Firmicutes
| Firmicutes | |
|---|---|
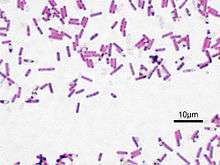 | |
| Bacillus subtilis, Gram stained | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| (unranked): | Terrabacteria |
| Phylum: | Firmicutes Gibbons and Murray 1978,[1] Murray, 1984[2] |
| Classes | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The Firmicutes (Latin: firmus, strong, and cutis, skin, referring to the cell wall) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure.[3] A few, however, such as Megasphaera, Pectinatus, Selenomonas and Zymophilus, have a porous pseudo-outer membrane that causes them to stain Gram-negative. Scientists once classified the Firmicutes to include all Gram-positive bacteria, but have recently defined them to be of a core group of related forms called the low-G+C group, in contrast to the Actinobacteria. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus).
Many Firmicutes produce endospores, which are resistant to desiccation and can survive extreme conditions. They are found in various environments, and the group includes some notable pathogens. Those in one family, the heliobacteria, produce energy through photosynthesis. Firmicutes play an important role in beer, wine, and cider spoilage.
Classes
The group is typically divided into the Clostridia, which are anaerobic, the Bacilli, which are obligate or facultative aerobes, and the Mollicutes, which are parasites.
On phylogenetic trees, the first two groups show up as paraphyletic or polyphyletic, as do their main genera, Clostridium and Bacillus.[4]
Phylogeny
The phylogeny is based on 16S rRNA-based LTP release 132 by The All-Species Living Tree Project[5], with the currently accepted taxonomy based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) [6], National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[7] and some non validated clade names from Genome Taxonomic Database.[8]
| Firmicutes classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Unassigned Clostridia s.s.
|
Notes:
♥ Clade names not lodged at National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) or listed in the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)
The family Synergistaceae (Clostridiales Family XV Incertae Sedis) and Thermodesulfobiaceae have been removed from Firmicutes based on the fact, they do not form a monophyletic clade with it.
Genera
More than 274 genera were considered as of 2016 to be within the Firmicutes phylum, notable genera of Firmicutes include:
Bacilli, order Bacillales
Bacilli, order Lactobacillales
Health implications
Firmicutes make up the largest portion of the mouse and human gut microbiome.[9] The division Firmicutes as part of the gut flora has been shown to be involved in energy resorption, and potentially related to the development of diabetes and obesity.[10][11][12][13]
Firmicutes spp. are part of a normal, healthy placental microbiome.[14][15]
Presence of Christensenella (Firmicutes, in class Clostridia), isolated from human faeces, has been found to correlate with lower body mass index.[16]
Laboratory detection
The presence of Firmicutes can be reliably detected with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques.[17]
References
- ↑ Gibbons, N. E. & Murray, R. G. E. 1978. Proposals concerning the higher taxa of bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:1–6, (PDF)
- ↑ Murray, R.G.E. (1984). The higher taxa, or, a place for everything...?. In: N.R. Krieg & J.G. Holt (ed.) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, vol. 1, The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, p. 31-34.
- ↑ "Firmicutes" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Wolf M, Müller T, Dandekar T, Pollack JD (May 2004). "Phylogeny of Firmicutes with special reference to Mycoplasma (Mollicutes) as inferred from phosphoglycerate kinase amino acid sequence data". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. (Comparative Study). 54 (Pt 3): 871–5. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02868-0. PMID 15143038.
- ↑ "16S rRNA-based LTP release 132 (full tree)". All-Species Living Tree Project. Silva Comprehensive Ribosomal RNA Database. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ J.P. Euzéby. "Firmicutes". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Archived from the original on January 27, 2013. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ Sayers; et al. "Firmicutes". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ "GTDB taxonomy". Genome Taxonomic Database. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
- ↑ Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2006). "Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine". Cell (Review). 124 (4): 837–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.017. PMID 16497592.
- ↑ Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006). "Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity". Nature (Clinical Trial). 444 (7122): 1022–3. doi:10.1038/4441022a. PMID 17183309.
- ↑ Henig, Robin Marantz (2006-08-13). "Fat Factors". New York Times Magazine. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ↑ Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (August 2005). "Obesity alters gut microbial ecology". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (Research Support). 102 (31): 11070–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504978102. PMC 1176910. PMID 16033867. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ↑ Komaroff AL. The Microbiome and Risk for Obesity and Diabetes. JAMA. Published online December 22, 2016. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.20099
- ↑ Mor, Gil; Kwon, Ja-Young (2015). "Trophoblast-microbiome interaction: a new paradigm on immune regulation". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 213 (4): S131–S137. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.039. ISSN 0002-9378. PMID 26428492.
- ↑ Todar, K. "Pathogenic E. coli". Online Textbook of Bacteriology. University of Wisconsin–Madison Department of Bacteriology. Retrieved 2007-11-30.
- ↑ Goodrich, Julia K.; Waters, Jillian L.; Poole, Angela C.; Sutter, Jessica L.; Koren, Omry; Blekhman, Ran; Beaumont, Michelle; Van Treuren, William; Knight, Rob; Bell, Jordana T.; Spector, Timothy D.; Clark, Andrew G.; Ley, Ruth E. (2014). "Human Genetics Shape the Gut Microbiome". Cell. 159 (4): 789–799. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053. ISSN 0092-8674.

- ↑ Haakensen M, Dobson CM, Deneer H, Ziola B (July 2008). "Real-time PCR detection of bacteria belonging to the Firmicutes Phylum". Int. J. Food Microbiol. (Research Support). 125 (3): 236–41. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.04.002. PMID 18501458. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
External links
- Phylum "Firmicutes" - J.P. Euzéby: List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature