to a task and pleased himself And made himself an auspicious, free servant. 4 One who isn’t capable of admiring his quality Would no doubt praise him for this task, 5 For such a task, of which this book is the basis Only an hypocrite can offer praise. 6 I, who am the enemy of pretence And have a sense of my own truthfulness, 7 If I don’t give him praise for this task It's proper that I find occasion to praise. 8 I have nothing to say to the perverse None know what I know of arts and letters, 9 In the whole world, this merchandise has no buyer. What profit could my Master hope from it? 10 It should be said, it's an excellent inventory So what's there to see that's worth seeing? 11 And if you talk with me of Laws and Rules Open your eyes, and in this ancient halting-place 12 Look at the Sahibs of England. Look at the style and practice of these, 13 See what Laws and Rules they have made for all to see What none ever saw, they have produced. 14 |
” |
| “ | Science and skills grew at the hands of these skilled ones
Their efforts overtook the efforts of the forebears. 15 This is the people that owns the right to Laws and Rules None knows to rule a land better than they, 16 Justice and Wisdom they’ve made as one They have given hundreds of laws to India. 17 The fire that one brought out of stone How well these skilled ones bring out from straw! 18 What spell have they struck on water That a vapour drives the boat in water! 19 Sometimes the vapour takes the boat down the sea Sometimes the vapour brings down the sky to the plains. 20 Vapour makes the sky-wheel go round and round Vapour is now like bullocks, or horses. 21 Vapour makes the ship speed Making wind and wave redundant. 22 Their instruments make music without the bow They make words fly high like birds: 23 Oh don’t you see that these wise people Get news from thousands of miles in a couple of breaths? 24 They inject fire into air And the air glows like embers, 25 Go to London, for in that shining garden The city is bright in the night, without candles. 26 Look at the businesses of the knowledgeable ones: In every discipline, a hundred innovators! 27 Before the Laws and Rules that the times now have All others have become things of yesteryears, 28 Wise and sensitive and prudent one, does your book Have such good and elegant Laws? 29 When one sees such a treasure house of gems Why should one glean corn from that other harvest? 30 Well, if you speak of its style, it's good No, it's much better than all else that you seek 31 But every good always has a better too If there's a head, there's also a crown for it. 32 Don’t regard that Generous Source as niggardly It's a Date-Palm which drops sweet light, like dates. 33 Worshipping the Dead is not an auspicious thing And wouldn’t you too think that it's no more than just words? 34 The Rule of silence pleases my heart, Ghalib You spoke well doubtless, not speaking is well too. 35 Here in this world your creed is to worship all the Prophet's children, Go past praising, your Law asks you to pray: 36 For Syed Ahmad Khan-e Arif Jang Who is made up entirely of wisdom and splendour 37 Let there be from God all that he might wish for Let an auspicious star lead all his affairs. 38 |
” |
The poem was unexpected, but it came at a time when Syed Ahmad Khan's thought and feelings were already inclining toward change. Ghalib seemed to be acutely aware of a European[English]-sponsored change in world polity, especially Indian polity. Syed Ahmad might well have been piqued at Ghalib's admonitions, but he would also have realized that Ghalib's reading of the situation, though not nuanced enough, was basically accurate. Syed Ahmad Khan may also have felt that he, being better informed about the English and the outside world, should have himself seen the change that now seemed to be just around the corner.[18] Sir Syed Ahmad Khan never again wrote a word in praise of the Ai’n-e Akbari and in fact gave up[21] taking active interest in history and archaeology, and became a social reformer.

Religious views
Ghalib placed a greater emphasis on seeking of God rather than ritualistic religious practices. Ghalib states:
| “ | The object of my worship lies beyond perception's reach; For men who see, the Ka'aba is a compass, nothing more."[10]:79 |
” |
Like many other Urdu poets, Ghalib was capable of writing profoundly religious poetry, yet was skeptical about some interpretations of the Islamic scriptures done by certain religious leaders.[10]:41 On the idea of paradise, he once wrote in a letter to a friend:
| “ | In paradise it is true that I shall drink at dawn the pure wine mentioned in the Qur'an, but where in paradise are the long walks with intoxicated friends in the night, or the drunken crowds shouting merrily? Where shall I find there the intoxication of Monsoon clouds? Where there is no autumn, how can spring exist? If the beautiful houris are always there, where will be the sadness of separation and the joy of union? Where shall we find there a girl who flees away when we would kiss her?.[10]:41 | ” |
He staunchly disdained the practices of certain Ulema, who in his poems represent narrow-mindedness and hypocrisy:[10]:41
| “ | The Sheikh hovers by the tavern door, but believe me, Ghalib, |
” |
In another verse directed towards certain maulavis (clerics), he criticized them for their ignorance and arrogant certitude: "Look deeper, it is you alone who cannot hear the music of his secrets".[10]:41 In his letters, Ghalib frequently contrasted the narrow legalism of the Ulema with "its pre-occupation with teaching the baniyas and the brats, and wallowing in the problems of menstruation and menstrual bleeding" and real spirituality for which you had to "study the works of the mystics and take into one's heart the essential truth of God's reality and his expression in all things".[10]:80
During the anti-British Rebellion in Delhi on 5 October 1857, three weeks after the British troops had entered through Kashmiri Gate, some soldiers climbed into Ghalib's neighbourhood and hauled him off to Colonel Burn (Colonel Brown کمانڈنگ آفیسر کرنل براؤن [22] for questioning.[10]:41 He appeared in front of the colonel wearing a Central Asian Turkic style headdress. The colonel, bemused at his appearance, inquired in broken Urdu, "Well? You Muslim?", to which Ghalib replied, "Half?" The colonel asked, "What does that mean?" In response, Ghalib said, "I drink wine, but I don't eat pork."[10]:41
- Praise of Muhammad
A large part of Ghalib's poetry focuses on the praise and veneration of Muhammad, which shows that Ghalib was a devout Muslim.[23] Ghalib wrote his Abr-i gauharbar (The Jewel-carrying Cloud) in honor of Muhammad.[24] Ghalib also wrote a qasida of 101 verses in dedication to Muhammad.[23] Ghalib described himself as a sinner who should be silent before Muhammad as he was not worthy of addressing Muhammad, who, according to him, was praised by God.[23]
Views on Hindustan
In his poem "Chiragh-i-Dair" (The Lamp of Temple) which was composed during his trip to Benares during the spring of 1827, Ghalib mused about the land of Hindustan (the Indian subcontinent) and how Qiyamah (Doomsday) has failed to arrive, in spite of the numerous conflicts plaguing it.[25]
| “ | Said I one night to a pristine seer (Who knew the secrets of whirling Time) |
” |
Poetry in Persian

" [27] Kulliyat-e-Ghalib Farsi", an anthology of Persian poetry [28] of well-known Urdu poet Mirza Asadullal Khan Ghalib first released at Maulana Azad National Urdu University (MANUU) and later released at Tehran by Ambassadors of India and Pakistan jointly at a function sponsored by Iranian Ministry of Arts and Culture in Tehran on 20 September 2010.This rare collection contains 11,337 verses of Ghalib, was compiled by Dr. Syed Taqi Abedi. Speaking at the occasion, Dr. Abidi said that study of Ghalib would be incomplete without his Persian poetry. "Although Ghalib had earned his reputation in Urdu literature, the poet of Mughal era was more inclined towards Persian and produced high-order poetry in that language. At the literary "ru-ba-ru session" (Face to Face Sitting) organized by the Haryana Urdu Academy,[29] where Dr. Taqi offered analytical study of the works of legendary poet Mirza Ghalib, both in Persian as well as Urdu.He informs that Ghalib wrote 1,792 couplets in Urdu by the year 1865 as against the 11,340 in Persian. He also opined that Ghalib was a visionary, a poet of humanism whose works are popular even after three centuries.
Contemporaries and disciples
Ghalib's closest rival was poet Zauq, tutor of Bahadur Shah Zafar II, the then emperor of India with his seat in Delhi. There are some amusing anecdotes of the competition between Ghalib and Zauq and exchange of jibes between them. However, there was mutual respect for each other's talent. Both also admired and acknowledged the supremacy of Meer Taqi Meer, a towering figure of 18th century Urdu Poetry. Another poet Momin, whose ghazals had a distinctly lyrical flavour, was also a famous contemporary of Ghalib. One of the towering figures in Urdu literature Altaf Hussain Hali was a disciple of Ghalib. Hali has also written a biography of Ghalib titled Yaadgaar-e-Ghalib.
Ghalib was not only a poet, he was also a prolific prose writer. His letters are a reflection of the political and social climate of the time. They also refer to many contemporaries like Mir Mehdi Majrooh, who himself was a good poet and Ghalib's lifelong acquaintance. The Poems written by Ghalib were tough to understand. He sometimes made the sentence syntax so complex that people had hard time in understanding that. Once Hakeem Agha Jaan Aish,[30] a poet of Ghalib's era, read a couplet in Mushaira for Ghalib:[31]
- اگر اپنا کہا تم آپ ہی سمجھے تو کیا سمجھے
- مزا کہنے کا جب ہے اک کہے اور دوسرا سمجھے
(It is not praised if you are the only one to understand what you speak
interesting is the situation when you speak and the others understand):
Ghalib felt bad for this and wrote:[32]
- نہ ستائش کی تمنّا نہ صلے کی پروا
- گر نہیں ہیں مرے اشعار میں معنی نہ سہی
(I don't need appreciation neither do I need any return
let not be if there is no meaning in my couplets)
This style was the definition of his uniqueness
In prose Ghalib brought a revolution in Urdu literature by developing an easy, simple and beautiful way of writing. Before Ghalib Urdu was a complex language, Ghalib introduced a simple style of prose in Urdu which is like a conversation.[33]
Ghalib's grave
Ghalib was buried in Hazrat Nizamuddin near the tomb of Nizamuddin Auliya. The side view of Mazar-e-Ghalib is shown in the image.

"
maze jahaan ke apnee nazar meiN KHaak naheeN
siwaa-e-KHoon-e-jigar, so jigar meiN KHaak naheeN"
[34]
(The happiness of the world is nothing for me
for my heart is left with no feeling besides blood.)
Films and TV serial on Ghalib
Indian cinema has paid a tribute to the legendary poet through a film (in sepia/black and white) named Mirza Ghalib (1954) in which Bharat Bhushan plays Ghalib and Suraiya plays his courtesan lover, Chaudvin. The musical score of the film was composed by Ghulam Mohammed and his compositions of Ghalib's famous ghazals are likely to remain everlasting favorites.
Pakistani cinema also paid tribute to the legendary poet, through another film also named Mirza Ghalib (1961). The film was directed and produced by M.M. Billoo Mehra for S.K. Pictures. The music was composed by Tassaduq Hussain. The film starred Pakistani film superstar Sudhir playing Ghalib and Madam Noor Jehan playing his courtesan lover, Chaudvin. The film was released on 24 November 1961 and reached average status at the box-office, however, the music remains memorable in Pakistan to this day.
Gulzar produced a TV serial, Mirza Ghalib (1988), telecast on DD National that was immensely successful in India. Naseeruddin Shah played the role of Ghalib in the serial, and it featured ghazals sung and composed by Jagjit Singh and Chitra Singh.[35] The serial's music has since been recognised as Jagjit Singh and Chitra Singh's magnum opus, enjoying a cult following in the Indian subcontinent.
Stage plays on Ghalib
Ghalib's life is the subject of hundreds of plays regularly performed in Northern India and Pakistan. These plays are based on his life and his personal and professional relationships.
Starting from the Parsi Theatre and Hindustani Theatre days, the first phase of his stage portrayal culminated in Sheila Bhatia's production, written by Mehdi Saheb. Mohd Ayub performed this role so many times that many theatre-goers used to call him Ghalib. The Sheila Bhatia production celebrated his famous ghazals which used to be presented one after another. Ghalib's character lacked subtlety and he was shown philandering with the courtesan, Chaudvin, famously played by Punjabi singer Madan Bala Sandhu. Later Begum Abida Ahmed, wife of the late President Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed, supported many very costly productions. This was perhaps the golden period of plays celebrating Ghalib's life, including many other productions such as Surendra Verma's play which was performed by the National School of Drama. Qaid-e-Hayat (Imprisonment of Life, 1983), written by Surendra Verma, talks about the personal life of the poet Ghalib, including his financial hardships and his tragic love for Katiba, a woman calligraphist, who was working on his diwan. Over the years, it has been directed by numerous theatre directors, including Ram Gopal Bajaj in 1989, at the National School of Drama. This period also saw numerous college and university productions performed by students' groups. Writers whose scripts were popular during this period include Jameel Shaidai, Danish Iqbal and Devender Singh. Ghalib also inspired a chain of comedies. One such classic comedy is Ghalib in New Delhi which has been staged more than three hundred times by Dr Sayeed Alam. Danish Iqbal's play Main Gaya Waqt Nahin Hoon and Sayeed's play Ghalib Ke Khutoot are still being performed at various Indian cities.
The late Sheila Bhatia began this trend on productions about Ghalib, in Delhi.[36]
Ghalib in today's culture
Ghazal maestros like Jagjit Singh, Mehdi Hassan, Abida Parveen, Farida Khanum, Tina Sani, Mohammed Rafi, Asha Bhosle, Begum Akhtar, Ghulam Ali, Lata Mangeshkar, Rahat Fateh Ali Khan have sung his ghazals.[37] Many singers from all over South Asia have sung many of his ghazals.
Google Doodle
Ghalib was commemorated on his 220th birth anniversary by Search Engine Google which showed a special doodle on its Indian home page for him on 27 December 2017.[38]
See also
References
- Mirza Ghalib Poetry in Urdu, November 16, 2016. [39]
- Specific
- 1 2 3 4 Varma, Pavan K. (1989). Ghalib, The Man, The Times. New Delhi: Penguin Books. p. 86. ISBN 0-14-011664-8.
- ↑ "Mirza Asadullah Khan Ghalib". Brittanica. Retrieved 2014-07-12.
- ↑ "Remembering 1857 in 2007 - The Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ "Ghalib in California". Dawn. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ "No memorial for Ghalib at his birthplace, Agra". 27 December 2013.
- ↑ Mirza Asadullah Khan Ghalib, Persian poetry of Mirza Ghalib, Pen Productions (2000), p. 7
- 1 2 "Mirza Ghalib". Megajoin.com. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ Siddiqi, Byjameela. "Mirza Ghalib: The "Godless" Lover by Byjameela Siddiqi". Sufism.ru. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ Genealogy of the Nawabs of Loharu Queensland University
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 William Dalrymple (2009). The Last Mughal: The Fall of a Dynasty, Delhi, 1857. Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-4088-0092-8.
- ↑ "Mirza Ghalib". Megajoin.com. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ Thackston, Wheeler: "A Millennium of Classical Persian Poetry," Ibex Publishers Inc. 1994, p.98
- ↑ "Shamsur Rahman Faruqui explains" (PDF).
- ↑ "Dr. Sarfaraz K. Niazi".
- ↑ Roman transliterations with English translation of uncommon words
- ↑ "Page at". Hinduonnet.com. 2003-05-06. Retrieved 2013-05-20.
- ↑ Amur, G. S. (1992). Creations & Transcreations. Calcutta: Writers Workshop. pp. 83–84. ISBN 8171893910. Retrieved 18 September 2017.
- 1 2 3 [From Antiquary to Social Revolutionary: Syed Ahmad Khan and the Colonial Experience By http://www.columbia.edu/itc/mealac/pritchett/00fwp/srf/srf_sirsayyid.pdf Shamsur Rahman Faruqi.] Archived at
- ↑ Hayat-i-Javed (A Biography of Sir Sayyid) by Altaf Husain Hali (1901), translated by David J. Matthews (New Delhi: Rupa and Company, 1994),
- ↑ The word a’in can mean all or any of the following: character, convention, temperament, habit, rule, path, law (ecclesiastical or secular), creed, praxis, quality, intention, organization, management, system, decoration, beauty. (Lughat Nama-e Dehkhoda). There are about eighty meanings in all, which seem to have developed over the centuries. Most were available to Abul Fazl; all were available to Ghalib.
- ↑ He did edit another two historical texts over the next few years, but neither of them was anything like the Ai’n-e Akbari.
- ↑ Yaadgaar e Haali by Altaf Hussain Haali 1897 pg 39
- 1 2 3 Annemarie Schimmel (1985), And Muhammad is His Messenger - The Veneration of the Prophet in Islamic Piety, University of North Carolina Press, p. 115
- ↑ Schimmel(1985), p.81
- ↑ Ghalib, 1797-1869: Life and Letters, Mirza Asadullah Khan Ghalib, Oxford University Press, 1994, Chapter 7
- ↑ India after Gandhi, Ramachandran Guha, Picador, 2007, Prologue
- ↑ Ref: serial No. 84, Publications of Ghalib Institute, New Delhi. at: http://www.ghalibinstitute.org/p/publication.html Archived 9 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://www.hindu.com/2009/03/20/stories/2009032059020200.htm
- ↑ "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - The Tribune Lifestyle".
- ↑ http://igmlnet.uohyd.ernet.in:8000/cgi-bin/gw/chameleon?sessionid=2568098490&skin=hcu_2010&lng=en&inst=consortium&host=localhost%2b1111%2bDEFAULT&patronhost=localhost%201111%20DEFAULT&searchid=180&sourcescreen=INITREQ&pos=1&itempos=1&rootsearch=SCAN&function=INITREQ&search=AUTHID&authid=308340&authidu=4%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D
- ↑ Mutaala-e-Ghalib, 2nd edition, Danish Mahal Aminuddaula park publisher Lakhnow, 1987, p9
- ↑ "Divan-e Ghalib: Ghazal index".
- ↑ http://www.columbia.edu/itc/mealac/pritchett/00urduhindilinks/abdulqadir/02ghalibprose.pdf
- ↑ "Mirza Ghalib". smriti.com. Retrieved 12 Jun 2014.
- ↑ Mirza Ghalib (1988) (TV) on IMDb
- ↑ "Ghalib and his troubles". The Hindu. 11 January 2008.
- ↑ "Ghalib forgotten on his 214th birth anniversary amid political chaos", Zaib Azkaar Hussain, The International News, 18 December 2011.
- ↑ "Mirza Ghalib: Legendary poet of the Urdu language". aljazeera.com. 2017-12-27. Retrieved 2017-12-27.
- ↑ alifseye, Mirza Ghalib Poetry in Urdu, November 16, 2016
Further reading
- Urdu letters of Mirza Asaduʼllāh Khan Galib, tr. by Daud Rahbar. SUNY Press, 1987. ISBN 0-88706-412-4.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Ghalib |
- Works by or about Ghalib at Internet Archive
- Works by Ghalib at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)





