Ezekiel 46
| Ezekiel 46 | |
|---|---|
 Book of Ezekiel 30:13–18 in an English manuscript from the early 13th century, MS. Bodl. Or. 62, fol. 59a. A Latin translation appears in the margins with further interlineations above the Hebrew. | |
| Book | Book of Ezekiel |
| Bible part | Old Testament |
| Order in the Bible part | 26 |
| Category | Nevi'im |
Ezekiel 46 is the forty-sixth chapter of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible.[1][2] This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Ezekiel, and is a part of the Books of the Prophets.[3][4] Chapters 40-48 give the ideal picture of a new temple. This chapter contains Ezekiel's vision of the ordinances for the prince in his worship, Ezekiel 46:1-8, and for the people, Ezekiel 46:9-15; an order for the prince's inheritance, Ezekiel 46:16-18; the courts for boiling and baking, Ezekiel 46:19-24.[5]
Text
- The original text is written in Hebrew language.
- This chapter is divided into 24 verses.
Textual versions
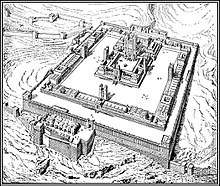
The visionary Ezekiel Temple plan drawn by the 19th-century French architect and Bible scholar Charles Chipiez
Some most ancient manuscripts containing this chapter in Hebrew language:
- Masoretic Text (10th century)
Ancient translations in Koine Greek:
- Septuagint (3rd century BC)
- Theodotion version (~AD 180)
Structure
NKJV groups this chapter into:
- Ezekiel 46:1-15 = The Manner of Worship
- Ezekiel 46:16-18 = The Prince and Inheritance Laws
- Ezekiel 46:19-24 = How the Offerings Were Prepared
Verse 15
- " Thus they shall prepare the lamb, the grain offering, and the oil, as a regular burnt offering every morning." (NKJV)[6]
- The vision was given on the 25th anniversary of Ezekiel's exile, "April 28, 573 BCE";[7] 14 years after the fall of Jerusalem and 12 years after the last messages of hope in chapter 39.[8]
- The prince is obliged to make daily offerings.[9]
Verse 24
- And he said to me, "These are the kitchens where the ministers of the temple shall boil the sacrifices of the people." (NKJV)[10]
- These kitchens belong to the Levites and are different from those for the priests in verse 19-20.[11]
See also
- Related Bible parts: Ezekiel 40, Ezekiel 43, Ezekiel 44, Ezekiel 45
Notes and references
- ↑ Halley, Henry H. Halley's Bible Handbook: an Abbreviated Bible Commentary. 23rd edition. Zondervan Publishing House. 1962.
- ↑ 'Holman Illustrated Bible Handbook'. Holman Bible Publishers, Nashville, Tennessee. 2012.
- ↑ J. D. Davis. 1960. A Dictionary of the Bible. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Baker Book House.
- ↑ Theodore Hiebert, et al. 1996. The New Interpreter's Bible: Volume: VI. Nashville: Abingdon.
- ↑ Robert Jamieson, Andrew Robert Fausset; David Brown. Jamieson, Fausset, and Brown's Commentary On the Whole Bible. 1871.

- ↑ Ezekiel 46:15
- ↑ The New Oxford Annotated Bible with the Apocrypha, Augmented Third Edition, New Revised Standard Version, Indexed. Michael D. Coogan, Marc Brettler, Carol A. Newsom, Editors. Publisher: Oxford University Press, USA; 2007. p. 1240 Hebrew Bible. ISBN 978-0195288810
- ↑ The Nelson Study Bible 1997, p. 1399.
- ↑ The New Oxford Annotated Bible with the Apocrypha, Augmented Third Edition, New Revised Standard Version, Indexed. Michael D. Coogan, Marc Brettler, Carol A. Newsom, Editors. Publisher: Oxford University Press, USA; 2007. p. 1248 Hebrew Bible. ISBN 978-0195288810
- ↑ Ezekiel 46:24
- ↑ The Nelson Study Bible 1997, p. 1411.
Bibliography
- Bromiley, Geoffrey W. (1995). International Standard Bible Encyclopedia: vol. iv, Q-Z. Eerdmans.
- Brown, Francis; Briggs, Charles A.; Driver, S. R. (1994). The Brown-Driver-Briggs Hebrew and English Lexicon (reprint ed.). Hendrickson Publishers. ISBN 978-1565632066.
- Clements, Ronald E (1996). Ezekiel. Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 9780664252724.
- Gesenius, H. W. F. (1979). Gesenius' Hebrew and Chaldee Lexicon to the Old Testament Scriptures: Numerically Coded to Strong's Exhaustive Concordance, with an English Index. Translated by Tregelles, Samuel Prideaux (7th ed.). Baker Book House.
- Joyce, Paul M. (2009). Ezekiel: A Commentary. Continuum. ISBN 9780567483614.
- The Nelson Study Bible. Thomas Nelson, Inc. 1997. ISBN 9780840715999.
External links
Jewish
Christian
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.