Erastin
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
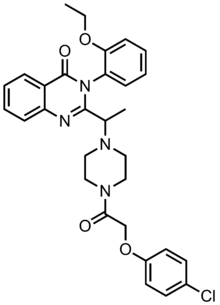
| Formula | C30H31ClN4O4 |
| Molar mass | 547.05 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Erastin is a small molecule capable of initiating ferroptotic cell death.[1] Erastin binds and inhibits VDAC2 and VDAC3[2] and functionally inhibits the cystine-glutamate antiporter System Xc-.[3] Cells treated with erastin are deprived of cysteine and are unable to synthesize the antioxidant glutathione. Depletion of glutathione eventually leads to excessive lipid peroxidation and cell death.
References
- ↑ Dixon, SJ; Lemberg, KM; Lamprecht, MR; Skouta, R; Zaitsev, EM; Gleason, CE; Patel, DN; Bauer, AJ; Cantley, AM; Yang, WS; Morrison B, 3rd; Stockwell, BR (25 May 2012). "Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death". Cell. 149 (5): 1060–72. PMID 22632970.
- ↑ Yagoda, N; von Rechenberg, M; Zaganjor, E; Bauer, AJ; Yang, WS; Fridman, DJ; Wolpaw, AJ; Smukste, I; Peltier, JM; Boniface, JJ; Smith, R; Lessnick, SL; Sahasrabudhe, S; Stockwell, BR (14 June 2007). "RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels". Nature. 447 (7146): 864–8. PMID 17568748.
- ↑ Dixon, SJ; Patel, DN; Welsch, M; Skouta, R; Lee, ED; Hayano, M; Thomas, AG; Gleason, CE; Tatonetti, NP; Slusher, BS; Stockwell, BR (20 May 2014). "Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis". eLife. 3: e02523. PMID 24844246.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.