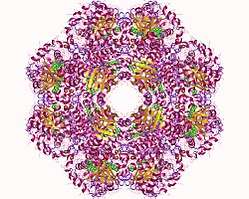
Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein
Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTPA gene.[5][6][7]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000137561 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000073988 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Ouahchi K, Arita M, Kayden H, Hentati F, Ben Hamida M, Sokol R, Arai H, Inoue K, Mandel JL, Koenig M (1995). "Ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency is caused by mutations in the alpha-tocopherol transfer protein". Nat Genet. 9 (2): 141–145. doi:10.1038/ng0295-141. PMID 7719340.
- ↑ Arita M, Sato Y, Miyata A, Tanabe T, Takahashi E, Kayden HJ, Arai H, Inoue K (1995). "Human alpha-tocopherol transfer protein: cDNA cloning, expression and chromosomal localization". Biochem J. 306 (2): 437–443. PMC 1136538. PMID 7887897.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TTPA tocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ataxia (Friedreich-like) with vitamin E deficiency)".
Further reading
- Gotoda T, Arita M, Arai H, et al. (1995). "Adult-onset spinocerebellar dysfunction caused by a mutation in the gene for the alpha-tocopherol-transfer protein". N. Engl. J. Med. 333 (20): 1313–8. doi:10.1056/NEJM199511163332003. PMID 7566022.
- Ben Hamida C, Doerflinger N, Belal S, et al. (1994). "Localization of Friedreich ataxia phenotype with selective vitamin E deficiency to chromosome 8q by homozygosity mapping". Nat. Genet. 5 (2): 195–200. doi:10.1038/ng1093-195. PMID 8252047.
- Hentati A, Deng HX, Hung WY, et al. (1996). "Human alpha-tocopherol transfer protein: gene structure and mutations in familial vitamin E deficiency". Ann. Neurol. 39 (3): 295–300. doi:10.1002/ana.410390305. PMID 8602747.
- Cavalier L, Ouahchi K, Kayden HJ, et al. (1998). "Ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency: heterogeneity of mutations and phenotypic variability in a large number of families". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62 (2): 301–10. doi:10.1086/301699. PMC 1376876. PMID 9463307.
- Schuelke M, Mayatepek E, Inter M, et al. (1999). "Treatment of ataxia in isolated vitamin E deficiency caused by alpha-tocopherol transfer protein deficiency". J. Pediatr. 134 (2): 240–4. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(99)70424-5. PMID 9931538.
- Cellini E, Piacentini S, Nacmias B, et al. (2003). "A family with spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 expansion and vitamin E deficiency ataxia". Arch. Neurol. 59 (12): 1952–3. doi:10.1001/archneur.59.12.1952. PMID 12470185.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Meier R, Tomizaki T, Schulze-Briese C, et al. (2003). "The molecular basis of vitamin E retention: structure of human alpha-tocopherol transfer protein". J. Mol. Biol. 331 (3): 725–34. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00724-1. PMID 12899840.
- Min KC, Kovall RA, Hendrickson WA (2004). "Crystal structure of human alpha-tocopherol transfer protein bound to its ligand: implications for ataxia with vitamin E deficiency". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (25): 14713–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.2136684100. PMC 299775. PMID 14657365.
- Morley S, Panagabko C, Shineman D, et al. (2004). "Molecular determinants of heritable vitamin E deficiency". Biochemistry. 43 (14): 4143–9. doi:10.1021/bi0363073. PMID 15065857.
- Müller-Schmehl K, Beninde J, Finckh B, et al. (2004). "Localization of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein in trophoblast, fetal capillaries' endothelium and amnion epithelium of human term placenta". Free Radic. Res. 38 (4): 413–20. doi:10.1080/10715760310001659611. PMID 15190938.
- Mariotti C, Gellera C, Rimoldi M, et al. (2004). "Ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency: neurological phenotype, clinical follow-up and novel mutations in TTPA gene in Italian families". Neurol. Sci. 25 (3): 130–7. doi:10.1007/s10072-004-0246-z. PMID 15300460.
- Wolf AT, Medcalf RL, Jern C (2005). "The t-PA -7351C>T enhancer polymorphism decreases Sp1 and Sp3 protein binding affinity and transcriptional responsiveness to retinoic acid". Blood. 105 (3): 1060–7. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-12-4383. PMID 15466927.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Klein RL, Semler AJ, Baynes JW, et al. (2005). "Glycation does not alter LDL-induced secretion of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from human aortic endothelial cells". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1043: 379–89. doi:10.1196/annals.1333.044. PMID 16037259.
- Qian J, Atkinson J, Manor D (2006). "Biochemical consequences of heritable mutations in the alpha-tocopherol transfer protein". Biochemistry. 45 (27): 8236–42. doi:10.1021/bi060522c. PMID 16819822.
- Attia J, Thakkinstian A, Wang Y, et al. (2007). "The PAI-1 4G/5G gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke: an association study and meta-analysis". Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases : the official journal of National Stroke Association. 16 (4): 173–9. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2007.03.002. PMID 17689414.
External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Ataxia with Vitamin E Deficiency
- OMIM entries on Ataxia with Vitamin E Deficiency
- Human TTPA genome location and TTPA gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.