8P/Tuttle
|
| |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Horace Parnell Tuttle |
| Discovery date | January 5, 1858 |
| Alternative designations |
1790 II; 1858 I; 1871 III; 1885 IV; 1899 III; 1912 IV; 1926 IV; 1939 X; 1967 V; 1980 XIII; 1994 XV |
| Orbital characteristics A | |
| Epoch | January 15, 2008 |
| Aphelion | 10.376340 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.027132 AU |
| Semi-major axis | 5.701737 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.819856 |
| Orbital period | 13.6 a[1] |
| Inclination | 54.9830° |
| Earth MOID | 0.095 AU (14,200,000 km)[2] |
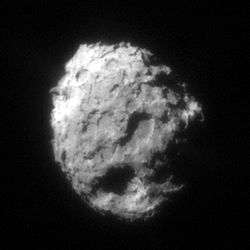
| Dimensions | 4.5 km contact binary[2] |
| Last perihelion | January 27, 2008 |
| Next perihelion | August 27, 2021[3] |
8P/Tuttle (also known as Tuttle's Comet or Comet Tuttle) is a periodic comet in the Solar System. It fits the classical definition of a Jupiter-family comet with an orbital period of less than 20 years, but does not fit the modern definition of (2 < TJupiter< 3).[2] Perihelion was late January 2008, and as of February was visible telescopically to Southern Hemisphere observers in the constellation Eridanus. On December 30, 2007 it was in close conjunction with spiral galaxy M33. On January 1, 2008 it passed Earth at a distance of 0.25282 AU (37,821,000 km; 23,501,000 mi).[2]
Comet 8P/Tuttle is responsible for the Ursid meteor shower in late December.[4]
Predictions that the 2007 Ursid meteor shower could be expected to be stronger than usual due to the return of the comet,[5] did not appear to materialize, as counts were in the range of normal distribution.
Contact binary
Radar observations of Comet Tuttle in January 2008 by the Arecibo Observatory show it to be a contact binary.[6][7] The comet nucleus is estimated at about 4.5 km in diameter, using the equivalent diameter of a sphere having a volume equal to the sum of a 3 km and 4 km sphere.[2]
Additional images
 Tuttle on December 3, 2007 from Mount Laguna, California
Tuttle on December 3, 2007 from Mount Laguna, California- About 1.2 degrees from M33 on December 30, 2007.

Footnotes
- ↑ Ley, Willy (September 1968). "Mission to a Comet". For Your Information. Galaxy Science Fiction. pp. 101–110.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 8P/Tuttle". NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 6 June 2008. Retrieved 25 February 2010.
- ↑ Kinoshita, Kazuo (24 January 2008). "8P/Tuttle". Comet Orbits.
- ↑ "Meteor Streams". NASA.gov. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ↑ Jenniskens, P.; Lyytinen, E.; Nissinen, M.; Yrjölä, I.; Vaubaillon, J. (December 2007). "Strong Ursid shower predicted for 2007 December 22" (PDF). WGN, Journal of the International Meteor Organization. 35 (6): 125–133. Bibcode:2007JIMO...35..125J.
- ↑ Schilling, Govert (14 October 2008). "Comet Tuttle's Split Personality". Science. Retrieved 25 October 2008.
- ↑ Harmon, J. K.; Nolan, M. C.; Howell, E. S.; Giorgini, J. D. (2008). Comet 8P/Tuttle: Arecibo Radar Observations of the First Bilobate Comet (PDF). 10th Asteroids, Comets, Meteors. 13–18 July 2008. Baltimore, Maryland. Lunar and Planetary Institute.
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java) / Horizons Ephemeris
- 8P/Tuttle – Seiichi Yoshida @ aerith.net
- 8P at Kronk's Cometography
- 8P/Tuttle time sequence
- Comet Tuttle Seen To Be Returning
- Comet 8P/Tuttle. Canary Islands, Tenerife. 06.01.2008
- NASA Orbital Diagram
| Numbered comets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Previous 7P/Pons–Winnecke |
8P/Tuttle | Next 9P/Tempel |