Fujiyoshida, Yamanashi
| Fujiyoshida 富士吉田市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
 Fujiyoshida city looking south | |||
| |||
 Location of Fujiyoshida in Yamanashi Prefecture | |||
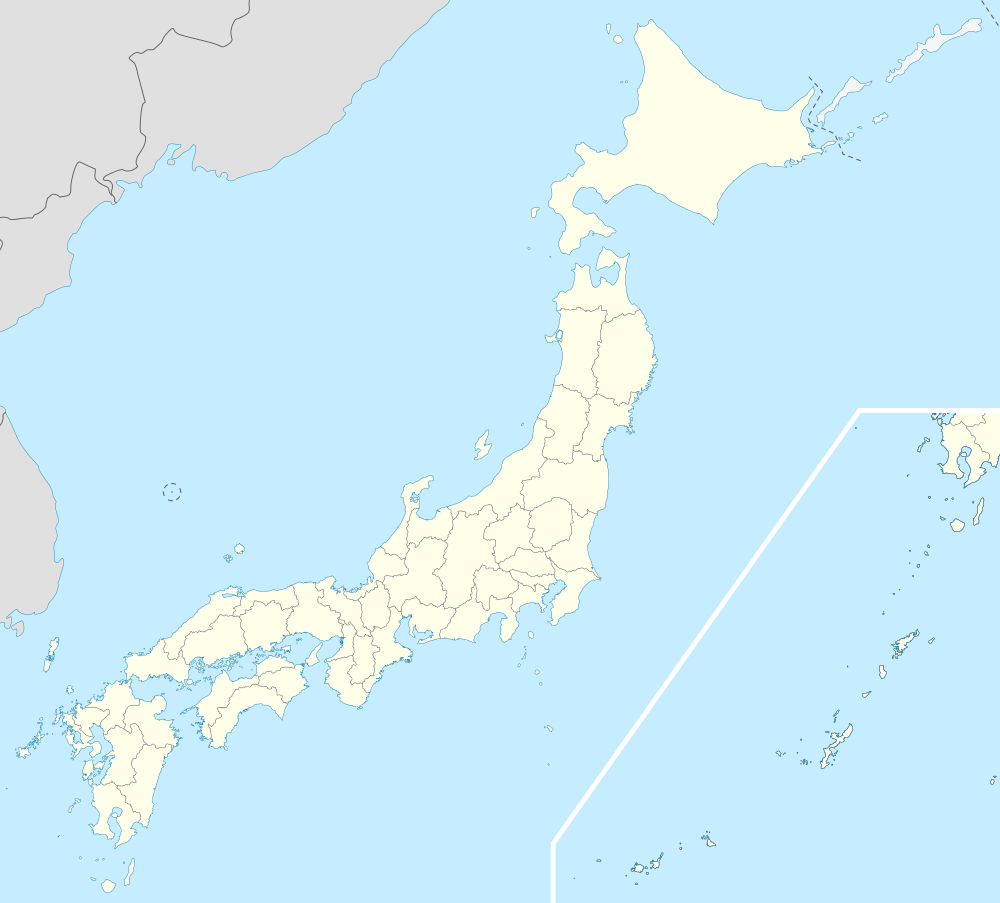 Fujiyoshida | |||
| Coordinates: 35°29′15.1″N 138°48′27.9″E / 35.487528°N 138.807750°ECoordinates: 35°29′15.1″N 138°48′27.9″E / 35.487528°N 138.807750°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Chūbu (Tōkai) | ||
| Prefecture | Yamanashi Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Shigeru Horiuchi | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 121.74 km2 (47.00 sq mi) | ||
| Population (February 1, 2016) | |||
| • Total | 50,426 | ||
| • Density | 414/km2 (1,070/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) | ||
| City symbols | |||
| • Tree | White birch | ||
| • Flower | Fujizakura | ||
| • Bird | Great spotted woodpecker | ||
| Phone number | 0555-22-1111 | ||
| Address | 6-1-1 Shimoyoshida, Fujiyoshida-shi, Yamanashi-ken 403-8601 | ||
| Website | http://www.city.fujiyoshida.yamanashi.jp/ | ||

Fujiyoshida (富士吉田市 Fujiyoshida-shi) is a city located in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. The city was founded on March 20, 1951.
As of February 2016, the city had an estimated population of 50,426, and a population density of 414 persons per km2. The total area is 121.74 square kilometres (47.00 sq mi).
Geography
Fujiyoshida lies at the base of Mount Fuji, and is built upon old lava flows. It is considered a high-elevation city in Japan, at 2,140 to 2,800 feet above sea level. The city is also located between two of the Fuji Five Lakes.
Neighboring municipalities
- Yamanashi Prefecture
- Shizuoka Prefecture
Economy
For several centuries, artisans around the Fujiyoshida area have produced high quality textiles,[1] and now the city is the center of commerce and high technology in southern Yamanashi Prefecture.
Education
- Showa University
- Fujiyoshida has seven elementary schools, six public and one private middle school, and three public and one private high school.
Transportation
Rail
Highway
Local attractions

- Kitaguchi Hongū Fuji Sengen Jinja, a Shinto shrine dedicated to the kami of Mount Fuji, the Kitaguchi Hongū Fuji Sengen Jinja is the historical starting point for pilgrims climbing the mountain. The main structure was originally built in 788 and underwent reconstruction in the 17th century. Additional buildings include a shrine dedicated to Takeda Shingen (1521–1573), and a red torii which is taken down and rebuilt every "Fuji Year" (60 years). The shrine has a local history museum which displays items from Fujiyoshida's past including household items, farm implements, clothing and samples of the cities' famous textiles.
- Fuji-Q Highland an amusement park with a variety of attractions suitable for adults and children.
- Mt. Fuji Visitors Center. It is home to interactive displays, videos, books and guides about Mount Fuji.
- Mt. Fuji Radar Dome Museum. A tribute to the meteorologists who built a radar research facility at the summit of Mt. Fuji, which features a room which simulates the conditions at the summit of the mountain.

- Arakurayama Sengen Park and the Chūrei-tō pagoda, built on a hilltop facing Mt. Fuji.
Sister cities

Notable people from Fujiyoshida
- Keiji Mutoh, professional wrestler [4]
References
- ↑ "Fujiyoshida Welcomes You". Fujiyoshida City International Affairs Desk. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ↑ "US-Japan Sister Cities by State". Asia Matters for America. Honolulu, HI: East-West Center. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ↑ "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ↑ "Player - Keiji Muto". Wrestle-1 Official Web Site (in Japanese). 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
External links
![]()

- Official Website (in Japanese)

