Choudhry Rahmat Ali
| Chaudhry Rahmat Ali | |
|---|---|
| Born |
16 November 1897 Balachaur, Hoshiarpur District, Punjab, British India |
| Died |
3 February 1951 (aged 53) Cambridge, England, United Kingdom |
| Academic work | |
| Notable works | "Pakistan Declaration" |
| Notable ideas |
Pakistan National Movement Coining of the word "Pakistan" |
Chaudhry Rehmat Ali (/ɑːˈliː/; Urdu: چودھری رحمت علی; 16 November 1897 – 3 February 1951) was a Pakistani Punjabi Muslim Gujjar nationalist who was one of the earliest proponents of the creation of the state of Pakistan. He is credited with creating the name "Pakistan" for a separate Muslim homeland in South Asia and is generally known as the founder of the Pakistan Movement and for its creation. He is best known as the author of a famous 1933 pamphlet titled "Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever", also known as the "Pakistan Declaration"[1][2][3][4].
The pamphlet started with a famous statement:
At this solemn hour in the history of India, when British and Indian statesmen are laying the foundations of a Federal Constitution for that land, we address this appeal to you, in the name of our common heritage, on behalf of our thirty million Muslim brethren who live in PAKSTAN [used as an acronym]
Education and career

Ali was born into family of the Gorci clan[5] in the town of Balachaur in the Hoshiarpur District of Punjab, Punjab, British India. Choudhry Rahmat Ali was one of the earliest advocates of the creation of the state of Pakistan. Rahmat Ali a Pakistani Muslim nationalist is generally recognized as the creator of the name “Pakistan” for a separate Muslim, homeland in South Asia and is known as the founder of the Pakistan National Movement. Ali was born in November 1897 into a Gujjar Muslim family in a District of Indian Punjab. From his early childhood, Rahmat Ali showed signs of great promise as a student. After completing his schooling, he joined the Islamia College in Lahore, after his graduation in 1918; he initially taught at Aitcheson College Lahore and later joined Punjab University in order to study law. However In 1930 he moved to England to join Emmanuel College Cambridge, in 1931. He obtained a BA degree in 1933 and MA in 1940 from the University of Cambridge. In 1943, he was called to the Bar, Middle Temple Inn, London. Rahmat Ali finished education in England, obtaining MA and LLB with honors from the universities of Cambridge and Dublin.After graduating from Islamia Madrassa Lahore in 1918, he taught at Aitchison College Lahore before joining Punjab University to study law. In 1930 he moved to England to join Emmanuel College, Cambridge in 1931. In 1933, he published a pamphlet, "Now or Never", coining the word Pakistan for the first time. In 1946, he founded Pakistan National Movement in England. Subsequently, he obtained a BA degree in 1933 and MA in 1940 from the University of Cambridge. In 1943, he was called to the Bar, from Middle Temple, London. Until 1947, he continued publishing various booklets about his vision for South Asia. The final Partition of India disillusioned him due to the mass killings and mass migrations it ended up producing. He was also dissatisfied with the distribution of areas among the two countries and considered it a major reason for the disturbances.
Philosophy
Ali believed that the Muslims of India had to reform politically to become a viable, independent community. He was inspired by Islamic history, he believed that Indian Muslims should similarly unite to survive in what he perceived to be an increasingly hostile India.
As such, Ali's writings, in addition to those of Muhammad Iqbal and others were major catalysts for the formation of Pakistan. He offered the name "Charsistan" for a Muslim homeland in the Bengal region, and "Nawazistan" for a Muslim homeland in the Deccan. He also suggested Dhania as a name for a South Asia of various religions.[6]
Ali is known for his steadfast dedication to the idea of Pakistan. After its formation in 1947, he argued on its behalf at the United Nations over the issue of Kashmir, and the rights of Muslim minority of India.
Conception of 'Pakistan'
In 1932, Ali moved to a now famous house in Cambridge, on 3 Humberstone Road. It was in one of the rooms of this house that he is said to have written the word 'Pakstan' for the first time. There are several accounts of the creation of the name. According to a friend, Abdul Kareem Jabbar, the name came up when Ali was walking along the banks of the Thames in 1932 with his friends Pir Ahsan-ud-din and Khwaja Abdul Rahim. According to Ali's secretary Miss Frost, he came up with the idea while riding on the top of a London bus.[7]
On 28 January 1933, Ali voiced the idea in a pamphlet titled "Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?".[8] The word 'Pakstan' referred to "the five Northern units of India, viz. : Punjab, North-West Frontier Province (Afghan Province), Kashmir, Sind and Baluchistan"".[9][10] By the end of 1933, 'Pakistan' had become common vocabulary, and an i was added to ease pronunciation (as in Afghan-i-stan).[11]
In a subsequent book, Ali discussed the etymology in further detail.[12]
- 'Pakistan' is both a Persian and an Urdu word. It is composed of letters taken from the names of all our South Asia homelands; that is, Punjab, Afghania, Kashmir, Sindh and Balochistan. It means the land of the Paks – the spiritually pure and clean.
Ali's biographer, K. K. Aziz writes[13] that "Rahmat Ali alone drafted this declaration[14] (in which the word Pakistan was used for the first time), but in order to make it "representative" he began to look around for people who would sign it along with him. This search did not prove easy, "for so firm was the grip of 'Muslim Indian Nationalism' on our young intellectuals at English universities that it took me (Rahmat Ali) more than a month to find three young men in London who offered to support and sign it."[15] Later on, his political opponents used the name of these signatories and other friends of Ali, as creator of word 'Pakistan'.
Iqbal and Jinnah

On 29 December 1930, Muhammad Iqbal delivered his monumental address. He said:[16]
I would like to see the Punjab, North-West Frontier Province, Sind and Baluchistan amalgamated into a single State. Self-government within the British Empire, or without the British Empire, the formation of a consolidated North-West Indian Muslim State appears to me to be the final destiny of the Muslims, at least of North-West India.
According to some scholars,[17] that Iqbal had not presented the idea of an autonomous Muslim State; rather he wanted a large Muslim province by amalgamating Punjab, Sindh, NWFP and Baluchistan into a big North-Western province within India.[18] They argued that "Iqbal never pleaded for any kind of partition of the country. Rather he was an ardent proponent of a 'true' federal setup for India.... And wanted a consolidated Muslim majority within the Indian Federation".[19]
Another Indian historian, Tara Chand. also held that Iqbal was not thinking in terms of partition of India but in terms of a federation of autonomous states within India.[20] Dr. Safdar Mehmood also asserted that in an Allahabad address Iqbal proposed a Muslim majority province within the Indian federation and not an independent state outside the Indian Federation.[21]
On 28 January 1933, Choudhry Rahmat Ali voiced his ideas in the pamphlet titled "Now or Never;[22] Are We to Live or Perish Forever?" The word 'Pakstan' referred to "the five Northern units of India, viz. : Punjab, North-West Frontier Province (Afghan Province), Kashmir, Sind and Baluchistan"". By the end of 1933, the word "Pakistan" became common vocabulary where an “I” was added to ease pronunciation (as in Afghan-i-stan). In a subsequent book Rehmat Ali discussed the etymology in further detail.[12] "Pakistan' is both a Persian and an Urdu word. It is composed of letters taken from the names of all our South Asia homelands; that is, Punjab, Afghania, Kashmir, Sindh and Balochistan. It means the land of the Pure".
The British and the Indian Press vehemently criticised these two different schemes and created a confusion about the authorship of the word "Pakistan" to such an extent that even Jawaharlal Nehru had to write: ""Iqbal was one of the early advocates of Pakistan and yet he appears to have realised its inherent danger and absurdity. Edward Thompson has written that in the course of conversation, Iqbal told him that he had advocated Pakistan because of his position as President of Muslim League session, but he felt sure that it would be injurious to India as a whole and to Muslims especially."[23]
In 1934, Choudhry Rahmat Ali and his friends met Muhammad Ali Jinnah and appealed for his support of the Pakistan idea. He replied; "My dear boys, don't be in a hurry; let the waters flow and they will find their own level"[25]
After the creation of Pakistan

While Choudhry Rahmat Ali was a leading figure for the conception of Pakistan, he lived most of his adult life in England. He had been voicing his dissatisfaction with the creation of Pakistan ever since his arrival in Lahore on 6 April 1948. He was unhappy over a smaller Pakistan than the one he had conceived in his 1933 pamphlet "Now Or Never".[24]
After the creation of Pakistan he returned to Pakistan in April 1948, planning to stay in this country, but he left again over disputes.
He died on 3 February 1951 in Cambridge. Fearing (correctly) that he may have died insolvent, the Master of Emmanuel College, Cambridge, Edward Welbourne, instructed that the College would cover the funeral expenses. He was buried on 20 February at Cambridge City Cemetery in Cambridge, England.[25] The funeral expenses and other medical expenses were repaid by the High Commissioner for Pakistan in November 1953, after what was described as “protracted correspondence” between the London office and relevant authorities in Pakistan.[26]
Works
- "Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?", also known as the "Pakistan Declaration", (1933)
- What Does the Pakistan National Movement Stand For? (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1933)
- Letters to the Members of the British Parliament (Cambridge, 8 July 1935)
- Islamic Fatherland and the Indian Federation: The Fight Will Go On for Pakistan (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1935)
- Letter to The Times, 8 December 1938
- The Millat of Islam and the Menace of Indianism (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1942)
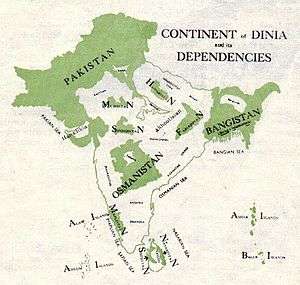
- The Millat and the Mission: Seven Commandments of Destiny for the 'Seventh' Continent of Dinia (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1942)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Faruqistan for the Muslims of Bihar and Orissa (Cambridge: The Faruqistan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Haideristan for Muslims of Hindoostan (Cambridge: The Haideristan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Maplistan for Muslims of South India (Cambridge: The Maplistan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Muinistan for Muslims of Rajistan (Cambridge: The Muinistan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Siddiqistan for Muslims of Central India (Cambridge: The Siddiqistan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Safiistan for Muslims of Western Ceylon (Cambridge: The Safiistan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Minorities: Foundation of Nasaristan for Muslims of Eastern Ceylon (Cambridge: The Nasaristan National Movement, 1943)
- The Millat and her Ten Nations: Foundation of the All-Dinia Milli Movement (Cambridge: The All-Dinia Milli Movement, 1944)
- Dinia: The Seventh Continent of the World (Cambridge: Dinia Continental Movement, 1946)
- India: The Continent of Dinia, or the Country of Doom (Cambridge: Dinia Continental Movement, 1946)
- The Pakistan National Movement and the British Verdict on India (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1946)
- Pakasia: The Historic Orbit of the Pak Culture (Cambridge: The Pakasia Cultural Movement, 1946)
- Osmanistan: The Fatherland of the Osman Nation (Cambridge: The Osmanistan National Movement, 1946)
- The Greatest Betrayal: How to Redeem the Millat? (Cambridge: Pakistan National Movement, 1947)
- Pakistan: The Fatherland of the Pak Nation, (Cambridge: Pakistan National Liberation Movement, 1947)
- The Muslim Minority in India and the Saving Duty of the U.N.O. (Cambridge: The All-Dinia Milli Liberation Movement, 1948)
- The Muslim Minority in India and the Dinian Mission to the U.N.O. (Cambridge: The All-Dinia Milli Liberation Movement, 1949)
- Pakistan or Pastan? Destiny or Disintegration? (Cambridge: The Pakistan National Liberation Movement, 1950)
- Complete Works of Rahmat Ali, ed. Khursheed Kamal Aziz (Islamabad: National Commission on Historical and Cultural Research, 1978)
See also
References
- ↑ "Rahmat Ali".
- ↑ "Iqbal".
- ↑ "Complete Works of Rahmat Ali".
- ↑ ""Death anniversary of Ch Rehmat Ali being observed"". Dunya News.
- ↑ Khursheed Kamal Aziz (1987). Rahmat Ali: a biography. Steiner Verlag Wiesbaden.
ISBN 3515050515,
ISBN 978-3-515-05051-7.
In the arian tribe his clan was Gorsi.
- ↑ "dinia".
- ↑ "Miss Frost,".
- ↑ Choudhary Rahmat Ali (1933).

- ↑ Choudhary Rahmat Ali; Mohd Aslam Khan; Sheikh Mohd Sadiq; Inayat Ullah Khan (28 January 1933), Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?
"At this solemn hour in the history of India, when British and Indian statesmen are laying the foundations of a Federal Constitution for that land, we address this appeal to you, in the name of our common heritage, on behalf of our thirty million Muslim brethren who live in PAKSTAN [sic] – by which we mean the five Northern units of India, viz.: Punjab, North-West Frontier Province (Afghan Province), Kashmir, Sind and Baluchistan – for your sympathy and support in our grim and fateful struggle against political crucifixion and complete annihilation." - ↑ Wolpert, Stanley A. (1984). Jinnah of Pakistan. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-503412-0.
- ↑ "Chaudhry Rehmat Ali". Story Of Pakistan.
- 1 2 Choudhry Rahmat Ali, 1947, Pakistan: the fatherland of the Pak nation, Cambridge
- ↑ Rahmat Ali: A Biography, by K. K. AZIZ, Vanguard, Lahore, 1987. p. 85
- ↑ "Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?" Archived 19 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Chaudhry Rahmat Ali, Pakistan
- ↑ A.R. Tariq (ed.), Speeches and Statements of Iqbal (Lahore: 1973),
- ↑ Khursheed Kamal Aziz. Rahmat Ali: a biography, 1987, pp. 351-362
- ↑ K. K. Aziz, Making of Pakistan (London: 1970), p. 81.
- ↑ Verinder Grover (ed.), Muhammad Iqbal: Poet Thinker of Modern Muslim India Vol. 25 (New Delhi: Deep & Deep Publications, 1995), pp. 666–67.
- ↑ Tara Chand, History of Freedom Movement in India Vol. III (New Delhi: 1972), p. 253.
- ↑ lang, 23, 24 & 25 March 2003; Also see, Safdar Mahmood, Iqbal, Jinnah aur Pakistan (Lahore: Khazina Ilm-wa-Adab, 2004), pp. 52–69.
- ↑ Full text of the pamphlet "Now or Never," published by Choudhry Rahmat Ali
- ↑ J.L. Nehru, Discovery ofIndia (New York: 1946), p. 353.
- ↑ Rahmat Ali: A Biography, by K. K. AZIZ, Vanguard, Lahore, 1987
- ↑ Khursheed Kamal Aziz. Rahmat Ali: a biography, 1987, pp. 340-345
- ↑ Emmanuel College Cambridge Archives
External links
- "Location of Newmarket Road Cemetery, Cambridge, UK (Graveyard)".
- "Eye-witness account of how Ch. Rehmat Ali began his Pakistan campaign through Woking Mission".
- "Ch. Rahmat Ali". Chaudhry Rahmat Ali Foundation. Archived from the original on 20 April 2006.
- "Chaudhary Rahmat Ali The man who conceived the idea of Pakistan". The Shelley family.
- "Chaudhary Rahmat Ali (1895–1951)". Story of Pakistan.
