DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome
| DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome | |
|---|---|
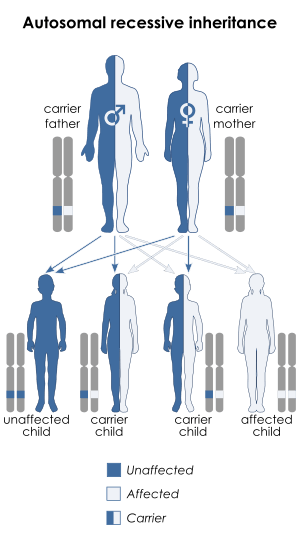 | |
| DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner |
DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome is an extremely rare disorder characterized by the skin and eye symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) occurring in association with microcephaly, progressive mental retardation, retarded growth and sexual development, deafness, choreoathetosis, ataxia and quadriparesis.[1]
Genetics
In at least some case, the gene lesion involves a mutation in the CSB gene.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ↑ http://hmg.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/9/8/1171?view=long&pmid=10767341
- ↑ Colella S, Nardo T, Botta E, Lehmann AR, Stefanini M (May 2000). "Identical mutations in the CSB gene associated with either Cockayne syndrome or the DeSanctis-cacchione variant of xeroderma pigmentosum". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (8): 1171–5. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.8.1171. PMID 10767341.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.