Chisos Mountains
| Chisos Mountains | |
|---|---|
 A photo of the Chisos mountain range from the desert to the east, 22 February 2002. | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Emory Peak |
| Elevation | 7,825 ft (2,385 m) |
| Coordinates | 29°14′45″N 103°18′14″W / 29.24583°N 103.30389°W |
| Geography | |
 Chisos Mtns | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| Range coordinates | 29°16′N 103°18′W / 29.267°N 103.300°WCoordinates: 29°16′N 103°18′W / 29.267°N 103.300°W |
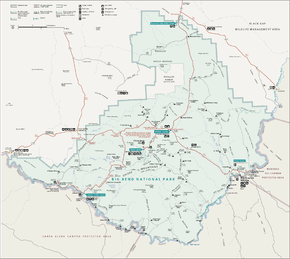
The Chisos Mountains are a mountain range located in the Big Bend area of West Texas, United States.[1] The mountain range is contained entirely within the boundaries of Big Bend National Park.[1] This is the only mountain range in the United States to be fully contained within the boundary of a national park. It is also the southernmost mountain range in the mainland United States.
The highest point in the Chisos Mountain range is Emory Peak at 7,825 ft (2,385 m) above sea level.[1]
Location
The Chisos Mountains are located in Big Bend National Park. The range of mountains extends twenty miles from Punta de la Sierra in the southwest to Panther Junction in the northeast. An extensive trail system and permit-required backcountry campsites are maintained by Big Bend National Park for its visitors.[2] The Northeast Rim and Southeast Rim trails are closed from February 1 through May 31 along with some of the backcountry campsites along these trails to protect the local peregrine falcon population.[2]
The mountain area is partly forested (recovering from logging and overgrazing prior to the area's inclusion in the National Park System in the 1930s), and surrounded by the Chihuahuan Desert. The nearby towns include Study Butte, Terlingua, Fort Stockton, 135 miles north, Alpine, 105 mi (169 km) northwest and Presidio, about 100 mi (160 km) west. Two Mexican towns (Boquillas and Santa Elena) border the park; and cross-border access was reopened in 2011.[3]
 Sunset from the South Rim in Big Bend National Park.
Sunset from the South Rim in Big Bend National Park. Rain approaching the South Rim of the Chisos.
Rain approaching the South Rim of the Chisos. View from the South Rim.
View from the South Rim.
Etymology
One of the multiple possibilities of the origin of the name is the option that it stems from hechizos, a Castilian word meaning "enchantment". Another possibility is the option that the word originated from chisos, a Native American word meaning "ghost" or "spirit".[4]
Peaks
- Emory Peak 7,825 ft (2,385 m)[1]
- Lost Mine Peak 7,535 ft (2,297 m)[1]
- Toll Mountain 7,415 ft (2,260 m)[1]
- Casa Grande Peak 7,325 ft (2,233 m)[1]
Climate
- Elevation: 5,300 feet (1,615 m)[5]
| Climate data for Chisos Basin, Texas (Aug 1, 1943–Mar 31, 2013) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 82 (28) |
84 (29) |
96 (36) |
96 (36) |
99 (37) |
103 (39) |
102 (39) |
99 (37) |
97 (36) |
94 (34) |
89 (32) |
87 (31) |
103 (39) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 58.3 (14.6) |
61.8 (16.6) |
68.7 (20.4) |
76.3 (24.6) |
82.8 (28.2) |
86.8 (30.4) |
84.8 (29.3) |
83.7 (28.7) |
79.5 (26.4) |
73.8 (23.2) |
65.2 (18.4) |
59.4 (15.2) |
73.4 (23) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 47.6 (8.7) |
50.4 (10.2) |
56.4 (13.6) |
63.9 (17.7) |
70.7 (21.5) |
75.1 (23.9) |
74.2 (23.4) |
73.2 (22.9) |
69.0 (20.6) |
62.9 (17.2) |
54.2 (12.3) |
48.7 (9.3) |
62.2 (16.8) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 36.9 (2.7) |
39.1 (3.9) |
44.1 (6.7) |
51.5 (10.8) |
58.5 (14.7) |
63.3 (17.4) |
63.7 (17.6) |
62.7 (17.1) |
58.6 (14.8) |
51.9 (11.1) |
43.2 (6.2) |
37.9 (3.3) |
51.0 (10.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −3 (−19) |
1 (−17) |
12 (−11) |
25 (−4) |
37 (3) |
45 (7) |
53 (12) |
52 (11) |
34 (1) |
19 (−7) |
13 (−11) |
4 (−16) |
−3 (−19) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.68 (17.3) |
0.58 (14.7) |
0.41 (10.4) |
0.62 (15.7) |
1.59 (40.4) |
2.21 (56.1) |
3.39 (86.1) |
3.12 (79.2) |
2.48 (63) |
1.51 (38.4) |
0.57 (14.5) |
0.51 (13) |
17.67 (448.8) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.8 (2) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.1 (0.3) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.4 (1) |
0.3 (0.8) |
2.1 (5.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.001 in) | 3.59 | 2.99 | 2.22 | 2.74 | 4.51 | 7.30 | 9.60 | 8.88 | 7.64 | 4.77 | 2.90 | 2.83 | 60.19 |
| Source: Western Regional Climate Center, Desert Research Institute[6] | |||||||||||||
Wildlife
- Ornithology
- Birds of the Chisos Mountains include 81 total known species that live within six different plant associations.[7] The six plant associations along with the number of known species within them include: the Arroyo-Mesquite-Acacia Association (31 species), the Lechuguilla-Creosotebush-Cactus Association (13 species), the Sotol-Grass Association (32 species), the Deciduous Woodland Association (42 species), the Pinyon-Juniper-Oak Association (32 Species), and the Cypress-Pine-Oak Association (24 species).[7]
- Myrmecology
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chisos Mountains. |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kohout, Martin Donell. "Chisos Mountains". Handbook of Texas Online. Retrieved 2013-07-02.
- 1 2 "Chisos Mountains Backcountry Campsites" (PDF). National Park Service U.S. Department of the Interior. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ↑ David Elkowitz (February 18, 2011). "Proposal to Open Boquillas Crossing". National Park Service. Retrieved 2013-07-02.
- ↑ "Chisos Mountains". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ↑ "US COOP Station Map". Western Regional Climate Center, Desert Research Institute. Retrieved May 6, 2015.
- ↑ "CHISOS BASIN, TEXAS (411715), Period of Record Monthly Climate Summary". Western Regional Climate Center, Desert Research Institute. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- 1 2 Wauer, Roland H. (July 23, 1971). "Ecological Distribution of Birds of the Chisos Mountains, Texas". The Southwestern Naturalist. 16 (1). JSTOR 3670095.
- ↑ Van Pelt, Arnold (May 20, 1983). "Ants of the Chisos Mountains, Texas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)". The Southwestern Naturalist. 28 (2). JSTOR 3671381.