Royal Proclamation of 1763
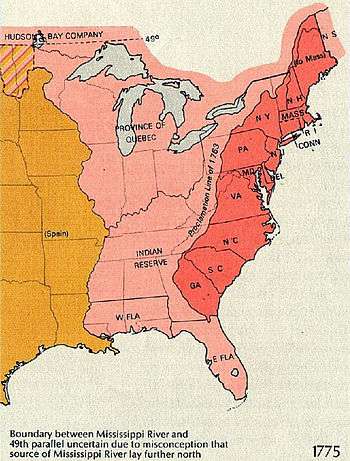
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on October 7, 1763, following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the Seven Years' War.[1] It forbade all settlement west of a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains, which was delineated as an Indian Reserve.[2] Exclusion from the vast region of Trans-Appalachia created discontent between Britain and colonial land speculators and potential settlers. The proclamation and access to western lands was one of the first significant areas of dispute between Britain and the colonies and would become a contributing factor leading to the American Revolution.[3]

| Part of a series on the |
| Constitution of Canada |
|---|
 |
| Constitutional history |
|
| Document list |
|
| Constitutional law |
|
|
|
The Royal Proclamation continues to be of legal importance to First Nations in Canada. The 1763 proclamation line is similar to the Eastern Continental Divide's path running northwards from Georgia to the Pennsylvania–New York border and north-eastwards past the drainage divide on the St. Lawrence Divide from there northwards through New England.
Background: Treaty of Paris
The Seven Years' War (with the French and Indian War as the North American theater) ended with the Treaty of Paris. Under this treaty, France ceded ownership of all of continental North America east of the Mississippi River, including Quebec, and the rest of Canada, to Britain. Spain received all French territory west of the Mississippi. Both Spain and Britain received some French islands in the Caribbean. France kept a few small islands used by fishermen,[4] modern-day Haiti and the rich sugar island of Guadeloupe.[5]
Provisions
New colonies
The Proclamation of 1763 dealt with the management of inherited French colonies from the French and Indian War, as well as regulating colonial expansion. It established new governments for several areas: the province of Quebec, the new colonies of West Florida and East Florida,[6] and a group of Caribbean islands, Grenada, Tobago, Saint Vincent, and Dominica, collectively referred to as the British Ceded Islands.[7] The Proclamation established the line at 45 degrees north latitude as the boundary between Quebec and New York (including a region not yet known as Vermont, which was then disputably considered a part of New York).
Proclamation line
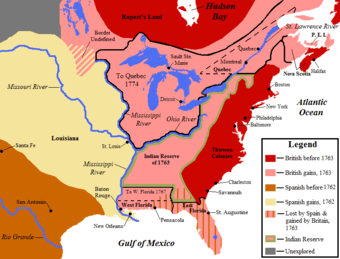
At the outset, the Royal Proclamation of 1763 defined the jurisdictional limits of the occupied territories of North America. Explaining parts of the frontier expansion in North America, in Colonial America and especially Canada colony of New France, a diminutive new colony, the Province of Quebec was carved. The territory northeast of the St. John River on the Labrador coast was placed under the Newfoundland Colony.[8] The lands west of Quebec and west of a line running along the crest of the Allegheny Mountains became Indian territory, temporarily barred to settlement, to the great disappointment of the land speculators of Virginia and Pennsylvania, who had started the Seven Years' War to gain these territories.[9]
The proclamation created a boundary line (often called the proclamation line) between the British colonies on the Atlantic coast and American Indian lands (called the Indian Reserve) west of the Appalachian Mountains. The proclamation line was not intended to be a permanent boundary between the colonists and Aboriginal lands, but rather a temporary boundary which could be extended further west in an orderly, lawful manner.[10][11] It was also not designed as an uncrossable boundary; people could cross the line, just not settle past it.[12] Its contour was defined by the headwaters that formed the watershed along the Appalachians. All land with rivers that flowed into the Atlantic was designated for the colonial entities, while all the land with rivers that flowed into the Mississippi was reserved for the native Indian population. The proclamation outlawed the private purchase of Native American land, which had often created problems in the past. Instead, all future land purchases were to be made by Crown officials "at some public Meeting or Assembly of the said Indians". Furthermore, British colonials were forbidden to settle on native lands, and colonial officials were forbidden to grant ground or lands without royal approval. Organized land companies asked for land grants, but were denied by King George lll.[13] The proclamation gave the Crown a monopoly on all future land purchases from American Indians.
British colonists and land speculators objected to the proclamation boundary since the British government had already assigned land grants to them. Including the wealthy owners of the Ohio company who protested the line to the governor of Virginia, as they had plans for settling the land to grow business.[14] Many settlements already existed beyond the proclamation line,[15] some of which had been temporarily evacuated during Pontiac's War, and there were many already granted land claims yet to be settled. For example, George Washington and his Virginia soldiers had been granted lands past the boundary. Prominent American colonials joined with the land speculators in Britain to lobby the government to move the line further west.[3][16]
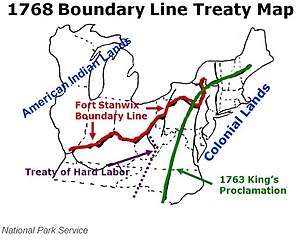
The colonist's demands were met and the boundary line was adjusted in a series of treaties with the Native Americans.[17] The first two of these treaties were completed in 1768; the Treaty of Fort Stanwix adjusted the border with the Iroquois Confederacy in the Ohio Country and the Treaty of Hard Labour adjusted the border with the Cherokee in the Carolinas.[18][19] The Treaty of Hard Labour was followed by the Treaty of Lochaber in 1770, adjusting the border between Virginia and the Cherokee.[20] These agreements opened much of what is now Kentucky and West Virginia to British settlement.[21] Although the land granted by the Virginian and North Carolinian government heavily favored the land companies, seeing as they had more wealthy backers than the poorer settlers who wanted to settle west to hopefully gain a fortune.[22]
Response
Many colonists disregarded the proclamation line and settled west which created tension between them and the Native Americans.[23] Pontiac's Rebellion (1763–1766) was a war involving Native American tribes, primarily from the Great Lakes region, the Illinois Country, and Ohio Country who were dissatisfied with British postwar policies in the Great Lakes region after the end of the Seven Years' War. They were able to take over a large number of the forts which commanded the waterways involved in trade within the region and export to Great Britain.[24] The Proclamation of 1763 had been in the works before Pontiac's Rebellion, but the outbreak of the conflict hastened the process.[15] British officials hoped the proclamation would reconcile American Indians to British rule and help to prevent future hostilities.
Some Native American peoples—primarily in the Great Lakes region—had a long and close relationship with France, and were dismayed to find that they were now under British sovereignty. They missed the amicable relationship with the French, along with the gifts they bestowed upon them, neither of which they had with the British.
Legacy
| Indigenous peoples in Canada |
|---|
|
|
History
|
|
Politics
|
|
Culture
|
|
Demographics
|
|
Linguistics
|
|
Religions
|
|
Index
|
|
Wikiprojects Portals
WikiProject
First Nations Inuit Métis |
Indigenous peoples
The Royal Proclamation continued to govern the cession of indigenous land in British North America, especially Upper Canada and Rupert's Land. Upper Canada created a platform for treaty making based on the Royal Proclamation. After loyalists moved into land after Britain's defeat in the American Revolution, the first impetus was created out of necessity.[25] The proclamation forms the basis of land claims of Indigenous peoples in Canada – First Nations, Inuit, and Métis. The Royal Proclamation of 1763 is thus mentioned in Section 25 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
According to historian Colin Calloway, "[settler] scholars disagree on whether the proclamation recognized or undermined tribal sovereignty".[26] The proclamation established the important precedent that the indigenous population had certain rights to the lands they occupied.
Some see the Royal Proclamation of 1763 as a "fundamental document" for First Nations land claims and self-government.[27] It is "the first legal recognition by the British Crown of Aboriginal rights"[28] and imposes a fiduciary duty of care on the Crown. The intent and promises made to the native in the Proclamation have been argued to be of a temporary nature, only meant to appease the Native peoples who were becoming increasingly resentful of "settler encroachments on their lands"[29] and were capable of becoming a serious threat to British colonial settlement.[30][31] Advice given by a Sir William Johnson, superintendent of Indian Affairs in North America, to the Board of Trade on August 30, 1764, expressed that:
The Indians all know we cannot be a Match for them in the midst of an extensive woody Country ... from whence I infer that if we are determined to possess Our Posts, Trade & ca securely, it cannot be done for a Century by any other means than that of purchasing the favour of the numerous Indian inhabitants.[32]
Some historians believe that "the British were trying to convince Native people that there was nothing to fear from the colonists, while at the same time trying to increase political and economic power relative to First Nations and other European powers".[33] Others argue that the Royal Proclamation along with the subsequent Treaty of Niagara, provide for an argument that "discredits the claims of the Crown to exercise sovereignty over First Nations"[34] and affirms Aboriginal "powers of self-determination in, among other things, allocating lands".[35]
United States

The influence of the Royal Proclamation of 1763 on the coming of the American Revolution has been variously interpreted. Many historians argue that the proclamation ceased to be a major source of tension after 1768, since the aforementioned later treaties opened up extensive lands for settlement. Others have argued that colonial resentment of the proclamation contributed to the growing divide between the colonies and the mother country. Some historians argue that even though the boundary was pushed west in subsequent treaties, the British government refused to permit new colonial settlements for fear of instigating a war with Native Americans, which angered colonial land speculators.[36] Others argue that the Royal Proclamation imposed a fiduciary duty of care on the Crown.[37]
George Washington was given 20,000 acres (81 km2) of wild land in the Ohio region for his services in the French and Indian War. In 1770, Washington took the lead in securing the rights of him and his old soldiers in the French War, advancing money to pay expenses in behalf of the common cause and using his influence in the proper quarters. In August 1770, it was decided that Washington should personally make a trip to the western region, where he located tracts for himself and military comrades and eventually was granted letters patent for tracts of land there. The lands involved were open to Virginians under terms of the Treaty of Lochaber of 1770, except for the lands located two miles (3.2 km) south of Fort Pitt, now known as Pittsburgh.[38]
In the United States, the Royal Proclamation of 1763 ended with the American Revolutionary War because Great Britain ceded the land in question to the United States in the Treaty of Paris (1783). Afterward, the U.S. government also faced difficulties in preventing frontier violence and eventually adopted policies similar to those of the Royal Proclamation. The first in a series of Indian Intercourse Acts was passed in 1790, prohibiting unregulated trade and travel in Native American lands. In 1823, the U.S. Supreme Court case Johnson v. M'Intosh[39] established that only the U.S. government, and not private individuals, could purchase land from Native Americans.
250th anniversary celebrations
In October 2013 the 250th anniversary of the Royal Proclamation was celebrated in Ottawa with a meeting of Indian leaders and Governor-General David Johnston.[40] The Aboriginal movement Idle No More held birthday parties for this monumental document at various locations across Canada.[41]
See also
- Indian removal
- Indian barrier state
- Northwest Territory
- Indian Reserve (1763)
- Halifax Treaties
- Territorial evolution of the Caribbean
Footnotes
- Fenge, Terry; Aldridge, Jim (1 November 2015). Keeping promises : the Royal Proclamation of 1763, aboriginal rights, and treaties in Canada. McGill–Queen's University Press. pp. 4, 38, 51, 201, 212, 257. ISBN 978-0-7735-9755-6. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- Middlekauff, Robert (2007). The Glorious Cause: The American Revolution, 1763–1789 (Revised Expanded ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 58–60. ISBN 978-0-1951-6247-9.
- Holton (1999), pp. 3–38, .
- Anderson, Fred (2007). Crucible of War: The Seven Years' War and the Fate of Empire in British North America, 1754–1766. Knopf Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-307-42539-3.
- Gibson, Carrie (2014). "Chapter 6: A World At War". Empire's Crossroads: A History of the Caribbean from Columbus to the Present Day. Open Road + Grove/Atlantic. ISBN 978-0-8021-9235-6.
- Gannon, Michael (2013). The History of Florida. Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida. pp. 144–147. ISBN 978-0-8130-6401-7.
- Niddrie, D. (December 1966). "Eighteenth-Century Settlement in the British Caribbean". Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers. 40 (40): 67–80. doi:10.2307/621569. JSTOR 621569.
- Eccles, W.J. (1972). France in America. Harper & Row. p. 220.
- Sosin, Jack M. (1961). Whitehall and the wilderness: the Middle West in British colonial policy, 1760–1775. University of Nebraska Press. p. 146.
- Markowitz, Harvey (1995). American Indians. Salem Press. p. 633. ISBN 978-0-89356-757-6.
- Vorsey, Louis De (1966). The Indian Boundary in the Southern Colonies, 1763–1775. University of North Carolina Press. p. 39.
- Taylor, Alan (2017). American Revolutions: A Continental History, 1750–1804. W. W. Norton. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-393-35476-8.
- Del Papa, Eugene M. (1975). "The Royal Proclamation of 1763: Its Effects Upon Virginia Land Companies". The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography. JSTOR. 83 (4): 406–411. JSTOR 4247979.
- Papa, Eugene M. Del (1975). "The Royal Proclamation of 1763: Its Effect upon Virginia Land Companies". The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography. 83 (4): 406–411. ISSN 0042-6636. JSTOR 4247979.
- Wood, Gordon S. (2002). The American Revolution: A History. Random House. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-58836-158-5.
- For information about Pontiac's War, see Middleton, Richard (2012). Pontiac's War: Its Causes, Course and Consequences. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-86416-3.
- Calloway (2007), p. 100.
- "Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1768)". Ohio History Central. Ohio Historical Society. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- "Treaty of Hard Labor with Cherokees". Envisaging The West. University of Nebraska–Lincoln. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- "Treaty of Lochaber 1770". Envisaging The West. University of Nebraska–Lincoln. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- Campbell, William J (2012). Speculators in Empire: Iroquoia and the 1768 Treaty of Fort Stanwix. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-4710-9.
- Friend, Craig Thompson (2005). "Liberty Is Pioneering: An American Birthright". OAH Magazine of History. 19 (3): 16–20. doi:10.1093/maghis/19.3.16. ISSN 0882-228X. JSTOR 25161942.
- [history.stste.gov/milestones/1750-1775/proclamation-line-1763 "Proclamation Line of 1763, Quebec Act of 1774 and Westward Expansion"] Check
|url=value (help). Office of the Historian. United States Department of State. Retrieved 5 March 2020. - McDonnell, Michael (2015). Masters of Empire: Great Lakes Indians and the Making of America. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. pp. 209–238. ISBN 978-0-374-71418-5.
- Miller, J.R. (2009). Compact, Contract, Covenant: Aboriginal Treaty-making in Canada. University of Toronto Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-8020-9741-5.
- Calloway (2007), p. 93.
- Borrows (1997), p. 155.
- Francis, Douglas R.; Jones, Richard; Smith, Donald B. (2009). Origins: Canadian History to Confederation (6th ed.). Toronto: Nelson Education. p. 157.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Francis, Jones & Smith (2009), p. 156.
- Stagg, Jack (1981). Anglo-Indian Relations In North America to 1763 and An Analysis of the Royal Proclamation of 7 October 1763 (Report). Indian and Northern Affairs Canada, Research Branch. p. 356.
- Borrows (1997), pp. 158–159.
- Quoted in Clark, Bruce (1990). Native Liberty, Crown Sovereignty: The Existing Aboriginal Right of Self-Government in Canada. McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 81. ISBN 978-0-7735-0767-8.
- Borrows (1997), p. 160.
- Borrows (1997), p. 164.
- Borrows (1997), p. 165.
- Holton, Woody (August 1994). "The Ohio Indians and the Coming of the American Revolution in Virginia". The Journal of Southern History. 60 (3): 453–478. doi:10.2307/2210989. JSTOR 2210989.
- "Royal Proclamation of 1763: Relationships, Rights and Treaties – Poster". Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada. November 27, 2013.
- "Letter from George Washington to George Mercer dated November 7, 1771, at Williamsburg". The writings of George Washington from the original manuscript sources. p. 68. Archived from the original on October 4, 2013.
- 21 U.S. (8 Wheat.) 543 (1823)
- MacKinnon, Leslie (October 6, 2013). "Royal Proclamation of 1763, Canada's 'Indian Magna Carta,' turns 250"". CBC News.
- Galloway, Gloria (October 7, 2013). "Royal Proclamation's 250th anniversary has First Nations reflecting on their rights". The Globe and Mail.
Sources
- Abernethy, Thomas Perkins (1959) [1937]. Western Lands and the American Revolution. New York: Russell & Russell.
- Borrows, John (1997). "Wampum at Niagara: The Royal Proclamation, Canadian Legal History, and Self-Government" (PDF). In Michael Asch (ed.). Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in Canada. Vancouver: UBC Press. ISBN 0-7748-0580-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) – Also Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in Canada, p. 155, at Google Books
- Calloway, Colin G. (2007). The Scratch of a Pen: 1763 and the Transformation of North America. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-533127-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Holton, Woody (1999). "Land Speculators versus Indians and the Privy Council". Forced Founders: Indians, Debtors, Slaves, and the Making of the American Revolution in Virginia. UNC Press Books. pp. 3–38. ISBN 978-0-8078-9986-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Del Papa, Eugene M. (October 1975). "The Royal Proclamation of 1763: Its Effect upon Virginia Land Companies". Virginia Magazine of History and Biography. 83 (4): 406–411. JSTOR 4247979.
- Holton, Woody (August 1994). "The Ohio Indians and the Coming of the American Revolution in Virginia". Journal of Southern History. 60 (3): 453–478. doi:10.2307/2210989. JSTOR 2210989.
- Marshall, Peter (October 1967). "Sir William Johnson and the Treaty of Fort Stanwix, 1768". Journal of American Studies. 1 (2): 149–179. doi:10.1017/S0021875800007830.
- Middleton, Richard (2007). Pontiac's War: Its Causes, Course and Consequences. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-86416-3.
- Sosin, Jack M. (1961). Whitehall and the wilderness: the Middle West in British colonial policy, 1760-1775. University of Nebraska Press. – The standard scholarly history of the proclamation and its effects.
- Stuart, Paul (1979). The Indian Office: growth & development of American institution, 1865-1900. UMI Research Press. ISBN 978-0-8357-1079-4.
Canada
- Cashin, Edward J. (1994). Governor Henry Ellis and the Transformation of British North America. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-0-8203-3125-6.
- Fenge, Terry; Aldridge, Jim, eds. (2015). Keeping Promises: The Royal Proclamation of 1763, Aboriginal Rights, and Treaties in Canada. McGill-Queen's University Press. ISBN 978-0-7735-9755-6.
- Lawson, Philip (1989). The Imperial Challenge: Quebec and Britain in the Age of the American Revolution. McGill-Queen's University Press. ISBN 978-0-7735-1205-4.
- Roth, Christopher F. (Fall 2002). "Without Treaty, without Conquest: Indigenous Sovereignty in Post-Delgamuukw British Columbia". Wíčazo Ša Review. 17 (2): 143–165. doi:10.1353/wic.2002.0020.
- Stonechild, Blair A. (1996). "Indian-White Relations in Canada, 1763 to the Present". In Frederick E. Hoxie, D. L. Birchfield (ed.). Encyclopedia of North American Indians. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 277–281. ISBN 978-0-395-66921-1.
- Tousignant, Pierre (1980). "The Integration of the Province of Quebec into the British Empire, 1763–91. Part 1: From the Royal Proclamation to the Quebec Act". Dictionary of Canadian Biography. 4. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
