1979 Tour de France
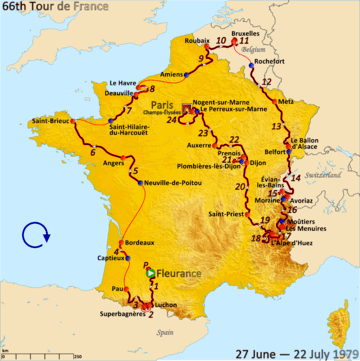 Route of the 1979 Tour de France | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dates | 27 June – 22 July | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stages | 24 + Prologue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance | 3,765 km (2,339 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Winning time | 103h 06' 50" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1979 Tour de France was the 66th edition of the Tour de France, one of cycling's Grand Tours. It took place between 27 June and 22 July, with 24 stages covering a distance of 3,765 km (2,339 mi). It was the only tour to finish at Alpe d'Huez twice. It was won by Bernard Hinault, who also won the points classification, and whose team won both team classifications. Remarkably Hinault and second place finisher Joop Zoetemelk finished nearly a half hour ahead of the other GC Contenders, and in modern history this was the only time the Yellow Jersey was challenged on the ride into Paris. The mountains classification was won by Giovanni Battaglin, and the young rider classification was won by Jean-René Bernaudeau.
Teams
The following 15 teams each sent 10 cyclists, for a total of 150.[1][2]
The teams entering the race were:[1]
Pre-race favourites
The big favourite was Hinault; not only was he the defending champion, but the large number of time trials made the race especially suited for him.[3] The only cyclist thought to be able to seriously challenge Hinault was Zoetemelk, the runner-up of the previous edition.[3]
Route and stages
The route for the 1979 Tour was revealed in November 1978. It was the shortest course since 1904, but with many climbs it was still considered hard.[4]
Since 1974, the Tour had always been composed of 22 stages, with some of them run as split stages. Following the riders' strike in the 1978 Tour against these split stages, the 1979 Tour included no split stages. To compensate for this, the total number of stages increased to 24.[3][5] The Tour had one rest day, in Les Menuires.[6]
| Stage | Date | Course | Distance | Type | Winner | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 27 June | Fleurance | 5 km (3.1 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 1 | 28 June | Fleurance to Luchon | 225 km (140 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 2 | 29 June | Luchon to Superbagnères | 24 km (15 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 3 | 30 June | Luchon to Pau | 180 km (110 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 4 | 1 July | Captieux to Bordeaux | 87 km (54 mi) | Team time trial | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | |
| 5 | 2 July | Neuville-de-Poitou to Angers | 145 km (90 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 6 | 3 July | Angers to Saint-Brieuc | 239 km (149 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 7 | 4 July | Saint-Hilaire-du-Harcouët to Deauville | 158 km (98 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 8 | 5 July | Deauville to Le Havre | 90 km (56 mi) | Team time trial | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | |
| 9 | 6 July | Amiens to Roubaix | 201 km (125 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 10 | 7 July | Roubaix to Brussels (Belgium) | 124 km (77 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 11 | 8 July | Brussels (Belgium) | 33 km (21 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 12 | 9 July | Rochefort (Belgium) to Metz | 193 km (120 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 13 | 10 July | Metz to Ballon d'Alsace | 202 km (126 mi) | Hilly stage | ||
| 14 | 11 July | Belfort to Évian-les-Bains | 248 km (154 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 15 | 12 July | Évian-les-Bains to Morzine Avoriaz | 54 km (34 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 16 | 13 July | Morzine Avoriaz to Les Menuires | 201 km (125 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 14 July | Les Menuires | Rest day | ||||
| 17 | 15 July | Les Menuires to Alpe d'Huez | 167 km (104 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 18 | 16 July | Alpe d'Huez | 119 km (74 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 19 | 17 July | Alpe d'Huez to Saint-Priest | 162 km (101 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 20 | 18 July | Saint-Priest to Dijon | 240 km (150 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 21 | 19 July | Dijon | 49 km (30 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 22 | 20 July | Dijon to Auxerre | 189 km (117 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 23 | 21 July | Auxerre to Nogent-sur-Marne | 205 km (127 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 24 | 22 July | Le Perreux-sur-Marne to Paris (Champs-Élysées) | 180 km (110 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| Total | 3,765 km (2,339 mi)[8] | |||||
Race overview
.jpg)
The prologue was won by Knetemann; Zoetemelk and Hinault both followed at four seconds.[3] The first stage took the riders immediately into the mountains. Bittinger won the stage, and the favourites stayed together.[3] The second stage was run as an individual climb time trial. Hinault won it, and became the new leader, with Zoetemelk and Agostinho almost one minute behind. Hinault also won the third stage, without gaining time on his rivals.[3] In the fifth stage, the team time trial, Hinault lost time, but stayed the leader by 12 seconds on Zoetemelk. The Peugeot team had selected the wrong tires, according to their team leader Hennie Kuiper; he punctured five times in that stage, and if he had been 31 seconds faster he would have been the race leader.[3]
In the ninth stage, over the cobbles also used in Paris–Roubaix,[9] Zoetemelk had joined an escape, and Hinault had to chase him. Hinault had to stop to replace a flat tire, was stopped by strikers, and finished more than three minutes behind Zoetemelk, losing the lead to him.[3] Hinault was not happy that the other cyclists escaped while he had a flat tire, and warned that "there are some riders who will suffer plenty after what happened today".[10] Five-time winner Jacques Anquetil was pleased with Hinault's performance, and predicted that Hinault won the Tour in that stage, because he had kept his losses limited.[10]
Hinault won back 36 seconds in the time trial of stage 11, and more than two minutes in the mountain time trial of stage 15, thus becoming the new leader.[3] Hinault won some more time in the next stages in bonification sprints. In the eighteenth stage, Zoetemelk beat Hinault, and won back 47 seconds. That eighteenth stage was scheduled to cross the Izoard, but the course was changed in the last minute.[3]
Before the last stage, Hinault had an advantage of more than three minutes on Zoetemelk, and almost 25 minutes on the next cyclists. Traditionally, the last stage is run at a slow pace, because the winners are already known. But Zoetemelk attacked, and Hinault chased him. Together they stayed away from the rest, and Hinault beat Zoetemelk in the sprint, winning his seventh stage of the race.[3] Besides the struggle for the first place, there was also a struggle for the last place, the lanterne rouge. After the 20th stage, Philippe Tesnière was last in the general classification, with Gerhard Schönbacher before him.[11] Tesnière had already finished last in the 1978 Tour de France, so he was aware of the publicity associated with being the lanterne rouge.
In the 21st stage, Tesnière therefore rode extra slow. Hinault took 1 hour, 8 minutes and 53 seconds to win the time trial, Schönbacher used 1 hour, 21 minutes and 52 seconds,[12] while Tesniere rode it in 1 hour, 23 minutes and 32 seconds; both were slower than all other cyclists.[13] Tesnière's time was more than 20% slower than Hinault's, which meant that he had missed the time cut, and was taken out of the race.[13] When Schönbacher was near the finish of the last stage, he stopped and kissed the road, before he crossed the finishline.[14]
Doping
For the first time in the Tour de France, doping tests were able to find anabolicals. The doping tests were performed by Manfred Donike in his lab in Köln.[15]
After the 17th stage, it was announced that Giovanni Battaglin, leader of the mountains classification, had tested positive after the 13th stage. He received a penalty of 10 minutes in the general classification, and lost all mountain points that he collected during that 13th stage, and an extra penalty of 10 points.[16] Frans Van Looy and Gilbert Chaumaz also tested positive for doping.[17]
After the race finished, Joop Zoetemelk was found to have used doping, which he later admitted to. Zoetemelk was fined with 10 minutes in the general classification, but kept his second place.[18]
Classification leadership
There were several classifications in the 1979 Tour de France, four of them awarding jerseys to their leaders. The most important was the general classification, calculated by adding each cyclist's finishing times on each stage. The cyclist with the least accumulated time was the race leader, identified by the yellow jersey; the winner of this classification is considered the winner of the Tour.[19] In previous years, the team time trials only counted for the team classification, and not for the general classification, except for the bonifications. From 1979 on, the team trial also counted for the general classification.[3]
Additionally, there was a points classification, where cyclists got points for finishing among the best in a stage finish, or in intermediate sprints. The cyclist with the most points lead the classification, and was identified with a green jersey.[19]
There was also a mountains classification. The organisation had categorized some climbs as either hors catégorie, first, second, third, or fourth-category; points for this classification were won by the first cyclists that reached the top of these climbs first, with more points available for the higher-categorized climbs. The cyclist with the most points lead the classification, and was identified with a polkadot jersey.[19]
Another classification was the young rider classification, decided the same way as the general classification.[20] Since 1975, the young rider classification had been contested by neo-professionals: cyclists aged 23 years or younger, or in their first two years as a professional cyclist. This changed in 1979: it was open for cyclists aged 24 or younger at 1 January.[20] The leader wore a white jersey.[21]
The fifth individual classification was the intermediate sprints classification. This classification had similar rules as the points classification, but only points were awarded on intermediate sprints. In 1979, this classification had no associated jersey.[22] In stages 6, 12, 14, 20, 22 and 23, there was a new system for time bonuses. In the intermediate sprints in these stages, the first three cyclists received time bonuses of 10, 6 and 3 seconds; a classification of these time bonuses was made on each of these stages, and the first three of this classification received extra time bonuses of 20, 10 and 5 seconds.[20]
The team classification, in 1978 calculated with the times of the five best cyclists per team, was in 1979 calculated with the times of the best four cyclists per team.[20] The riders in the team that lead this classification wore yellow caps.[23] There was also a team points classification. After each stage, the stage rankings of the best three cyclists per team were added, and the team with the least total lead this classification, and were identified by green caps.[24] Inoxpran, Teka, Magniflex and Splendor–Euro Soap did not finish the race with four or more cyclists, so they were not eligible for the team classification. Magniflex and Splendor–Euro Soap did not finish the race with three or more cyclists, so they were not eligible for the team points classification.
In addition to the classifications above, there were several minor classifications; in total the 1979 Tour de France contained sixteen competitions, each with its own sponsor.[25] The combativity award was initially given to Joop Zoetemelk;[26] he was later disqualified after his doping offence (see below) and Hennie Kuiper received the award.[1]
Final standings
| Legend | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Denotes the winner of the general classification | Denotes the winner of the points classification | ||
| Denotes the winner of the mountains classification | Denotes the winner of the young rider classification | ||
General classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane | 103h 06' 50" | |
| 2 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | + 3' 07" | |
| 3 | Flandria–Ça va seul | + 26' 53" | |
| 4 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | + 28' 02" | |
| 5 | Renault–Gitane | + 32' 43" | |
| 6 | Inoxpran | + 38' 12" | |
| 7 | DAF Trucks–Aida | + 38' 38" | |
| 8 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 39' 06" | |
| 9 | Kas–Campagnolo | + 40' 38" | |
| 10 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | + 44' 35" |
Points classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane | 253 | |
| 2 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | 157 | |
| 3 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 109 | |
| 4 | Flandria–Ça va seul | 104 | |
| 5 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 79 | |
| 6 | Kas–Campagnolo | 67 | |
| 7 | Splendor–Euro Soap | 66 | |
| 8 | DAF Trucks–Aida | 65 | |
| 9 | Inoxpran | 64 | |
| 10 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | 61 |
Mountains classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inoxpran | 239 | |
| 2 | Renault–Gitane | 196 | |
| 3 | La Redoute–Motobécane | 158 | |
| 4 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 141 | |
| 5 | Kas–Campagnolo | 118 | |
| 6 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 108 | |
| 7 | Flandria–Ça va seul | 96 | |
| 8 | Renault–Gitane | 67 | |
| 9 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 67 | |
| 10 | Flandria–Ça va seul | 49 |
Young rider classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane | 103h 39' 33" | |
| 2 | Kas–Campagnolo | + 7' 55" | |
| 3 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 26' 30" | |
| 4 | DAF Trucks–Aida | + 59' 08" |
Intermediate sprints classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kas–Campagnolo | 93 | |
| 2 | Renault–Gitane | 82 | |
| 3 | Renault–Gitane | 53 | |
| 4 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | 31 | |
| 5 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 30 |
Team classification
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane | 414h 45' 46" |
| 2 | Flandria–Ça va seul | + 10' 29" |
| 3 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 15' 22" |
| 4 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | + 23' 12" |
| 5 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | + 40' 50" |
| 6 | Kas–Campagnolo | + 1h 18' 51" |
| 7 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | + 2h 20' 07" |
| 8 | La Redoute–Motobécane | + 2h 29' 24" |
| 9 | Fiat | + 3h 31' 12" |
| 10 | DAF Trucks–Aida | + 3h 39' 46" |
Team points classification
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane | 1008 |
| 2 | IJsboerke–Warncke Eis | 1057 |
| 3 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 1165 |
| 4 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 1353 |
| 5 | Flandria–Ça va seul | 1407 |
| 6 | La Redoute–Motobécane | 1558 |
| 7 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 1602 |
| 8 | Kas–Campagnolo | 1767 |
| 9 | DAF Trucks–Aida | 2050 |
| 10 | Fiat | 2064 |
Aftermath
The Tour organisation did not like the attention that the last-placed riders received, and for the next year made a new rule that after several stages the last-placed cyclist in the general classification would be removed from the race.[29]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "66ème Tour de France 1979" (in French). Mémoire du cyclisme. Archived from the original on 19 August 2012. Retrieved 26 September 2016.
- ↑ "Historique du Tour de France – Year 1979: The starters". Amaury Sport Organisation. Retrieved 18 September 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 McGann, Bill; McGann, Carol (2008). The Story of the Tour de France: 1965–2007. Dog Ear Publishing. pp. 117–122. ISBN 1-59858-608-4. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ↑ "Tour '79: kort maar hevig". De Waarheid (in Dutch). Koninklijke Bibliotheek. 2 November 1978. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- ↑ "Tour de France zonder halve etappes". Leeuwarder courant (in Dutch). Koninklijke Bibliotheek. 23 June 1979. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- 1 2 Augendre 2016, p. 70.
- ↑ Zwegers, Arian. "Tour de France GC Top Ten". CVCC. Archived from the original on 10 June 2009. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ↑ Augendre 2016, p. 109.
- ↑ Boyce, Barry (2010). "66th Tour de France 1979: A Hinault-Zoetemelk Battle". Cycling Revealed. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- 1 2 "The Tour, year 1979". Amaury Sport Organisation. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ↑ "Tour: Clasificaciones Oficiales". El Mundo Deportivo (in Spanish). 19 July 1979. p. 21. Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑ "66ème Tour de France 21ème étape". Mémoire du cyclisme (in French). Archived from the original on 26 September 2012. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Kostbare vergissing Tesnière". Leidsch Dagblad (in Dutch). Regionaal Archief Leiden. 20 July 1979. p. 9. Archived from the original on 8 October 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑ Beerthuyzen, Maurice (29 July 2007). "Gerhard Schönbacher: de koning van de rode lantaarn". Sportgeschiedenis (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑ de Mondenard, Jean-Pierre (2004). Dictionnaire du dopage (in French). Elsevier Masson. p. 800. ISBN 978-2-294-00714-9. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ↑ "Battaglin positivo". El Mundo Deportivo (in Spanish). 16 July 1979. p. 32. Retrieved 8 September 2010.
- ↑ "Geen dopinggevallen in laatste Tourweek". Nieuwsblad van het Noorden (in Dutch). De Krant van Toen. 25 July 1979. p. 7. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ↑ "Zoetemelk geeft gebruik van verboden middelen in Tour toe". Nieuwsblad van het Noorden (in Dutch). De Krant van Toen. 16 August 1979. p. 1. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 Christian, Sarah (2 July 2009). "Tour de France demystified – Evaluating success". RoadCycling.co.nz Ltd. Archived from the original on 9 February 2013. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Bonificaties en punten". Het vrije volk (in Dutch). De Arbeiderspers. 28 June 1979. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
- ↑ "TDF guides: White jersey". TeamSky.com. BSkyB. 22 June 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Mark, Eddy van der. "Tour Xtra: Intermediate Sprints Classification". Chippewa Valley Cycling Club. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Chauner, David; Halstead, Michael (1990). The Tour de France Complete Book of Cycling. Villard. ISBN 0-679-72936-4. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Mark, Eddy van der. "Tour Xtra: Other Classifications & Awards". Chippewa Valley Cycling Club. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Thompson, Christopher S. (2008). The Tour de France: A Cultural History. University of California Press. p. 47. ISBN 0-520-25630-1. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ↑ "Zoetemelk strijdlustigste". Leeuwarder Courant (in Dutch). De krant van toen. 23 July 1979. p. 13. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Clasificaciones oficiales". El Mundo Deportivo (in Spanish). 23 July 1979. p. 29. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- ↑ "Tour-eindstanden". Leeuwarder Courant (in Dutch). De krant van toen. 23 July 1979. p. 13. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- ↑ "Ander gevecht om laatste plaats". Nieuwsblad van het Noorden (in Dutch). De Krant van Toen. 10 October 1979. p. 35. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
Sources
- Augendre, Jacques (2016). Guide historique [Historical guide] (PDF). Tour de France (in French). Paris: Amaury Sport Organisation. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
External links
![]()