colony
English
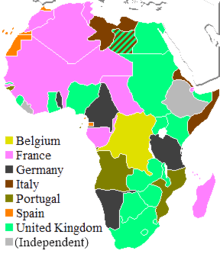
Map showing African colonies (region ruled by another country) in 1913.

A colony (group of organisms living together) of king penguins.
Etymology
From Latin colōnia (“colony”), from colōnus (“farmer; colonist”), from colō (“till, cultivate, worship”), from earlier *quelō, from Proto-Indo-European *kʷel- (“to move; to turn (around)”).
Noun
colony (plural colonies)
- A governmental unit created on land of another country owned by colonists from a country.
- 1719, “An ACT, Stating the due Aſſize of Bread”, in The Charter Granted by His Majeſty, King Charles the Second, to the Colony of Rhode-Iſland, and Providence-plantations in America, John Allen, page 59:
- And be it further Enacted by the Authority aforeſaid, That in every Town in the Colony, where Bread is Baken for Sale, there ſhall be Choſen one Clerk of the Market, or more, as each Town ſhall find needful, at their Annual Election of Town Officers, who ſhall duly be Engaged, to the faithful performance of ſaid Office, as other Town Officers are ; […]
-
- A settlement of emigrants who move to a new place, but remain culturally tied to their place of origin
- Region or governmental unit created by another country and generally ruled by another country.
- Bermuda is a crown colony of Great Britain.
- (India) An apartment complex.
- Our colony is quite small, but each apartment is large.
- A group of people with the same interests or ethnic origin concentrated in a particular geographic area
- The Amana Colonies in Iowa were settled by people from Germany.
- A group of organisms of same or different species living together in close association.
- ant colony
- a colony of specialized polyps and medusoids
- A collective noun for rabbits.
Derived terms
- colonial (adj., n.)
- colonialism (n.)
- colonise, colonize
- colonist (n.)
- colonyhood (n.)
- bird colony
- leper colony
- nudist colony
- penal colony
- space colony
Translations
region or governmental unit
|
|
group of organisms
This article is issued from
Wiktionary.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.