Frankfurt (Oder)
| Frankfurt | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Frankfurt an der Oder in July 2011 | |||
| |||
 Frankfurt | |||
| Coordinates: 52°21′N 14°33′E / 52.350°N 14.550°ECoordinates: 52°21′N 14°33′E / 52.350°N 14.550°E | |||
| Country | Germany | ||
| State | Brandenburg | ||
| District | Urban district | ||
| Government | |||
| • Lord Mayor | René Wilke (Die Linke) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 147.61 km2 (56.99 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 19-135 m (−424 ft) | ||
| Population (2017-12-31)[1] | |||
| • Total | 58,237 | ||
| • Density | 390/km2 (1,000/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | ||
| Postal codes | 15201–15236 | ||
| Dialling codes | 0335 | ||
| Vehicle registration | FF | ||
| Website | www.frankfurt-oder.de | ||
Frankfurt (Oder) (also Frankfurt an der Oder, German: [ˈfʁaŋkfʊɐ̯t ʔan deːɐ̯ ˈʔoːdɐ]; abbreviated Frankfurt a. d. Oder, Frankfurt a. d. O., Frankf. a. d. O., lit. 'Frankfurt on the Oder') is a town in Brandenburg, Germany, located on the west side of the Oder River, on the Germany-Poland border, about 80 kilometres (50 mi) east of Berlin. Until the end of Second World War, the city of Słubice, Poland, was a neighbourhood of Frankfurt. Until 1990 Frankfurt an der Oder was part of East Germany.
At the end of the 1980s, it reached a population peak with more than 87,000 inhabitants. The number dropped below 70,000 in 2002 and was just above 60,000 in 2010.[2]
The city's recorded history began in the 13th century as merchant and trading place in the Holy Roman Empire.
The official name Frankfurt (Oder) and the older Frankfurt an der Oder are used to distinguish it from the larger city of Frankfurt am Main.
History

In 1249 the settlement became part of the Margraviate of Brandenburg. The town of Frankfurt received its charter in 1253 at the Brandendamm. The early settlers lived on the western banks of the Oder; later the town was extended to the eastern bank. In the late Middle Ages, the town dominated the river trade between Breslau and Stettin. In years 1373-1415 along with Brandenburg it was part of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown. In 1430, Frankfurt joined the Hanseatic League.

In April 1631, during the Thirty Years' War, Frankfurt was the site of the Battle of Frankfurt an der Oder between the Swedish Empire and the Holy Roman Empire.[3] After a two-day siege, Swedish forces, supported by Scottish auxiliaries,[4] stormed the town and detroyed lots of buildings, eg. the Georgen Hospital.[3] The result was a Swedish victory.[3][4]
The city was briefly occupied by the Russian Imperial Army during the Seven Years' War, in August 1759, in the prelude to the battle of Kunersdorf.[5]
With the dissolution of the Margraviate of Brandenburg during the Napoleonic Wars, Frankfurt became part of the Province of Brandenburg in 1815. In the 19th century, Frankfurt played an important role in trade. Centrally positioned in the Kingdom of Prussia between Berlin and Posen (Poznań), on the river Oder with its heavy traffic, the town housed the second-largest annual trade fair (Messe) of the German Reich, surpassed only by that in Leipzig.
There was no fighting for the town in 1945 during World War II even though the town was declared a fortress (Festung) in an attempt to block the Red Army's route to Berlin. The nearly empty town was burned down. The postwar German-Polish border ran along the Oder, separating the Dammvorstadt on the eastern bank - which became the Polish town of Słubice - from the rest of Frankfurt. While part of communist East Germany, Frankfurt was administered within Bezirk Frankfurt (Oder). It became part of the reconstituted state of Brandenburg with German reunification in 1990.
Today, Frankfurt and Słubice have friendly relations and run several common projects and facilities. Poland joined the European Union on 1 May 2004, and implemented the Schengen Agreement on 21 December 2007 leading to the removal of permanent border controls.
In the post-communist era, Frankfurt has suffered from high unemployment and low economic growth. Its population has fallen significantly from around 87,000 at the time of German reunification in 1990.
FC Viktoria Frankfurt is the town's local football team.
In March 2008, the Jewish community of Frankfurt celebrated its first Torah dedication since the Holocaust. The procession of the new Torah scroll began from the spot where the town's Frankfurter Synagogue stood prior to World War II, 500 meters from Germany's current border with Poland. Celebrants marched with the scroll into the town's Chabad-Lubavitch centre, where they danced with the Torah, which had been donated by members of the Chabad-Lubavitch community in Berlin.
Names
Demography

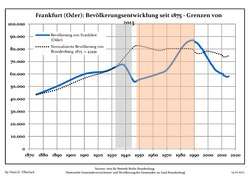 Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state)
Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state)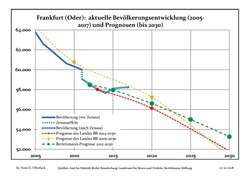 Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2005-2030 (yellow line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2014-2030 (red line); Projection by the Bertelsmann Foundation for 2012-2030 (green line)
Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2005-2030 (yellow line); Projection by the Brandenburg state for 2014-2030 (red line); Projection by the Bertelsmann Foundation for 2012-2030 (green line)
| Frankfurt (Oder): Population development within the current boundaries (2017)[8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
European university
The Margraviate of Brandenburg's first university was Frankfurt's Alma Mater Viadrina, founded in 1506 by Joachim I Nestor, Elector of Brandenburg. An early chancellor, Bishop Georg von Blumenthal (1490–1550), was a notable opponent of the Protestant Reformation, as he remained a Catholic. Frankfurt also trained the noted archbishop Albert of Brandenburg around 1510, who also became a vocal opponent of the Reformation. The university attracted many German and Polish students. It was closed in 1811, and its assets divided between two new universities founded under King Frederick William III: Frederick William University of Berlin, presently Humboldt University; and Silesian Frederick William University in Breslau, presently the University of Wrocław.
The university was refounded in 1991 with a European emphasis as the Viadrina European University, in close cooperation with the Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań; they jointly run the Collegium Polonicum in Słubice.
Transportation
The Frankfurt (Oder) Bahnhof is a station served by the Berlin-Warszawa Express and has regular regional connections to Magdeburg and Cottbus. Within the city, there is a network of five tram lines.
International relations
_panorama_01.jpg)
Frankfurt (Oder), being located on the border to Poland, plays a special role in connection with German–Polish relations and European integration. The European University Viadrina has one of its buildings in Poland, in the neighbouring town of Słubice. The university also has a number of projects and initiatives dedicated to bringing Poland and Germany together, and offers its students pro bono Polish courses. Another project that contributes to German–Polish integration in Frankfurt (Oder) is the Fforst House, a German-Polish student project, which has been granted support by the town's administration[9] and by the Viadrina,[10] having been described by the former president of the university, Gesine Schwan, as the place where "Europe begins".[11]
Twin towns and sister cities
Frankfurt (Oder) is twinned with:
|
Notable people
- Juste Chevillet (1729–1802) a French engraver, e.g. Histoire Naturelle of Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
- Wilhelm Christian Benecke von Gröditzberg (1779-1860) a German banker, merchant, estate owner and art collector
- Robert von Puttkamer (1828–1900) a Prussian statesman, he also introduced reforms in German orthography
- Victor von Podbielski (1844-1916) Polish origin, Prussian general, secretary of state, head of the Reichspostamt, Prussian Minister of Agriculture
- Hermann Wissmann (1853–1905) a German explorer and administrator in Africa
- Georg Michaelis (1857–1936) was Chancellor of Germany for a few months in 1917, grew up in Frankfurt (Oder)
- Lucie Hein (1910-1965) an East German politician (SED), she served as the senior mayor of Frankfurt 1960 to 1965
- Gerhard Neumann (1917–1997) a German-American aviation engineer and executive for GE Aviation
- Zvi Aharoni (1921–2012) an Israeli Mossad agent instrumental in the capture of Adolf Eichmann
- Dieter Sauberzweig (1925-2005) a prominent commentator on German cultural politics (Kulturpolitiker).
- Karl-Heinz Schröter (born 1954) a German politician (Social Democratic Party)
- Alexey Gordeyev (born 1955) a Russian politician, served as the Governor of Voronezh Oblast since 2009
- Manuela Schwesig (born 1974) a German politician (SPD), fifth Minister‐President of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Claudia Hiersche (born 1977) a German host and actress, known for her portrayal of a lesbian TV soap opera character
- Franziska Giffey (born 1978) a German politician, Federal Minister of Family Affairs, Senior Citizens, Women and Youth in the Fourth Merkel Cabinet
- René Wilke (born 1984) a German politician, mayor-elect of Frankfurt (Oder)
Military
- Konstantin Schmidt von Knobelsdorf (1860–1936) a Prussian military officer and a general in the WWI
- Vizeadmiral Hubert von Rebeur-Paschwitz (1863–1933) a German admiral and served as the German Naval attaché to Washington
- Franz von Rintelen (1878–1949) a German Naval Intelligence officer in the United States during WWI.
- Erich Hoepner (1886–1944) a German officer who served in both World Wars, executed for his role in the 20 July Plot of 1944.
- Fritz-Hubert Gräser (1888–1960) a German general in the Wehrmacht
- Theodor Busse (1897–1986) a German Army officer during WWI and WWII
- Karl-Jesko von Puttkamer (1900–1981) a German admiral who was naval adjutant to Adolf Hitler during WWII
- Rudolf Brandt (1909–1948), German Nazi SS officer, executed for war crimes
- Paul-Heinrich Dähne (1921–1945) a German Luftwaffe flying ace
- Günter Kießling (1925–2009) a German general in the Bundeswehr
Science
- Johann Sigismund Elsholtz (1623–1688) a German naturalist, pioneer in hygiene, nutrition and on holistic health
- Bernhard Siegfried Albinus (1697–1770) a German-born Dutch anatomist
- Karl August von Bergen (1704–1759) a German anatomist and botanist, he showed the distribution of cellular membranes in animals
- Heinrich Adolf von Bardeleben (1819–1895) a German surgeon, used Joseph Lister's methodology for antiseptic treatment of wounds
- Hermann Rudolph Aubert (1826–1892) a German physiologist, he researched psychophysics and experimented dark adaptation
- Georg Hermann Quincke (1834–1924) a German physicist, modified the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius
- Heinrich Quincke (1842–1922) a German internist and surgeon, introduced the lumbar puncture
- Reinhold Wilhelm Buchholz (1837–1876) a German zoologist who worked in herpetology, carcinology and ichthyology
- Friedrich Loeffler (1852–1915) a German bacteriologist at the University of Greifswald
- Heinrich Seilkopf (1895–1968) a German meteorologist, in 1939 he discovered the jet stream
Sport
- Hermann Weingärtner (1864–1919) a German gymnast, competed at the 1896 Summer Olympics in Athens
- Klaus Köste (1943–2012) a German gymnast, gold medalist in the vault at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich
- Maik Bullmann (born 1967) a German Greco-Roman wrestler, competed at the 1992 and 1996 Summer Olympics
- Sebastian Köber (born 1979) a German boxer, the Heavyweight bronze medalist at the 2000 Summer Olympics
- Markus Thätner (born 1985) an amateur German Greco-Roman wrestler, competed at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing
- Florian Schmidt (born 1986) a German sport shooter, competed in the 2008 and the 2012 Summer Olympics
Writers, painters and musicians
- Bartholomäus Ringwaldt (1532- c.1599) a German didactic poet and Lutheran pastor
- Heinrich von Kleist (1777–1811) a German poet, dramatist, novelist, short story writer and journalist
- Anton von Werner (1843–1915) a German painter of notable political and military events in the Kingdom of Prussia
- Marie Goslich (1859-1936) a German journalist, photographer and magazine editor
- Herbert Bohme (1907–1971) a German poet who wrote poems and battle hymns for the Nazi Party
- Anne Pätzke (born 1982) a German illustrator and writer, also known as trenchmaker
Films set in Frankfurt
In recent years, Frankfurt has been the setting for several notable German films:
- Halbe Treppe (Grill Point, 2002)
- Lichter (Distant Lights, 2003)
- Die Kinder sind tot (The Children Are Dead, a documentary about a 1999 murder-by-neglect in Frankfurt, 2004)
- No Exit (2004, documentary about Neo-Nazis)
- Kombat Sechzehn (Combat Sixteen, 2005)
Gallery
- The Gothic town hall
- The town archives and the C.P.E. Bach Concert Hall
 The Oderturm, tallest building in Frankfurt an der Oder
The Oderturm, tallest building in Frankfurt an der Oder- The neo-Gothic post office
- The Friedenskirche
- The Oder bridge linking Frankfurt with Słubice
- View of northern Frankfurt river front
- Main railway station
- Große Scharrnstraße, rebuilt in the late 1980s
 The Paulinenhof settlement, built in the 1920s for railway employees
The Paulinenhof settlement, built in the 1920s for railway employees Old East German passport stamp from Frankfurt (Oder).
Old East German passport stamp from Frankfurt (Oder). Reunified Germany passport stamp from same border crossing.
Reunified Germany passport stamp from same border crossing. Schengen passport stamp for the same border crossing.
Schengen passport stamp for the same border crossing._32.jpg) The Flutstein, Oderpromenade.
The Flutstein, Oderpromenade. Nicolaus Copernicus monument in Frankfurt (Oder)
Nicolaus Copernicus monument in Frankfurt (Oder) Red Army monument in Frankfurt (Oder)
Red Army monument in Frankfurt (Oder)
See also
References
- ↑ "Bevölkerung im Land Brandenburg nach amtsfreien Gemeinden, Ämtern und Gemeinden 31. Dezember 2017 (Fortgeschriebene amtliche Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)". Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg (in German). 2018.
- ↑ "Bevölkerungsprognose (Ergänzungsbericht)" (PDF) (in German). Kommunalen Statistikstelle der Stadt Frankfurt (Oder). February 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-28. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- 1 2 3 Bröckling (1998), p.57
- 1 2 Mackillop (2003), p.64
- ↑ Anisimov, Evgeniǐ Viktorovich (1|995) Empress Elizabeth: Her Reign and Her Russia, 1741-1761. Academic International Press, p. 132. ISBN 0875691404
- ↑ Mapa Polski 1:500 000 Wojskowy Instytut Geograficzny Sztabu Generalnego W.P., Warszawa 1947
- ↑ Koleje Pomorza 1:1100 000, marzec 1946
- ↑ Detailed data sources are to be found in the Wikimedia Commons.Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia Commons
- ↑ Ad-hoc-news.de
- ↑ Euv-frankfurt-o.de
- ↑ Berlinonline.de
Bibliography
- Bröckling, Ulrich; Sikora, Michael (1998). Armeen und ihre Deserteure: Vernachlässigte Kapital einer Militärgeschichte der Neuzeit (in German). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. ISBN 3-525-01365-5. Retrieved 2009-08-27.
- Mackillop, Andrew; Murdoch, Steve (2003). Military governors and imperial frontiers c. 1600-1800: A study of Scotland and empires. BRILL. ISBN 90-04-12970-7. Retrieved 2009-08-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Frankfort-on-Oder. |

- The City of Frankfurt (Oder) has a website (available in English translation as well as in German and in Polish) with some limited commerce and cultural information.
- Slubice.pl - official site of Frankfurt's border town Słubice
- Frankfurt.pl & Slubice.de - a student project
- Tram-ff.de


- Frankfort a.d.O. Notgeld (emergency banknotes)

.png)
_durch_die_Schweden_1631.png)