Flag of Sri Lanka
 | |
| Name |
Lion Flag Sinha Flag |
|---|---|
| Use | Civil and state flag, civil ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 22 May 1972 |
| Design | A yellow field with two panels: the smaller hoist-side panel has only two vertical bands of green and saffron and the larger fly-side panel is the maroon field depicting the golden lion holding the kastane sword in its right fore paw in the center and four bo leaves on each corner and the yellow field appears as a border around the entire flag and extends in between the two panels, all bordering together. |
 Variant flag of Sri Lanka | |
| Use | Civil ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1972 |
| Design | A red field with the flag of Sri Lanka in the canton. |
 Variant flag of Sri Lanka | |
| Use | Blue ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1972 |
| Design | A blue field with the flag of Sri Lanka in the canton. |
 Variant flag of Sri Lanka | |
| Use | President's Colour |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1972 |
| Design | A defaced flag of Sri Lanka with Coat of arms of Sri Lanka |
 Variant flag of Sri Lanka | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1972 |
| Design | A white field with the flag of Sri Lanka in the canton. |
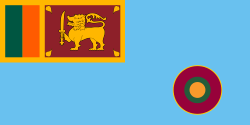 Variant flag of Sri Lanka | |
| Use | Air Force ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 2010 |
| Design | A defaced sky blue ensign with the flag of Sri Lanka in the canton and Air Force roundel. |
The flag of Sri Lanka (Sinhalese: ශ්රී ලංකාවේ ජාතික කොඩිය, translit. Śrī Laṃkāvē jāthika kodiya; Tamil: இலங்கையின் தேசியக்கொடி, translit. Ilankaiyin teciyakkoṭi), also called the Lion Flag or Sinha Flag, consists of a gold lion holding a kastane sword in its right fore-paw in a maroon background with four gold bo leaves in each corner. This is bordered by gold, and to its left are two vertical stripes of equal size in green and saffron, with the saffron stripe closest to the lion. The lion and the maroon background represent the Sinhalese, while the saffron border and four Bo leaves represent Buddhism and the four Buddhist concepts of Mettā, Karuṇā, Muditā and Upeskhā respectively. The stripes represent the two main minorities: the orange representing the Sri Lankan Tamils and the green representing Muslims.
It was adopted in 1950 following the recommendations of a committee appointed by the 1st Prime Minister of Ceylon, D.S. Senanayake.
History
The symbol of a lion in Sri Lankan heraldry dates back to 486 BC, when Vijaya, the first King of Sri Lanka, arrived on the island from India and brought with him a standard depicting a lion.[1]. The symbol appears to have influenced subsequent monarchs, being used extensively by them and becoming a symbol of freedom and hope: King Dutugemunu embarked on his campaign against Ellalan- an invading South Indian ruler- in 162 BC bearing a banner depicting a lion carrying a sword in its right forepaw , a symbol of the Sun and one of the Moon.[1]
This basic design continued to be in use until 1815, when the Kandyan Convention ended the reign of the country's last native monarch, Sri Vikrama Rajasinha, replacing his royal standard (used as the Flag of the Kingdom of Kandy) with the Union Flag as the nation's accepted flag.[1] The government of British Ceylon later established its own flag, while Sri Vikrama Rajasinha's standard was taken to England and kept at the Royal Hospital Chelsea.[1]
As the independence movement in Sri Lanka gained strength in the early 20th century, E. W. Perera and D. R. Wijewardena discovered the original Lion Flag in Chelsea.[1] A photo of it was published in Dinamina, in a special edition marking a century since the loss of self-rule and Sri Lankan independence.[1] The flag provoked much interest from the public who, for the first time since the fall of the Kandyan Kingdom, had seen its actual design.[1]
Member of Parliament for Batticaloa, Mudaliyar A. Sinnalebbe, suggested in Parliament on January 16, 1948 that the Lion Flag should be accepted as the national flag.[2] In 1948, the flag was adopted as the national flag of the Dominion of Ceylon, undergoing two changes: one in 1953 and a redesign in 1972.[1] A notable feature of 1972's adaptation of the Kandyan standard was the replacement of the four spearheads at the flag's corners by four bo leaves, a design choice made under the direction of Nissanka Wijeyeratne, Permanent Secretary to the Ministry of Cultural Affairs and Chairman of the National Emblem and Flag Design Committee.[1][3]
- Historical flags of Sri Lanka
 Standard of Sri Vikrama Rajasinha of Kandy, used as the Kingdom of Kandy's flag, c.1798–1815
Standard of Sri Vikrama Rajasinha of Kandy, used as the Kingdom of Kandy's flag, c.1798–1815 Flag of British Ceylon, 1815–1948
Flag of British Ceylon, 1815–1948.svg.png) Flag of the Dominion of Ceylon, 1948–1951
Flag of the Dominion of Ceylon, 1948–1951.svg.png) Flag of the Dominion of Ceylon (Republic), 1951 and 1972
Flag of the Dominion of Ceylon (Republic), 1951 and 1972
Symbolism
The national flag of Sri Lanka represents the country and its heritage as a rallying device. Most symbols in the flag have been given distinctive meanings.[4][5]
| Symbol | Represents |
|---|---|
| The lion | The Sinhala people |
| The bo leaves | The four Buddhist virtues of loving-kindness, compassion, sympathetic joy and equanimity |
| The sword of the lion | The sovereignty of the nation |
| The curly hair on the lion's head | Religious observance, wisdom and meditation |
| The eight hairs on lion's tail | The Noble Eightfold Path |
| The beard of the lion | Purity of words |
| The handle of the sword | The elements of water, fire, air and earth |
| The nose of the lion | Intelligence |
| The two front paws of the lion | Purity in handling wealth |
| Orange stripe | The Tamil ethnicity |
| Green stripe | The Muslim faith and Moor ethnicity |
| Gold border | Other minority ethnicities |
| The maroon background | Other minority faiths |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "The Sri Lankan National Flag". sundaytimes.lk. The Sunday Times. 4 February 2018. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ↑ "The proposer of the lion flag: Mudlr. Sinnalebbe". Daily News. 4 February 2004. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ↑ Volker Preuß. "Sri Lanka (Ceylon)" (in German). Retrieved 2003-09-07.
- ↑ "National symbols of Sri Lanka". gov.lk. Government of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ↑ Karunarathne, Waruni (27 April 2015). "Controversy Over Flag At Demo". thesundayleader.lk. Sunday Leader. Archived from the original on 26 March 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flags of Sri Lanka. |