Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (/ˈtɒləmi/; Greek: Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr "Ptolemy the Saviour"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a companion and historian of Alexander the Great of the Kingdom of Macedon in northern Greece who became ruler of Egypt, part of Alexander's former empire. Ptolemy was pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC[1] to his death. He was the founder of the Ptolemaic dynasty which ruled Egypt until the death of Cleopatra in 30 BC, turning the country into a Hellenistic kingdom and Alexandria into a centre of Greek culture.
| Ptolemy I Soter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Bust of Ptolemy I in the Louvre | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharaoh and Basileus of the Ptolemaic Kingdom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 305/304 – 282 BC (Ptolemaic dynasty) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Alexander IV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor | Ptolemy II Philadelphus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | c. 367 BC Macedon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | January 282 BC (aged 84–85) Alexandria, Egypt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spouse(s) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Children | With Thaïs (mistress):
With Eurydice:
With Berenice I:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Relatives | Menelaus (half-brother) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
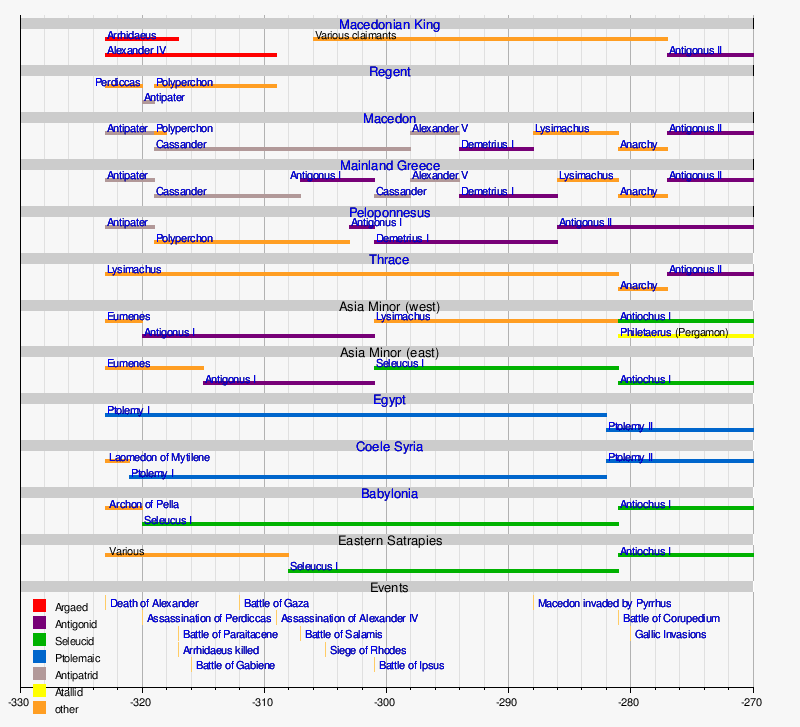
Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Alexandria in a new tomb. Afterwards he joined a coalition against Perdiccas, the royal regent over Philip III of Macedon. The latter invaded Egypt but was assassinated by his own officers in 320 BC, allowing Ptolemy I to consolidate his control over the country. After a series of wars between Alexander's successors, Ptolemy gained a claim to Judea in southern Syria which was disputed with the Syrian king Seleucus I Nicator, his former ally. He also took control of Cyprus and Cyrenaica, the latter of which was placed under the control of Ptolemy's stepson Magas.
Ptolemy I may have married Thaïs, his mistress during the life of Alexander; he is known to have married the Persian noblewoman Artakama on Alexander's orders. He later married Eurydice, daughter of the Macedonian regent Antipater; their sons Ptolemy Keraunos and Meleager ruled in turn as kings of Macedon. Ptolemy's final marriage was to Eurydice's cousin and lady-in-waiting, Berenice I. Ptolemy I died in 282 BC and was succeeded by his son with Berenice, Ptolemy II.
Early life and career
A Macedonian,[2] Ptolemy was born in 367 BC.[3] Ptolemy's mother was Arsinoe. According to Satyrus the Peripatetic, Arsinoe was a descendant of Alexander I of Macedon and thus a member of the Argead dynasty, claiming ultimate descent from Heracles. Ostensibly, Ptolemy's father was Lagus, a Macedonian nobleman from Eordaea, but many ancient sources claim that he was actually an illegitimate son of Philip II of Macedon. If true, this would have made Ptolemy the half-brother of Alexander. It is probable that this is a later myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic dynasty.[4]
Ptolemy served with Alexander from his first campaigns, and was among the seven somatophylakes (bodyguards) of Alexander. He played a principal part in the later campaigns in Afghanistan and India.[5] He participated in the Battle of Issus, commanding troops on the left wing under the authority of Parmenion. Later he accompanied Alexander during his journey to the Oracle in the Siwa Oasis where he was proclaimed a son of Zeus.[6] Ptolemy had his first independent command during the campaign against the rebel Bessus whom Ptolemy captured and handed over to Alexander for execution.[7]
Successor of Alexander
When Alexander died in 323 BC, Ptolemy is said to have instigated the settlement of the empire made at Babylon. Through the Partition of Babylon, he was appointed satrap of Egypt, under the nominal kings Philip III Arrhidaeus and the infant Alexander IV; the former satrap, the Greek Cleomenes, stayed on as his deputy. Ptolemy quickly moved, without authorisation, to subjugate Cyrenaica.[5]
By custom, kings in Macedonia asserted their right to the throne by burying their predecessor. Probably because he wanted to pre-empt Perdiccas, the imperial regent, from staking his claim in this way, Ptolemy took great pains in acquiring the body of Alexander the Great. On his deathbed, Alexander the Great wished to be buried at the Temple of Zeus Ammon in the Siwa Oasis of ancient Libya instead of the royal tombs of Aigai in Macedon.[8] However, his successors including Perdiccas attempted to bury his body in Macedon instead. In late 322 or early 321 BC, the body of Alexander the Great was in Syria, on its way to Macedon, when it was captured by Ptolemy I Soter. He brought Alexander's remains back to Egypt, interring them at Memphis, but they were later moved to Alexandria where a tomb of Alexander the Great was constructed for them.[9] Shortly after this event, Ptolemy openly joined the coalition against Perdiccas. Perdiccas appears to have suspected Ptolemy of aiming for the throne himself, and may have decided that Ptolemy was his most dangerous rival. Ptolemy executed Cleomenes for spying on behalf of Perdiccas; this removed the chief check on his authority, and allowed Ptolemy to obtain the huge sum that Cleomenes had accumulated.[10]
Rivalry and wars

Other: Carthage Rome Greek colonies
In 321 BC, Perdiccas attempted to invade Egypt, only to fall at the hands of his own men.[11] Ptolemy's decision to defend the Nile against Perdiccas ended in fiasco for Perdiccas, with the loss of 2,000 men. This failure was a fatal blow to Perdiccas' reputation, and he was murdered in his tent by two of his subordinates. Ptolemy immediately crossed the Nile, to provide supplies to what had the day before been an enemy army. Ptolemy was offered the regency in place of Perdiccas; but he declined.[12] Ptolemy was consistent in his policy of securing a power base, while never succumbing to the temptation of risking all to succeed Alexander.[13]
In the long wars that followed between the different Diadochi, Ptolemy's first goal was to hold Egypt securely, and his second was to secure control in the outlying areas: Cyrenaica and Cyprus, as well as Syria, including the province of Judea. His first occupation of Syria was in 318, and he established at the same time a protectorate over the petty kings of Cyprus. When Antigonus One-Eye, master of Asia in 315, showed expansionist ambitions, Ptolemy joined the coalition against him, and on the outbreak of war, evacuated Syria. In Cyprus, he fought the partisans of Antigonus, and re-conquered the island (313). A revolt in Cyrene was crushed the same year.[5]
In 312, Ptolemy and Seleucus, the fugitive satrap of Babylonia, both invaded Syria, and defeated Demetrius Poliorcetes ("besieger of cities"), the son of Antigonus, in the Battle of Gaza. Again he occupied Syria, and again—after only a few months, when Demetrius had won a battle over his general, and Antigonus entered Syria in force—he evacuated it. In 311, a peace was concluded between the combatants. Soon after this, the surviving 13-year-old king, Alexander IV, was murdered in Macedonia on the orders of Cassander, leaving the satrap of Egypt absolutely his own master.[5]
The peace did not last long, and in 309 Ptolemy personally commanded a fleet which detached the coastal towns of Lycia and Caria from Antigonus, then crossed into Greece, where he took possession of Corinth, Sicyon and Megara (308 BC). In 306, a great fleet under Demetrius attacked Cyprus, and Ptolemy's brother Menelaus was defeated and captured in another decisive Battle of Salamis. Ptolemy's complete loss of Cyprus followed.[5]
The satraps Antigonus and Demetrius now each assumed the title of king; Ptolemy, as well as Cassander, Lysimachus and Seleucus I Nicator, responded by doing the same. In the winter of 306 BC, Antigonus tried to follow up his victory in Cyprus by invading Egypt; but Ptolemy was strongest there, and successfully held the frontier against him. Ptolemy led no further overseas expeditions against Antigonus.[14] However, he did send great assistance to Rhodes when it was besieged by Demetrius (305/304). The Rhodians granted divine honours to Ptolemy as a result of the lifting of the siege.[15]
When the coalition against Antigonus was renewed in 302, Ptolemy joined it, and invaded Syria a third time, while Antigonus was engaged with Lysimachus in Asia Minor. On hearing a report that Antigonus had won a decisive victory there, he once again evacuated Syria. But when the news came that Antigonus had been defeated and slain by Lysimachus and Seleucus at the Battle of Ipsus in 301, he occupied Syria a fourth time.[14]
The other members of the coalition had assigned all Syria to Seleucus, after what they regarded as Ptolemy's desertion, and for the next hundred years, the question of the ownership of southern Syria (i.e., Judea) produced recurring warfare between the Seleucid and Ptolemaic dynasties. Henceforth, Ptolemy seems to have involved himself as little as possible in the rivalries between Asia Minor and Greece; he lost what he held in Greece, but reconquered Cyprus in 295/294. Cyrenaica, after a series of rebellions, was finally subjugated in about 300 and placed under his stepson Magas.[14]
Marriages, children, and succession
While Alexander was alive, Ptolemy had three children with his mistress Thaïs, who may also have been his wife: Lagus; Leontiscus; and Eirene, who was given in marriage to Eunostos of Soloi in Cyprus. During the Susa weddings, Ptolemy married Persian noblewoman Artakama, as ordered by Alexander the Great.[16] Around 322 BC, he married Eurydice, daughter of Antipater, regent of Macedonia. They had five children before she was repudiated: three sons–Ptolemy Keraunos, king of Macedon from 281 BC to 279 BC; his brother and successor Meleager, who ruled for two months in 279 BC; and a 'rebel in Cyprus' who was put to death by his half-brother Ptolemy II Philadelphus–as well as the daughters Ptolemais, who married Demetrius I of Macedon, and Lysandra, first married to Alexander V of Macedon and after to Lysimachus' son Agathocles.[16][17][18][19][20][21] Ptolemy married once more to Berenice, Eurydice's cousin, who had come to Egypt as Eurydice's lady-in-waiting with the children from her first marriage to Philip. Their children were Arsinoe II, Philotera, and Ptolemy II. Their eldest child Arsinoe married Lysimachus, then her half-brother Ptolemy Keraunos, and finally her full brother Ptolemy II.[17][22]
In 285, Ptolemy made his son by Berenice, Ptolemy II Philadelphus, his co-regent. His eldest legitimate son, Ptolemy Keraunos, fled to the court of Lysimachus. Ptolemy I died in January 282 aged 84 or 85.[3] Shrewd and cautious, he had a compact and well-ordered realm to show at the end of forty years of war. His reputation for good nature and liberality attached the floating soldier-class of Macedonians and other Greeks to his service, and was not insignificant; nor did he wholly neglect conciliation of the natives. He was a ready patron of letters, founding the Great Library of Alexandria.[23] The Ptolemaic dynasty which he founded ruled Egypt for nearly three hundred years. It was a Hellenistic kingdom known for its capital Alexandria, which became a centre of Greek culture. Ptolemaic rule ended with the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC.[24]
Lost history of Alexander's campaigns
Ptolemy himself wrote an eyewitness history of Alexander's campaigns (now lost).[25] In the second century AD, Ptolemy's history was used by Arrian of Nicomedia as one of his two main primary sources (alongside the history of Aristobulus of Cassandreia) for his own extant Anabasis of Alexander, and hence large parts of Ptolemy's history can be assumed to survive in paraphrase or précis in Arrian's work.[26] Arrian cites Ptolemy by name on only a few occasions, but it is likely that large stretches of Arrian's Anabasis reflect Ptolemy's version of events. Arrian once names Ptolemy as the author "whom I chiefly follow",[27] and in his Preface writes that Ptolemy seemed to him to be a particularly trustworthy source, "not only because he was present with Alexander on campaign, but also because he was himself a king, and hence lying would be more dishonourable for him than for anyone else".[28]
Ptolemy's lost history was long considered an objective work, distinguished by its straightforward honesty and sobriety,[14] but more recent work has called this assessment into question. R. M. Errington argued that Ptolemy's history was characterised by persistent bias and self-aggrandisement, and by systematic blackening of the reputation of Perdiccas, one of Ptolemy's chief dynastic rivals after Alexander's death.[29] For example, Arrian's account of the fall of Thebes in 335 BC (Anabasis 1.8.1–1.8.8, a rare section of narrative explicitly attributed to Ptolemy by Arrian) shows several significant variations from the parallel account preserved in Diodorus Siculus (17.11–12), most notably in attributing a distinctly unheroic role in proceedings to Perdiccas. More recently, J. Roisman has argued that the case for Ptolemy's blackening of Perdiccas and others has been much exaggerated.[30]
Euclid
Ptolemy personally sponsored the great mathematician Euclid. He found Euclid's seminal work, the Elements, too difficult to study, so he asked if there were an easier way to master it. According to Proclus Euclid famously quipped: "Sire, there is no Royal Road to geometry."[31]
See also
- History of Ptolemaic Egypt
- Serapis, Greco-Egyptian god, promoted by Ptolemy
References
Citations
- Hölbl, Günther (2013). A History of the Ptolemaic Empire. Routledge. p. 21. ISBN 9781135119836.
- Jones, Prudence J. (2006). Cleopatra: A Sourcebook. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 14. ISBN 9780806137414.
They were members of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Macedonian Greeks, who ruled Egypt after the death of its conqueror, Alexander the Great.
- Ptolemy I at Livius.org
- Carney, Elizabeth (2010). Philip II and Alexander The Great: Father and Son, Lives and Afterlives. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-973815-1.
- Chisholm 1911, p. 616.
- Grimal, Nicolas (1992). A History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford: Blackwell Books. p. 382. ISBN 978-0-631-19396-8.
- Arrian (1976). de Sélincourt, Aubrey (ed.). Anabasis Alexandri (The Campaigns of Alexander). Harmondsworth: Penguin Books. III, 30. ISBN 978-0-14-044253-3.
- Lauren O'Connor (2008). "The Remains of Alexander the Great: The God, The King, The Symbol". Constructing the Past. Retrieved 28 March 2019..
- Saunders, Nicholas (2007), Alexander's Tomb: The Two-Thousand Year Obsession to Find the Lost Conqueror, Basic Books, p. 41, ISBN 0465006213CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Green, Peter (1990). Alexander to Actium. University of California Press. pp 13–14. ISBN 9780520083493.
- Anson, Edward M (Summer 1986). "Diodorus and the Date of Triparadeisus". The American Journal of Philology (The Johns Hopkins University Press) 107 (2): 208–217. doi:10.2307/294603. JSTOR 294603.
- Peter Green p14
- Peter Green pp 119
- Chisholm 1911, p. 617.
- Siege of Rhodes at Livius.org
- Ogden, Daniel (1999). Polygamy Prostitutes and Death. The Hellenistic Dynasties. London: Gerald Duckworth & Co. Ltd. p. 150. ISBN 07156 29301.
- Clayman, Dee L. (2014). Berenice II and the Golden Age of Ptolemaic Egypt. Oxford University Press. p. 65. ISBN 9780195370881.
- Macurdy, Grace Harriet (1985). Hellenistic Queens (Reprint of 1932 ed.). Chicago: Ares Publishers. ISBN 978-0-89005-542-7.
- Hölbl, Gūnther (2001). A History of the Ptolemaic Empire. Routledge. pp. 35–36. ISBN 978-0-06-019439-0.
- McKechnie, Paul; Guillaume, Philippe (16 October 2008). Ptolemy II Philadelphus and his World. Brill. p. 43. ISBN 978-9047424208.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, "Demetrius", 32, 46
- Berenice I at Livius.org
- Phillips, Heather A., "The Great Library of Alexandria?". Library Philosophy and Practice, August 2010
- Ptolemaic Dynasty at Ancient History Encyclopedia
- Jacoby, Felix (1926). Die Fragmente der griechischen Historiker, Teil 2, Zeitgeschichte. – B. Spezialgeschichten, Autobiographien und Memoiren, Zeittafeln [Nr. 106-261]. Berlin: Weidmann. pp. 752–769, no. 138, "Ptolemaios Lagu". OCLC 769308142.
- Bosworth, A. B. (1988). From Arrian to Alexander: Studies in Historical Interpretation. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 13–14. ISBN 978-0198148630.
- Anabasis 6.2.4
- Anabasis, Prologue
- Errington, R. M. (1969-01-01). "Bias in Ptolemy's History of Alexander". The Classical Quarterly. 19 (2): 233–242. JSTOR 637545.
- Roisman, Joseph (1984-01-01). "Ptolemy and His Rivals in His History of Alexander". The Classical Quarterly. 34 (2): 373–385. JSTOR 638295.
- Robinson, Victor (2005). The Story of Medicine. Whitefish, Montana: Kessinger Publishing. p. 80. ISBN 978-1-4191-5431-7.
Sources

Bibliography
- Walter M. Ellis: Ptolemy of Egypt, London: Routledge. 1993. ISBN 9780415100205
- Christian A. Caroli: Ptolemaios I. Soter – Herrscher zweier Kulturen, Konstanz: Badawi. 2007. ISBN 9783938828052
- Waterfield, Robin (2011). Dividing the Spoils – The War for Alexander the Great's Empire (hardback). New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-957392-9.
- McKechnie, Paul and Jennifer A. Cromwell (eds). Ptolemy I and the Transformation of Egypt, 404–282 BCE. Leiden, NL; Boston, MA: Brill, 2018. ISBN 978-90-04-36696-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ptolemy I. |
- Ptolemy Soter I at LacusCurtius — (Chapter II of E. R Bevan's House of Ptolemy, 1923)
- Ptolemy I (at Egyptian Royal Genealogy, with genealogical table)
- Livius, Ptolemy I Soter by Jona Lendering
- Ptolemy I Soter entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
- A genealogical tree of Ptolemy, though not necessarily reliable Alexander the Great
Ptolemy I Soter Ptolemaic Dynasty Born: 367 BC Died: 282 BC | ||
| Preceded by Alexander IV |
Pharaoh of Egypt 305/304–282 BC |
Succeeded by Ptolemy II Philadelphus |