Axel jump
| Figure skating element | |
|---|---|
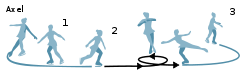 A single Axel jump. | |
| Element name: | Axel jump |
| Alternative name: | Axel Paulsen jump |
| Scoring abbreviation: | A |
| Element type: | Jump |
| Take-off edge: | Forward outside |
| Landing edge: | Back outside |
| Inventor: | Axel Paulsen |
The Axel is a figure skating jump with a forward take off. It is named after Norwegian figure skater Axel Paulsen who, in 1882, was the first skater to perform the jump. Compared to other common figure skating jumps, an Axel has an extra ½ rotation in the air because of its forward take off. Most skaters perform the jump with counterclockwise rotation, taking off from the left forward outside edge and landing on the right back outside edge. The Axel can also be done as a double jump with 2½ rotations, or as a triple jump with 3½ rotations, or a quadruple Axel with 4½ rotations, but no skater has yet accomplished a quadruple Axel in competition.
Value in competition
The Axel jump is considered the most technically difficult jump among six types of jumps in single figure skating. According to ISU judging system, a triple Axel jump has a base value of 8.5 points, while a double Axel has that of 3.3 points. This makes a triple Axel the highest base-valued triple jump, above other triple jumps such as the triple Lutz (6 points), triple flip (5.3 points), triple loop (5.1 points), triple Salchow (4.4 points), and triple toe loop (4.3 points).[1]
Axel jumps comparison
| Jumps (rotation) | Base Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| single Axel | 1.1 | Senior skaters normally do not perform this jump. |
| double Axel | 3.3 | Most female skaters perform this. |
| triple Axel | 8.5 | Male skaters regularly perform this. Only nine female skaters have landed this in international competitions. |
| quadruple Axel | 15.0 | This jump has not been attempted in a formal competition. |
Triple jumps comparison
| Jumps (types) | Base Value |
|---|---|
| triple Axel | 8.5 |
| triple Lutz | 6.0 |
| triple flip | 5.3 |
| triple loop | 5.1 |
| triple Salchow | 4.4 |
| triple toeloop | 4.3 |
Axel technique
To perform an Axel, the skater typically approaches the jump on a right back outside edge in a strongly held check position before stepping on a left forward outside edge. He or she vaults over the toe pick of the left skate and "steps up" into the jump with the right leg. The skater crosses the left foot in front of the right, which is known as a back spin position (similar to the loop jump), to bring the center of rotation around the right side of the body. This act is often described as a weight shift in the air. Uncrossing the legs during the landing checks the rotation and allows the skater to flow out of the jump with good speed. Most skaters do this when they think they are not going to land the jump and downgrade the jump.
It is common for skaters to skid the forward take off edge, especially on double and triple Axel jumps, rather than vaulting directly off a clean edge. The skid helps the blade grip the ice on the take off, and is considered an acceptable technique as long as the skid does not make the skater pre-rotate the jump or take off the back of the blade. When the skater makes a mistake in the timing of the jump so that the blade slips off the edge instead of gripping the ice, the result is called a "waxel," often resulting in a fall.
Computerized bio-mechanical studies of skaters performing double and triple Axel jumps have shown skaters typically do not achieve as much height on triple Axel jumps as they do on double Axel jumps. This may seem counter-intuitive because higher jumps ought to give a skater more time to complete the rotation. Instead, during the triple Axel, skaters do not take a big "step up" so that they can pull into the rotation position more quickly.
Axel history
Men
- Axel Paulsen (NOR) was the first skater to perform the jump named after him, in 1882. He performed this feat wearing speed skates rather than figure skates.
- Dick Button (USA) was the first skater credited with a double Axel jump in competition. He performed this at the 1948 Winter Olympics, although footage of the jump shows that it may have been underrotated. Button's coach Gus Lussi was responsible for developing the modern Axel jump technique.
- Vern Taylor (CAN) was the first to land a triple Axel in competition at the 1978 World Figure Skating Championships. It has since become a standard jump for male competitors, but it is rare for female skaters to successfully land them or attempt them in a competition setting.
- Brian Orser (CAN) was the first skater to put two triple Axel jumps in the same program and the first to accomplish this at the World level at the 1987 World Figure Skating Championships; since he also landed one in the short program, he additionally was the first skater to land three triple Axel jumps in the same competition.
Women
- In the early years of skating, jumping was the exclusive domain of men. Sonja Henie is generally acknowledged as the first female skater to perform an Axel jump. Today, however, her Axel technique (preserved in her many films) would be considered very poor, since her jumps were badly pre-rotated without a "step up", giving them more the character of a jumped spin.
- In 1953, Carol Heiss was the first woman to perform a double Axel.
- Thirty-five years later, Midori Ito (JPN) became the first woman to land the triple Axel jump in competition, when she first performed it at the 1988 NHK Trophy. Since then, eight other women (Tonya Harding (USA), Yukari Nakano (JPN), Ludmila Nelidina (RUS), Mao Asada (JPN), Elizaveta Tuktamysheva (RUS), Rika Kihira (JPN), Mirai Nagasu (USA), and Alysa Liu (USA)) have succeeded in completing the jump in international competition, while another woman, Kimmie Meissner (USA), first completed the jump at the 2005 U.S. Figure Skating Championships.
- Midori Ito (JPN), Mao Asada (JPN), and Mirai Nagasu (USA) are the only women who have landed triple Axel jumps in Olympic games.
- Tonya Harding (USA) was the first woman to land two triple Axel jumps in the same competition (1991 Skate America).
- Mao Asada (JPN) was the first junior ladies competitor in history to land the triple Axel jump successfully, at the 2004–05 Junior Grand Prix Final. This feat was next accomplished by fellow Japanese skater Rika Kihira who landed the jump at the 2016 JGP Ljubljana.
- Mao Asada (JPN) was the first woman to land three triple Axel jumps in the same competition (2010 Winter Olympics).
- Elizaveta Tuktamysheva (RUS) is the first woman to land four triple jumps in a short program including a triple Axel: 3A, 3Lz, 3T-3T (2015 World Championships)
- Rika Kihira (JPN) was the first woman to land a triple Axel-triple toeloop combination (2017-2018 JGP Final).
- Mirai Nagasu (USA) landed the triple Axel jump at the 2017 Rostelecom Cup in Moscow, Russia. She was the first female athlete from the United States ever to land the triple Axel jump during an Olympic competition, at the 2018 Winter Olympics in Pyeongchang, South Korea.[2]
- Alysa Liu (USA) landed the triple Axel jump at the 2018 CS Asian Figure Skating Trophy, making her the youngest female athlete in history to land the jump successfully in international competition.
Pairs
- Rena Inoue and John Baldwin, Jr. (USA), became the first pair to perform a throw triple Axel in competition at the 2006 U.S. Figure Skating Championships, and then made Olympic and ISU history by landing it again at the 2006 Winter Olympics.
Axel variations
The jump with half a rotation from forward outside to backward outside is called a waltz jump or a three jump in some countries. Any other rotational jump with a forward takeoff is generally considered to be a variation of the Axel. These include:
- A delayed Axel is similar to a regular Axel, but the skater takes a very open body position on the ascent of the jump before pulling in to complete the rotation, in a similar way to the saut de basque in ballet. Robin Cousins mastered this variation.
- In an open Axel, the skater maintains an open body position throughout the jump without delaying the rotation.
- A tuck Axel has the same take-off and landing as a regular Axel, but the skater pulls the legs up into a tuck or sit spin position in the air.
- A half Axel is a jump with a regular Axel take-off but with only one rotation, landed forward (typically on the left toe pick and right forward inside edge, for a counterclockwise jump). This jump is sometimes also called a bell jump or a once around. This jump can also be used as a stage between the waltz jump and the single axel.
- A one-foot Axel is a 1½ rotation jump with a regular Axel take-off that lands on the back inside edge of the takeoff foot—the left foot, for a counterclockwise jump. This jump is sometimes known (especially in artistic roller skating) as a Colledge, after 1937 World Champion Cecilia Colledge. In the late 1980s, Jill Trenary made this jump as the first half of a combination (the other half being the triple Salchow) her signature move.
- An inside Axel is a 1½ rotation jump that takes off from a forward inside edge and lands on the back outside edge of the same foot – the right foot, for a counterclockwise jump. This jump is sometimes known as a Böckl, after its inventor Willy Böckl.
In addition, an Axel entrance can be used as a take-off for flying spins. An Axel sit spin is also known as a flying reverse sit spin, and is essentially an Axel jump landed in a back sit spin. Rarely, skaters may also attempt a double Axel sit spin. In a flying open Axel sit spin, also known as a death drop, the skater achieves an almost horizontal position in the air (by kicking the takeoff leg backwards and to the side, instead of bringing it forward) before landing in a back sit spin.
In general, the International Skating Union's new ISU Judging System discourages skaters from including variety jumps such as Axel variants in their competitive programs, because they count towards the maximum number of permitted jumps but carry a much lower point value than any double or triple jump that the skater could perform instead. Likewise, the IJS treats all flying spins equally and does not reward the additional difficulty of a double Axel sit spin.
A toe Axel is not a real jump but is instead the name given to a flawed double toe loop jump.
References
- ↑ "Sports Briefing". Nytimes.com. 10 June 2004. Retrieved 8 January 2015.
- ↑ https://www.nytimes.com/2018/02/12/sports/nagasu-triple-axel-olympics.html
- Ellen Labrecque, The Science of a Triple Axel. Cherry Lake Publishing, 2016. ISBN 978-1-63362-677-5.
- John Misha Petkevich, Sports Illustrated Figure Skating: Championship Techniques. Sports Illustrated, 1989. ISBN 0-452-26209-7.
- Nancy Kerrigan, Artistry on Ice: Figure Skating Skills and Style. Human Kinetics, 2003. ISBN 0-7360-3697-0.
- Josef Dědič, Single Figure Skating for Beginners and Champions. Olympia, 1982.
- United States Figure Skating Association Media Guide.