FTH1
Ferritin heavy chain is a ferroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FTH1 gene.[5][6]
Function
This gene encodes the heavy subunit of ferritin, the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is composed of 24 subunits of the heavy and light ferritin chains. Variation in ferritin subunit composition may affect the rates of iron uptake and release in different tissues. A major function of ferritin is the storage of iron in a soluble and nontoxic state. Defects in ferritin proteins are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed, but their biological validity has not been determined.[6]
Interactions
FTH1 has been shown to interact with Ferritin light chain.[7][8]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000167996 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024661 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Hentze MW, Keim S, Papadopoulos P, O'Brien S, Modi W, Drysdale J, Leonard WJ, Harford JB, Klausner RD (Oct 1986). "Cloning, characterization, expression, and chromosomal localization of a human ferritin heavy-chain gene". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 83 (19): 7226–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.19.7226. PMC 386688. PMID 3020541.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: FTH1 ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1".
- ↑ Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- ↑ Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C, Brembeck FH, Goehler H, Stroedicke M, Zenkner M, Schoenherr A, Koeppen S, Timm J, Mintzlaff S, Abraham C, Bock N, Kietzmann S, Goedde A, Toksöz E, Droege A, Krobitsch S, Korn B, Birchmeier W, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (Sep 2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
Further reading
- Percy ME, Wong S, Bauer S, Liaghati-Nasseri N, Perry MD, Chauthaiwale VM, Dhar M, Joshi JG (Jan 1998). "Iron metabolism and human ferritin heavy chain cDNA from adult brain with an elongated untranslated region: new findings and insights". The Analyst. 123 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1039/a706355e. PMID 9581019.
- Arosio P, Adelman TG, Drysdale JW (Jun 1978). "On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 253 (12): 4451–8. PMID 659425.
- Lawson DM, Artymiuk PJ, Yewdall SJ, Smith JM, Livingstone JC, Treffry A, Luzzago A, Levi S, Arosio P, Cesareni G (Feb 1991). "Solving the structure of human H ferritin by genetically engineering intermolecular crystal contacts". Nature. 349 (6309): 541–4. doi:10.1038/349541a0. PMID 1992356.
- Costanzo F, Colombo M, Staempfli S, Santoro C, Marone M, Frank R, Delius H, Cortese R (Jan 1986). "Structure of gene and pseudogenes of human apoferritin H". Nucleic Acids Research. 14 (2): 721–36. doi:10.1093/nar/14.2.721. PMC 339460. PMID 3003694.
- Chou CC, Gatti RA, Fuller ML, Concannon P, Wong A, Chada S, Davis RC, Salser WA (Feb 1986). "Structure and expression of ferritin genes in a human promyelocytic cell line that differentiates in vitro". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 6 (2): 566–73. doi:10.1128/mcb.6.2.566. PMC 367547. PMID 3023856.
- Hentze MW, Caughman SW, Rouault TA, Barriocanal JG, Dancis A, Harford JB, Klausner RD (Dec 1987). "Identification of the iron-responsive element for the translational regulation of human ferritin mRNA". Science. 238 (4833): 1570–3. doi:10.1126/science.3685996. PMID 3685996.
- Boyd D, Vecoli C, Belcher DM, Jain SK, Drysdale JW (Sep 1985). "Structural and functional relationships of human ferritin H and L chains deduced from cDNA clones". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (21): 11755–61. PMID 3840162.
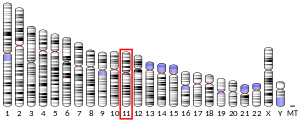
- Worwood M, Brook JD, Cragg SJ, Hellkuhl B, Jones BM, Perera P, Roberts SH, Shaw DJ (1985). "Assignment of human ferritin genes to chromosomes 11 and 19q13.3----19qter". Human Genetics. 69 (4): 371–4. doi:10.1007/BF00291657. PMID 3857215.
- Dörner MH, Salfeld J, Will H, Leibold EA, Vass JK, Munro HN (May 1985). "Structure of human ferritin light subunit messenger RNA: comparison with heavy subunit message and functional implications". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (10): 3139–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.10.3139. PMC 397730. PMID 3858810.
- Costanzo F, Santoro C, Colantuoni V, Bensi G, Raugei G, Romano V, Cortese R (Jan 1984). "Cloning and sequencing of a full length cDNA coding for a human apoferritin H chain: evidence for a multigene family". The EMBO Journal. 3 (1): 23–7. PMC 557292. PMID 6323167.
- Boyd D, Jain SK, Crampton J, Barrett KJ, Drysdale J (Aug 1984). "Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for human ferritin heavy chain". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 81 (15): 4751–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.15.4751. PMC 391568. PMID 6589621.
- Addison JM, Fitton JE, Lewis WG, May K, Harrison PM (Nov 1983). "The amino acid sequence of human liver apoferritin". FEBS Letters. 164 (1): 139–44. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(83)80037-4. PMID 6653779.
- Dhar MS, Joshi JG (Dec 1993). "Differential processing of the ferritin heavy chain mRNA in human liver and adult human brain". Journal of Neurochemistry. 61 (6): 2140–6. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07452.x. PMID 7504084.
- Connor JR, Snyder BS, Arosio P, Loeffler DA, LeWitt P (Aug 1995). "A quantitative analysis of isoferritins in select regions of aged, parkinsonian, and Alzheimer's diseased brains". Journal of Neurochemistry. 65 (2): 717–24. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65020717.x. PMID 7616228.
- Kato S, Sekine S, Oh SW, Kim NS, Umezawa Y, Abe N, Yokoyama-Kobayashi M, Aoki T (Dec 1994). "Construction of a human full-length cDNA bank". Gene. 150 (2): 243–50. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90433-2. PMID 7821789.
- Dhar M, Chauthaiwale V, Joshi JG (Apr 1993). "Sequence of a cDNA encoding the ferritin H-chain from an 11-week-old human fetal brain". Gene. 126 (2): 275–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(93)90380-L. PMID 7916709.
- Qi Y, Dawson G (Oct 1994). "Hypoxia specifically and reversibly induces the synthesis of ferritin in oligodendrocytes and human oligodendrogliomas". Journal of Neurochemistry. 63 (4): 1485–90. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63041485.x. PMID 7931301.
- Rogers JT (Mar 1996). "Ferritin translation by interleukin-1and interleukin-6: the role of sequences upstream of the start codons of the heavy and light subunit genes". Blood. 87 (6): 2525–37. PMID 8630420.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (Sep 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.