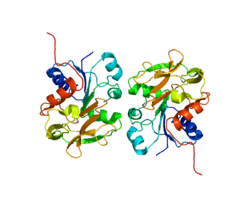GMP synthase (glutamine—hydrolysing)
| GMP synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 GMP synthetase, human | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 6.3.5.2 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37318-71-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| GMP synthetase C terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 escherichia coli gmp synthetase complexed with amp and pyrophosphate.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | GMP_synt_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00958 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001674 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00405 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1gpm | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1gpm | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, (EC 6.3.5.2) also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.[6]
In the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides, IMP is the branch point metabolite at which point the pathway diverges to the synthesis of either guanine or adenine nucleotides. In the guanine nucleotide pathway, there are 2 enzymes involved in converting IMP to GMP, namely IMP dehydrogenase (IMPD1), which catalyzes the oxidation of IMP to XMP, and GMP synthetase, which catalyzes the amination of XMP to GMP.[6]
Enzymology
In enzymology, a GMP synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- ATP + xanthosine 5'-phosphate + L-glutamine + H2O AMP + diphosphate + GMP + L-glutamate
The 4 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, xanthosine 5'-phosphate, L-glutamine, and H2O, whereas its 4 products are AMP, diphosphate, GMP, and L-glutamate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, specifically those forming carbon-nitrogen bonds carbon-nitrogen ligases with glutamine as amido-N-donor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is xanthosine-5'-phosphate:L-glutamine amido-ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include GMP synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing), guanylate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing), guanosine monophosphate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing), xanthosine 5'-phosphate amidotransferase, and guanosine 5'-monophosphate synthetase. This enzyme participates in purine metabolism and glutamate metabolism. At least one compound, Psicofuranin is known to inhibit this enzyme.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 5 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1GPM, 1WL8, 2A9V, 2D7J, and 2DPL.
References
- ↑ Tesmer JJ, Klem TJ, Deras ML, Davisson VJ, Smith JL (January 1996). "The crystal structure of GMP synthetase reveals a novel catalytic triad and is a structural paradigm for two enzyme families". Nat. Struct. Biol. 3 (1): 74–86. doi:10.1038/nsb0196-74. PMID 8548458.
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000163655 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027823 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: GMPS guanine monphosphate synthetase".
Further reading
- Page T, Bakay B, Nyhan WL (1984). "Human GMP synthetase". Int. J. Biochem. 16 (1): 117–20. doi:10.1016/0020-711X(84)90061-2. PMID 6698284.
- Nakamura J, Straub K, Wu J, Lou L (1995). "The glutamine hydrolysis function of human GMP synthetase. Identification of an essential active site cysteine". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (40): 23450–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.40.23450. PMID 7559506.
- Nakamura J, Lou L (1995). "Biochemical characterization of human GMP synthetase". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (13): 7347–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.13.7347. PMID 7706277.
- Hirst M, Haliday E, Nakamura J, Lou L (1994). "Human GMP synthetase. Protein purification, cloning, and functional expression of cDNA". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (38): 23830–7. PMID 8089153.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Fedorova L, Kost-Alimova M, Gizatullin RZ, et al. (1997). "Assignment and ordering of twenty-three unique NotI-linking clones containing expressed genes including the guanosine 5'-monophosphate synthetase gene to human chromosome 3". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 5 (2): 110–6. PMID 9195163.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Pegram LD, Megonigal MD, Lange BJ, et al. (2001). "t(3;11) translocation in treatment-related acute myeloid leukemia fuses MLL with the GMPS (GUANOSINE 5' MONOPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE) gene". Blood. 96 (13): 4360–2. PMID 11110714.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Guo D, Han J, Adam BL, et al. (2005). "Proteomic analysis of SUMO4 substrates in HEK293 cells under serum starvation-induced stress". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 337 (4): 1308–18. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.09.191. PMID 16236267.
- Abrams R & Bentley M (1959). "Biosynthesis of nucleic acid purines. III. Guanosine 5'-phosphate formation from xanthosine 5'-phosphate and L-glutamine". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 79: 91&ndash, 110. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(59)90383-2.
- LAGERKVIST U (1958). "Biosynthesis of guanosine 5'-phosphate. II. Amination of xanthosine 5'-phosphate by purified enzyme from pigeon liver". J. Biol. Chem. 233 (1): 143&ndash, 9. PMID 13563458.
External links
- GMP+synthetase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)