Carbon–carbon bond
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms.[1] The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp3-hybridized orbitals, but single bonds formed between carbon atoms with other hybridizations do occur (e.g. sp2 to sp2). In fact, the carbon atoms in the single bond need not be of the same hybridization. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds in compounds called alkenes or triple bonds in compounds called alkynes. A double bond is formed with an sp2-hybridized orbital and a p-orbital that is not involved in the hybridization. A triple bond is formed with an sp-hybridized orbital and two p-orbitals from each atom. The use of the p-orbitals forms a pi bond.
Chains and branching
Carbon is one of the few elements that can form long chains of its own atoms, a property called catenation. This coupled with the strength of the carbon–carbon bond gives rise to an enormous number of molecular forms, many of which are important structural elements of life, so carbon compounds have their own field of study: organic chemistry.
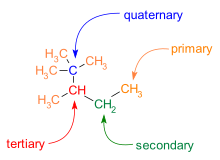
Branching is also common in C−C skeletons. Different carbon atoms can be described by the number of carbon neighbors they each have:
- Primary carbon: one carbon neighbor
- Secondary carbon: two carbon neighbors
- Tertiary carbon: three carbon neighbors
- Quaternary carbon: four carbon neighbors
In "structurally complex organic molecules", it is the three-dimensional orientation of the carbon–carbon bonds at quaternary loci which dictates the shape of the molecule.[2] Further, quaternary loci are found in many biologically active small molecules, such as cortisone and morphine.[2]
Synthesis
Carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions are organic reactions in which a new carbon–carbon bond is formed. They are important in the production of many man-made chemicals such as pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Some examples of reactions which form carbon–carbon bonds are aldol reactions, Diels–Alder reaction, the addition of a Grignard reagent to a carbonyl group, a Heck reaction, a Michael reaction and a Wittig reaction.
The directed synthesis of desired three-dimensional structures for tertiary carbons was largely solved during the late 20th century, but the same ability to direct quaternary carbon synthesis did not start to emerge until the first decade of the 21st century.[2]
Bond strengths and lengths
Relative to most bonds, a carbon–carbon bond is very strong.[3]
| C–C bond | Molecule | Bond dissociation energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| CH3−CH3 | ethane | 90 |
| C6H5−CH3 | toluene | 102 |
| C6H5−C6H5 | biphenyl | 114 |
| CH3C(O)−CH3 | acetone | 84 |
| CH3−CN | acetonitrile | 136 |
| CH3−CH2OH | ethanol | 88 |
The values given above represent bond dissociation energies that are commonly encountered; occasionally, outliers may deviate drastically from this range. In the highly congested hexakis(3,5-di-tert-butyl)ethane, the bond dissociation energy to form the stabilized triarylmethyl radical is only 8 kcal/mol.[4] On the opposite extreme, the central carbon–carbon single bond of diacetylene is very strong at 160 kcal/mol, as the single bond joins two carbons of sp hybridization.[5] Carbon–carbon multiple bonds are generally stronger; the double bond of ethylene and triple bond of acetylene have been determined to have bond dissociation energies of 174 and 230 kcal/mol, respectively.[6]
A typical carbon–carbon single bond has a length of 154 pm, while a typical double bond and triple bond are 134 pm and 120 pm, respectively. Also a consequence of its severe steric congestion, hexakis(3,5-di-tert-butyl)ethane has a greatly elongated central bond with a length of 167 nm. On the other hand, a very short triple bond of 115 pm has been observed for the iodonium species [HC≡C–I+Ph][CF3SO3–], due to the strongly electron-withdrawing iodonium moiety.[7]
See also
- An extensive list is presented here: list of carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions
- The chemistry of carbon bonded to other elements in the periodic table:
| Compounds of carbon with other elements in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Dembicki, Harry (2016-10-06). Practical Petroleum Geochemistry for Exploration and Production. Elsevier. p. 7. ISBN 9780128033517.
- 1 2 3 Quasdorf, Kyle W.; Overman, Larry E. (2014). "Review: Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of quaternary carbon stereocentres". Nature (paper). 516 (7530): 181–191. Bibcode:2014Natur.516..181Q. doi:10.1038/nature14007. PMC 4697831. PMID 25503231.
- ↑ Yu-Ran Luo and Jin-Pei Cheng "Bond Dissociation Energies" in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition.
- ↑ Rösel, Sören; Balestrieri, Ciro; Schreiner, Peter R. (2017). "Sizing the role of London dispersion in the dissociation of all-meta tert-butyl hexaphenylethane". Chemical Science. 8 (1): 405–410. doi:10.1039/c6sc02727j. ISSN 2041-6520. PMC 5365070. PMID 28451185.
- ↑ "NIST Webbook".
- ↑ Blanksby, Stephen J.; Ellison, G. Barney (April 2003). "Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Molecules". Accounts of Chemical Research. 36 (4): 255–263. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.616.3043. doi:10.1021/ar020230d. ISSN 0001-4842. PMID 12693923.
- ↑ 1927-, Streitwieser, Andrew, (1992). Introduction to organic chemistry. Heathcock, Clayton H., 1936-, Kosower, Edward M. (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. p. 574. ISBN 978-0139738500. OCLC 52836313.