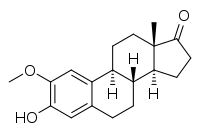
2-Methoxyestrone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(8R,9S,13S,14S)-3-Hydroxy-2-methoxy-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one | |
| Other names
2-ME1; 2-MeOE1; 2-MeO-E1; 2-Hydroxyestrone 2-methyl ether; 2-Methoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-ol-17-one; 2-Methoxy-3-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H24O3 | |
| Molar mass | 300.40 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Methoxyestrone (2-ME1) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estrone that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 2-hydroxyestrone.[1][2][3] Unlike estrone but similarly to 2-hydroxyestrone and 2-methoxyestradiol, 2-methoxyestrone has very low affinity for the estrogen receptor and lacks significant estrogenic activity.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/hmdb00010
- ↑ Hemnes AR (16 December 2015). Gender, Sex Hormones and Respiratory Disease: A Comprehensive Guide. Humana Press. pp. 32–. ISBN 978-3-319-23998-9.
- ↑ Lauritzen C, Studd JW (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 378–379. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ↑ Bhavnani BR, Nisker JA, Martin J, Aletebi F, Watson L, Milne JK (2000). "Comparison of pharmacokinetics of a conjugated equine estrogen preparation (premarin) and a synthetic mixture of estrogens (C.E.S.) in postmenopausal women". Journal of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation. 7 (3): 175–83. doi:10.1016/s1071-5576(00)00049-6. PMID 10865186.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.