Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the core SMN complex, which is required for pre-mRNA splicing in the nucleus. The encoded protein is found in the nucleoplasm, in nuclear "gems" (Gemini of Cajal bodies), and in the cytoplasm. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000142252 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000044709 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 3 Baccon J, Pellizzoni L, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (Aug 2002). "Identification and characterization of Gemin7, a novel component of the survival of motor neuron complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (35): 31957–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203478200. PMID 12065586.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: GEMIN7 gem (nuclear organelle) associated protein 7".
- ↑ Pellizzoni L, Baccon J, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (Mar 2002). "Purification of native survival of motor neurons complexes and identification of Gemin6 as a novel component". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (9): 7540–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110141200. PMID 11748230.
- ↑ Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, et al. (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
Further reading
- Carissimi C, Saieva L, Gabanella F, Pellizzoni L (Dec 2006). "Gemin8 is required for the architecture and function of the survival motor neuron complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (48): 37009–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607505200. PMID 17023415.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C, Brembeck FH, Goehler H, Stroedicke M, Zenkner M, Schoenherr A, Koeppen S, Timm J, Mintzlaff S, Abraham C, Bock N, Kietzmann S, Goedde A, Toksöz E, Droege A, Krobitsch S, Korn B, Birchmeier W, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (Sep 2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
- Grimmler M, Otter S, Peter C, Müller F, Chari A, Fischer U (Oct 2005). "Unrip, a factor implicated in cap-independent translation, associates with the cytosolic SMN complex and influences its intracellular localization". Human Molecular Genetics. 14 (20): 3099–111. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi343. PMID 16159890.
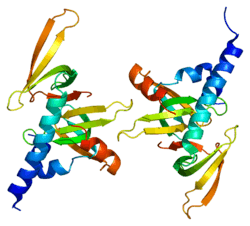
PDB gallery |
|---|
1y96: crystal structure of the Gemin6/Gemin7 heterodimer from the human SMN complex |