Dimagnesium phosphate
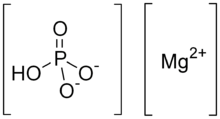 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Magnesium hydrogen phosphate; Magnesium phosphate dibasic | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.930 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HMgO4P | |
| Molar mass | 120.28 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 2.13 g/cm3 trihydrate |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36, R37, R38 |
| NFPA 704 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimagnesium phosphate is a compound with formula MgHPO4. It is a Mg2+ salt of monohydrogen phosphate. The trihydrate is well known, occurring as a mineral.[1]
It can be formed by reaction of stoichiometric quantities of magnesium oxide with phosphoric acid.
- MgO + H3PO4 → MgHPO4 + H2O
Dissolving monomagnesium phosphate in water, forms phosphoric acid and depositing a solid precipitate of dimagnesium phosphate trihydrate:
- Mg(H2PO4)2 + 3 H2O → Mg(HPO4).3H2O + H3PO4
The compound is used as a nutritional supplement, especially for infants and athletes. Its E number is E343.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Klaus Schrödter; Gerhard Bettermann; Thomas Staffel; Friedrich Wahl; Thomas Klein; Thomas Hofmann (2008). Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3.
- ↑ relevant part of the German “Zusatzstoff-Zulassungsverordnung”, the official German implementation of the respective regulation of the European Union
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
