Afghanistan
Afghanistan (/æfˈɡænɪstæn, æfˈɡɑːnɪstɑːn/ (![]()
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan | |
|---|---|
 Flag
 National emblem
| |
Anthem: Millī Surūd ملي سرود ("National Anthem") | |
.svg.png) | |
| Capital and largest city | Kabul 33°N 65°E |
| Official languages | Dari 27 million (77%) (L1 + L2), Pashto 16.8 million (48%)[2] |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Afghan[Note 1][6][7] |
| Government | Unitary presidential Islamic republic |
• President | Ashraf Ghani |
• 1st Vice President | Amrullah Saleh |
• 2nd Vice President | Sarwar Danish |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| House of Elders | |
| House of the People | |
| Formation | |
• Hotak Empire | 21 April 1709 |
• Durrani Empire | October 1747 |
• Emirate | 1823 |
• Recognized | 19 August 1919 |
• Kingdom | 9 June 1926 |
• Republic | 17 July 1973 |
• Current constitution | 26 January 2004 |
| Area | |
• Total | 652,230[8] km2 (251,830 sq mi) (40th) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 32,225,560[9] (43rd) |
• Density | 46/km2 (119.1/sq mi) (174th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $72.911 billion[10] (96th) |
• Per capita | $2,024[10] (169th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $21.657 billion[10] (111st) |
• Per capita | $601[10] (177th) |
| Gini (2008) | low · 1st |
| HDI (2018) | low · 170th |
| Currency | Afghani (Afs) (AFN) |
| Time zone | UTC+4:30 Solar Calendar (D†) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +93 |
| ISO 3166 code | AF |
| Internet TLD | .af افغانستان. |
Human habitation in Afghanistan dates back to the Middle Paleolithic Era, and the country's strategic location along the Silk Road connected it to the cultures of the Middle East and other parts of Asia. The land has historically been home to various peoples and has witnessed numerous military campaigns, including those by Alexander the Great, Mauryas, Muslim Arabs, Mongols, British, Soviets, and by the United States with allied countries. The land also served as the source from which the Kushans, Hephthalites, Samanids, Saffarids, Ghaznavids, Ghorids, Khaljis, Mughals, Hotaks, Durranis, and others have risen to form major empires.
The political history of the modern state of Afghanistan began with the Hotak and Durrani dynasties in the 18th century, with Ahmad Shah Abdali being considered as the founder of the state. In the late 19th century, Afghanistan became a buffer state in the "Great Game" between British India and the Russian Empire. Its border with British India, the Durand Line, was formed in 1893 but it is not recognized by the Afghan government and it has led to strained relations with Pakistan since the latter's independence in 1947.[13][14] In the First Anglo-Afghan War, the British East India Company seized control of Afghanistan briefly, but following the Third Anglo-Afghan War in 1919 the country was free of foreign influence, eventually becoming a monarchy under Amanullah Khan, until almost 50 years later when Zahir Shah was overthrown and a republic was established. In 1978, after a second coup Afghanistan first became a socialist state and then a Soviet protectorate. This evoked the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s against mujahideen rebels. By 1996 most of Afghanistan was captured by the Islamic fundamentalist group the Taliban, who ruled as a totalitarian regime for over five years. Following the 9/11 attacks, an intervention by the US and its allies forcibly removed the Taliban from power, and a new democratically-elected government was formed, but the Taliban still control a significant portion of the country.
Afghanistan is a unitary presidential Islamic republic. The country has high levels of terrorism, poverty, child malnutrition, and corruption. It is a member of the United Nations, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, the Group of 77, the Economic Cooperation Organization, and the Non-Aligned Movement. Afghanistan's economy is the world's 96th largest, with a gross domestic product (GDP) of $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity; the country fares much worse in terms of per-capita GDP (PPP), ranking 169th out of 186 countries as of 2018.
Etymology
The name Afghānistān (Pashto: افغانستان) is believed to be as old as the ethnonym Afghan, which is documented in the 10th-century geography book Hudud ul-'alam.[15] The root name "Afghan" was used historically in reference to a member of the ethnic Pashtuns,[16] and the suffix "-stan" means "place of" in Persian. Therefore, Afghanistan translates to land of the Afghans[17] or, more specifically in a historical sense, to land of the Pashtuns. However, the modern Constitution of Afghanistan states that the word "Afghan" shall apply to every citizen of Afghanistan."[6]
History
.jpg)
Excavations of prehistoric sites suggest that humans were living in what is now Afghanistan at least 50,000 years ago, and that farming communities in the area were among the earliest in the world. An important site of early historical activities, many believe that Afghanistan compares to Egypt in terms of the historical value of its archaeological sites.[18][19]
The country sits at a unique nexus point where numerous civilizations have interacted and often fought. It has been home to various peoples through the ages, among them the ancient Iranian peoples who established the dominant role of Indo-Iranian languages in the region. At multiple points, the land has been incorporated within vast regional empires, among them the Achaemenid Empire, the Macedonian Empire, the Indian Maurya Empire, and the Islamic Empire.[20] For its success in resisting foreign occupation during the 19th and 20th centuries, Afghanistan has been called the "graveyard of empires,"[21] though it is unknown who coined the phrase.[22]
Many empires and kingdoms have also risen to power in Afghanistan, such as the Greco-Bactrians, Kushans, Hephthalites, Kabul Shahis, Saffarids, Samanids, Ghaznavids, Ghurids, Khaljis, Kartids, Timurids, Mughals, and finally the Hotak and Durrani dynasties that marked the political origins of the modern state.[23]
Pre-Islamic period
Archaeological exploration done in the 20th century suggests that the geographical area of Afghanistan has been closely connected by culture and trade with its neighbors to the east, west, and north. Artifacts typical of the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Bronze, and Iron Ages have been found in Afghanistan. Urban civilization is believed to have begun as early as 3000 BCE, and the early city of Mundigak (near Kandahar in the south of the country) may have been a colony of the nearby Indus Valley Civilization. More recent findings established that the Indus Valley Civilisation stretched up towards modern-day Afghanistan, making the ancient civilization today part of Pakistan, Afghanistan, and India. In more detail, it extended from what today is northwest Pakistan to northwest India and northeast Afghanistan. An Indus Valley site has been found on the Oxus River at Shortugai in northern Afghanistan.[24][25] There are several smaller IVC colonies to be found in Afghanistan as well.


After 2000 BCE, successive waves of semi-nomadic people from Central Asia began moving south into Afghanistan; among them were many Indo-European-speaking Indo-Iranians. These tribes later migrated further into South Asia, Western Asia, and toward Europe via the area north of the Caspian Sea. The region at the time was referred to as Ariana.[18][26]
The religion Zoroastrianism is believed by some to have originated in what is now Afghanistan between 1800 and 800 BCE, as its founder Zoroaster is thought to have lived and died in Balkh. Ancient Eastern Iranian languages may have been spoken in the region around the time of the rise of Zoroastrianism. By the middle of the 6th century BCE, the Achaemenids overthrew the Medes and incorporated Arachosia, Aria, and Bactria within its eastern boundaries. An inscription on the tombstone of Darius I of Persia mentions the Kabul Valley in a list of the 29 countries that he had conquered.[27]
Alexander the Great and his Macedonian forces arrived in Afghanistan in 330 BCE after defeating Darius III of Persia a year earlier in the Battle of Gaugamela. Following Alexander's brief occupation, the successor state of the Seleucid Empire controlled the region until 305 BCE when they gave much of it to the Maurya Empire as part of an alliance treaty. The Mauryans controlled the area south of the Hindu Kush until they were overthrown in about 185 BCE. Their decline began 60 years after Ashoka's rule ended, leading to the Hellenistic reconquest by the Greco-Bactrians. Much of it soon broke away from them and became part of the Indo-Greek Kingdom. They were defeated and expelled by the Indo-Scythians in the late 2nd century BCE.[3][28]
During the first century BCE, the Parthian Empire subjugated the region but lost it to their Indo-Parthian vassals. In the mid-to-late first century CE the vast Kushan Empire, centered in Afghanistan, became great patrons of Buddhist culture, making Buddhism flourish throughout the region. The Kushans were overthrown by the Sassanids in the 3rd century CE, though the Indo-Sassanids continued to rule at least parts of the region. They were followed by the Kidarites who, in turn, were replaced by the Hephthalites. They were replaced by the Turk Shahi in the 7th century. The Buddhist Turk Shahi of Kabul was replaced by a Hindu dynasty before the Saffarids conquered the area in 870, this Hindu dynasty was called Hindu Shahi.[29] Much of the northeastern and southern areas of the country remained dominated by Buddhist culture.[30][31]
Islamization and Mongol invasion


Arab Muslims brought Islam to Herat and Zaranj in 642 CE and began spreading eastward; some of the native inhabitants they encountered accepted it while others revolted. Before Islam was introduced, people of the region were mostly Buddhists and Zoroastrians, but there were also Surya and Nana worshipers, Jews, and others. The Zunbils and Kabul Shahi were first conquered in 870 CE by the Saffarid Muslims of Zaranj. Later, the Samanids extended their Islamic influence south of the Hindu Kush. It is reported that Muslims and non-Muslims still lived side by side in Kabul before the Ghaznavids rose to power in the 10th century.[32][33][34]
By the 11th century, Mahmud of Ghazni defeated the remaining Hindu rulers and effectively Islamized the wider region,[35] with the exception of Kafiristan.[36] Mahmud made Ghazni into an important city and patronized intellectuals such as the historian Al-Biruni and the poet Ferdowsi.[37] The Ghaznavid dynasty was overthrown by the Ghurids, whose architectural achievements included the remote Minaret of Jam. The Ghurids controlled Afghanistan for less than a century before being conquered by the Khwarazmian dynasty in 1215.[38]
In 1219 AD, Genghis Khan and his Mongol army overran the region. His troops are said to have annihilated the Khorasanian cities of Herat and Balkh as well as Bamyan.[39] The destruction caused by the Mongols forced many locals to return to an agrarian rural society.[40] Mongol rule continued with the Ilkhanate in the northwest while the Khalji dynasty administered the Afghan tribal areas south of the Hindu Kush until the invasion of Timur, who established the Timurid Empire in 1370.
In the early 16th century, Babur arrived from Fergana and captured Kabul from the Arghun dynasty. In 1526, he invaded Delhi in India to replace the Lodi dynasty with the Mughal Empire.[41] Between the 16th and 18th century, the Uzbek Khanate of Bukhara, Iranian Safavids, and Indian Mughals ruled parts of the territory.[42] Before the 19th century, the northwestern area of Afghanistan was referred to by the regional name Khorasan. Two of the four capitals of Khorasan (Herat and Balkh) are now located in Afghanistan, while the regions of Kandahar, Zabulistan, Ghazni, Kabulistan, and Afghanistan formed the frontier between Khorasan and Hindustan.[43][44][45]
Hotak dynasty and Durrani Empire
In 1709, Mirwais Hotak, a local Ghilzai tribal leader, successfully rebelled against the Safavids. He defeated Gurgin Khan and made Afghanistan independent.[46] Mirwais died of natural causes in 1715 and was succeeded by his brother Abdul Aziz, who was soon killed by Mirwais' son Mahmud for treason. Mahmud led the Afghan army in 1722 to the Persian capital of Isfahan, captured the city after the Battle of Gulnabad and proclaimed himself King of Persia.[46] The Afghan dynasty was ousted from Persia by Nader Shah after the 1729 Battle of Damghan.
In 1738, Nader Shah and his forces captured Kandahar, the last Hotak stronghold, from Shah Hussain Hotak, at which point the incarcerated 16-year-old Ahmad Shah Durrani was freed and made the commander of an Afghan regiment. Soon after, the Persian and Afghan forces invaded India. By 1747, the Afghans chose Durrani as their head of state.[47] Durrani and his Afghan army conquered much of present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan, the Khorasan and Kohistan provinces of Iran, and Delhi in India.[48] He defeated the Indian Maratha Empire, and one of his biggest victories was the 1761 Battle of Panipat.
In October 1772, Durrani died of natural causes and was buried at a site now adjacent to the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar. He was succeeded by his son, Timur Shah, who transferred the capital of Afghanistan from Kandahar to Kabul in 1776. After Timur's death in 1793, the Durrani throne passed down to his son Zaman Shah, followed by Mahmud Shah, Shuja Shah and others.[49]

By the early 19th century, the Afghan empire was under threat from the Persians in the west and the Sikh Empire in the east. Fateh Khan, leader of the Barakzai tribe, had installed 21 of his brothers in positions of power throughout the empire. After his death, they rebelled and divided up the provinces of the empire between themselves. During this turbulent period, Afghanistan had many temporary rulers until Dost Mohammad Khan declared himself emir in 1826.[50] The Punjab region was lost to Ranjit Singh, who invaded Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and in 1834 captured the city of Peshawar.[51] In 1837, during the Battle of Jamrud near the Khyber Pass, Akbar Khan and the Afghan army failed to capture the Jamrud fort from the Sikh Khalsa Army, but killed Sikh Commander Hari Singh Nalwa, thus ending the Afghan-Sikh Wars. By this time the British were advancing from the east and the first major conflict during "The Great Game" was initiated.[52]
British influence and independent kingdom

In 1838, the British marched into Afghanistan and arrested Dost Mohammad, sent him into exile in India and replaced him with the previous ruler, Shah Shuja.[53][54] Following an uprising, the 1842 retreat from Kabul of British-Indian forces and the annihilation of Elphinstone's army, and the Battle of Kabul that led to its recapture, the British placed Dost Mohammad Khan back into power and withdrew their military forces from Afghanistan. In 1878, the Second Anglo-Afghan War was fought over perceived Russian influence, Abdur Rahman Khan replaced Ayub Khan, and Britain gained control of Afghanistan's foreign relations as part of the Treaty of Gandamak of 1879. In 1893, Mortimer Durand made Amir Abdur Rahman Khan sign a controversial agreement in which the ethnic Pashtun and Baloch territories were divided by the Durand Line. This was a standard divide and rule policy of the British and would lead to strained relations, especially with the later new state of Pakistan. Shia-dominated Hazarajat and pagan Kafiristan remained politically independent until being conquered by Abdur Rahman Khan in 1891–1896.

After the Third Anglo-Afghan War and the signing of the Treaty of Rawalpindi on 19 August 1919, King Amanullah Khan declared Afghanistan a sovereign and fully independent state. He moved to end his country's traditional isolation by establishing diplomatic relations with the international community and, following a 1927–28 tour of Europe and Turkey, introduced several reforms intended to modernize his nation. A key force behind these reforms was Mahmud Tarzi, an ardent supporter of the education of women. He fought for Article 68 of Afghanistan's 1923 constitution, which made elementary education compulsory. The institution of slavery was abolished in 1923.[55]

Some of the reforms that were put in place, such as the abolition of the traditional burqa for women and the opening of several co-educational schools, quickly alienated many tribal and religious leaders, and this led to the Afghan Civil War (1928–1929). Faced with the overwhelming armed opposition, Amanullah Khan abdicated in January 1929, and soon after Kabul fell to Saqqawist forces led by Habibullah Kalakani.[56] Prince Mohammed Nadir Shah, Amanullah's cousin, in turn defeated and killed Kalakani in October 1929, and was declared King Nadir Shah.[57] He abandoned the reforms of Amanullah Khan in favor of a more gradual approach to modernization but was assassinated in 1933 by Abdul Khaliq, a fifteen-year-old Hazara student.[58]
Mohammed Zahir Shah, Nadir Shah's 19-year-old son, succeeded to the throne and reigned from 1933 to 1973. The tribal revolts of 1944–1947 saw Zahir Shah's reign being challenged by Zadran, Safi and Mangal tribesmen led by Mazrak Zadran and Salemai among others. Until 1946, Zahir Shah ruled with the assistance of his uncle, who held the post of Prime Minister and continued the policies of Nadir Shah. Another of Zahir Shah's uncles, Shah Mahmud Khan, became Prime Minister in 1946 and began an experiment allowing greater political freedom, but reversed the policy when it went further than he expected. He was replaced in 1953 by Mohammed Daoud Khan, the king's cousin and brother-in-law, and a Pashtun nationalist who sought the creation of a Pashtunistan, leading to highly tense relations with Pakistan.[59] During his ten years at the post until 1963, Daoud Khan pressed for social modernization reforms and sought a closer relationship with the Soviet Union. Afterward, the 1964 constitution was formed, and the first non-royal Prime Minister was sworn in.[60]
King Zahir Shah, like his father Nadir Shah, had a policy of maintaining national independence while pursuing gradual modernization, creating nationalist feeling, and improving relations with the United Kingdom. Close relations with the Muslim states Turkey, the Kingdom of Iraq and Iran/Persia were also pursued, while further international relations were sought by joining the League of Nations in 1934. The 1930s saw the development of roads, infrastructure, the founding of a national bank, and increased education. Road links in the north played a large part in a growing cotton and textile industry.[60] The country built close relationships with the Axis powers, with Germany having the largest share in Afghan development at the time.[61] However, Afghanistan remained neutral and was neither a participant in World War II nor aligned with either power bloc in the Cold War thereafter. However, it was a beneficiary of the latter rivalry as both the Soviet Union and the United States vied for influence by building Afghanistan's main highways, airports, and other vital infrastructure. On a per capita basis, Afghanistan received more Soviet development aid than any other country. Afghanistan had, therefore, good relations with both Cold War enemies. In 1973, while the King was on an official overseas visit, Daoud Khan launched a bloodless coup and became the first President of Afghanistan, abolishing the monarchy.
PDPA coup d'état and Soviet war


In April 1978, the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) seized power in the Saur Revolution, a coup d'état against then-President Mohammed Daoud Khan. The PDPA declared the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, with its first President named as Nur Muhammad Taraki.[62]
Opposition to PDPA reforms, such as its land redistribution policy and modernization of civil and marriage laws, led to unrest which became an open revolt by October 1978, first in eastern Afghanistan. That uprising quickly expanded into a civil war waged by guerrilla mujahideen against regime forces countrywide. The Pakistani government provided these rebels with covert training centers, while the Soviet Union sent thousands of military advisers to support the PDPA regime.[63] The United States supported Afghan mujahideen fighters through Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI).[64]
Meanwhile, increasing friction between the competing factions of the PDPA — the dominant Khalq and the more moderate Parcham — resulted (in July–August 1979) in the dismissal of Parchami cabinet members and the arrest of Parchami military officers under the pretext of a Parchami coup.[65]
In September 1979, President Taraki was assassinated in a coup within the PDPA orchestrated by fellow Khalq member Hafizullah Amin, who assumed the presidency. The situation in the country deteriorated under Amin and thousands of people went missing.[66] The Soviet Union was displeased with Amin's government and decided to intervene and invade the country on 24 December 1979, killing Amin just 3 days later, when the Soviet Army entered Kabul.[67]
A Soviet-organized regime, led by Parcham's Babrak Karmal but inclusive of both factions (Parcham and Khalq), filled the vacuum. Soviet troops in more substantial numbers were deployed to stabilize Afghanistan under Karmal, marking the beginning of the Soviet–Afghan War.[68] The United States continued to support the mujahideen through Pakistan's ISI[64] and Saudi Arabia, delivering billions of dollars in cash and weapons including two thousand FIM-92 Stinger surface-to-air missiles.[69][70]
The war lasted until 1989. Soviet forces, their Afghan proxies and rebels killed between 562,000[71] and 2 million Afghans,[72][73][74][75][76][77][78] and displaced about 6 million people who subsequently fled Afghanistan, mainly to Pakistan and Iran.[79] Many countryside villages were bombed and some cities such as Herat and Kandahar were also damaged from air bombardment. Pakistan's North-West Frontier Province functioned as an organisational and networking base for the anti-Soviet Afghan resistance, with the province's influential Deobandi ulama playing a major supporting role in promoting the 'jihad'.[80]
Faced with mounting international pressure and numerous casualties, the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan in 1989, but continued to support Afghan President Mohammad Najibullah until 1992.[81]
Proxy and civil war and Islamic jihad 1989–96
.png)
After the Soviet withdrawal, the conflict between the mujahideen and the PDPA continued.[82] President Najibullah, who had become president in 1987, tried to build support for his government by moving away from socialism to pan-Afghan nationalism and portraying his government as Islamic.[83]
Nevertheless, Najibullah did not win any significant support. In March 1989, mujahideen groups launched an attack on Jalalabad, instigated by the Pakistani ISI, but the attack failed.[84] With the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991 and the ending of Russian support, President Najibullah was left without foreign aid. In March 1991, mujahideen forces attacked and conquered the city of Khost.
In March 1992, President Najibullah agreed to step aside and make way for a mujahideen coalition government. At this time there were seven main mujahideen groups: Hezb-e Islami (Gulbuddin faction), Hezb-e Islami (Khalis faction), Jamiat-e Islami, Islamic Dawah Organisation of Afghanistan, the National Islamic Front for Afghanistan, the National Liberation Front, and the Islamic Revolution Movement. Their leaders came together in Peshawar, Pakistan, to negotiate a coalition government, but Hezbi Islami's leader Gulbuddin Hekmatyar refused to confer and instead invaded Kabul. This kicked off a civil war, starting 25 April 1992, between initially three, but within weeks five or six mujahideen groups.[85][86][87] Kabul was heavily bombarded and partially destroyed by the fighting.[88]

As the war continued in 1993–95, the mujahideen committed widespread rape, murder and extortion.[86][89][88] In January–June 1994, 25,000 people died in Kabul due to fighting between an alliance of Abdul Rashid Dostum's Junbish with Hekmatyar's Hezbi Islami against Ahmad Shah Massoud's Jamiat forces.[90] The Taliban emerged in September 1994 as a movement and militia of Pashtun students (talib) from Islamic madrassas (schools) in Pakistan,[88][91] pledged to rid Afghanistan of 'warlords and criminals',[92] and soon had military support from Pakistan.[93] In November 1994 the Taliban took control of Kandahar city after forcing out local Pashtun leaders.[88] The Taliban in early 1995 attempted to capture Kabul but were repelled by forces under Massoud. The Taliban grew stronger and in September 1996 attacked and occupied Kabul after Massoud and Hekmatyar had withdrawn their troops from the city.[94][95]
Taliban Emirate and Northern Alliance
In late September 1996, the Taliban, in control of Kabul and most of Afghanistan,[96] proclaimed the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. The Taliban were condemned internationally for the harsh enforcement of their interpretation of Islamic sharia law, which resulted in the brutal treatment of many Afghans, especially women.[97][98] During their rule, the Taliban and their allies committed massacres against Afghan civilians, denied UN food supplies to 160,000 starving civilians and conducted a policy of scorched earth, burning vast areas of fertile land and destroying tens of thousands of homes.[99][100][101][102][103][104]
After the fall of Kabul to the Taliban, Massoud and Dostum formed the Northern Alliance. The Taliban defeated Dostum's forces during the Battles of Mazar-i-Sharif (1997–98). Pakistan's Chief of Army Staff, Pervez Musharraf, began sending thousands of Pakistanis to help the Taliban defeat the Northern Alliance.[105][93][106][107][108] From 1996 to 2001, the al-Qaeda network of Osama bin Laden and Ayman al-Zawahiri was also operating inside Afghanistan.[109] Around 400,000 Afghans died in internal conflicts between 1990 and 2001.[110]
On 9 September 2001, Massoud was assassinated by two Arab suicide attackers in Panjshir province. Two days later, the 11 September attacks were carried out in the United States. The US government suspected Osama bin Laden as the perpetrator of the attacks, and demanded that the Taliban hand him over.[111] The Taliban offered to hand over Bin Laden to a third country for trial, but not directly to the US. Washington refused that offer.[112] Instead, the US launched the October 2001 Operation Enduring Freedom. The majority of Afghans supported the American invasion of their country.[113][114] During the initial invasion, US and UK forces bombed al-Qaeda training camps. Working with the Northern Alliance, the US removed the Taliban from power.[115]
Recent history (2002–present)


In December 2001, after the Taliban government was overthrown, the Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration and provide basic security.[116][117] Taliban forces meanwhile began regrouping inside Pakistan, while more coalition troops entered Afghanistan and began rebuilding the war-torn country.[118][119]
Shortly after their fall from power, the Taliban began an insurgency to regain control of Afghanistan. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban, but failed to fully defeat them. Afghanistan remains one of the poorest countries in the world due to a lack of foreign investment, government corruption, and the Taliban insurgency.[120][121]
Meanwhile, the Afghan government was able to build some democratic structures, and the country changed its name to the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. Attempts were made, often with the support of foreign donor countries, to improve the country's economy, healthcare, education, transport, and agriculture. ISAF forces also began to train the Afghan National Security Forces. Following 2002, nearly five million Afghans were repatriated.[122]
By 2009, a Taliban-led shadow government began to form in parts of the country.[123] In 2010, President Karzai attempted to hold peace negotiations with the Taliban leaders, but the rebel group refused to attend until mid-2015 when the Taliban supreme leader finally decided to back the peace talks.[124]
In September 2014 Ashraf Ghani became President after the 2014 presidential election where for the first time in Afghanistan's history power was democratically transferred.[125][126][127][128][129] On 28 December 2014, NATO formally ended ISAF combat operations in Afghanistan and transferred full security responsibility to the Afghan government. The NATO-led Operation Resolute Support was formed the same day as a successor to ISAF.[130][131] Thousands of NATO troops remained in the country to train and advise Afghan government forces[132] and continue their fight against the Taliban.[133] It was estimated in 2015 that "about 147,000 people have been killed in the Afghanistan war since 2001. More than 38,000 of those killed have been civilians".[134] A report titled Body Count concluded that 106,000–170,000 civilians have been killed as a result of the fighting in Afghanistan at the hands of all parties to the conflict.[135]
Geography

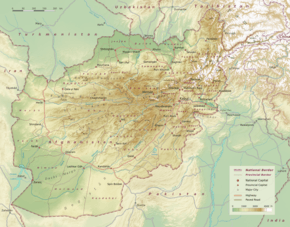
A landlocked mountainous country with plains in the north and southwest, Afghanistan is located at the crossroads of South Asia[137][138] and Central Asia.[139][140][141] The country's highest point is Noshaq, at 7,492 m (24,580 ft) above sea level.[8] It has a continental climate with harsh winters in the central highlands, the glaciated northeast (around Nuristan), and the Wakhan Corridor, where the average temperature in January is below −15 °C (5 °F), and hot summers in the low-lying areas of the Sistan Basin of the southwest, the Jalalabad basin in the east, and the Turkestan plains along the Amu River in the north, where temperatures average over 35 °C (95 °F) in July. The lowest point lies in Jowzjan Province along the Amu River bank, at 258 m (846 ft) above sea level.[8]

Despite having numerous rivers and reservoirs, large parts of the country are dry. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world.[142] Afghanistan receives snow during the winter in the Hindu Kush and Pamir Mountains, and the melting snow in the spring season enters the rivers, lakes, and streams.[143][144] However, two-thirds of the country's water flows into the neighboring countries of Iran, Pakistan, and Turkmenistan. The state needs more than US$2 billion to rehabilitate its irrigation systems so that the water is properly managed.[145]
The northeastern Hindu Kush mountain range, in and around the Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, is in a geologically active area where earthquakes may occur almost every year.[146] They can be deadly and destructive, causing landslides in some parts or avalanches during the winter.[147] The last strong earthquakes were in 1998, which killed about 6,000 people in Badakhshan near Tajikistan.[148] This was followed by the 2002 Hindu Kush earthquakes in which over 150 people were killed and over 1,000 injured. A 2010 earthquake left 11 Afghans dead, over 70 injured, and more than 2,000 houses destroyed.
The country's natural resources include: coal, copper, iron ore, lithium, uranium, rare earth elements, chromite, gold, zinc, talc, barite, sulfur, lead, marble, precious and semi-precious stones, natural gas, and petroleum, among other things.[149][150] In 2010, US and Afghan government officials estimated that untapped mineral deposits located in 2007 by the US Geological Survey are worth at least $1 trillion.[151]
At over 652,230 km2 (251,830 sq mi),[152] Afghanistan is the world's 41st largest country,[153] slightly bigger than France and smaller than Burma, about the size of Texas in the United States. It borders Pakistan in the south and east; Iran in the west; Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan in the north; and China in the far east.[154]
Demographics
| Year | Million | % growth rate (annual average) |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 7,752,117 | / |
| 1960 | 8,883,947 | +1.46% |
| 1970 | 10,893,772 | +2.26% |
| 1980 | 13,411,060 | +2.31% |
| 1990 | 11,869,873 | -1.15% |
| 2000 | 21,606,992 | +8.20% |
| 2010 | 29,185,511 | +3.51% |
| 2020 | 38,928,341 | +3.33% |
The population of Afghanistan was estimated at 38.0 million in 2019. About 23.9% of them are urbanite, 71.4% live in rural areas, and the remaining 4.7% are nomadic.[9] An additional 3 million or so Afghans are temporarily housed in neighboring Pakistan and Iran, most of whom were born and raised in those two countries. The current population growth rate is 2.37%,[8] one of the highest in the world outside of Africa. This population is expected to reach 82 million by 2050 if current population trends continue.[158]
The population of Afghanistan increased steadily until the 1980s, when civil war caused millions to flee to other countries such as Pakistan.[159] As of 2013, Afghanistan was the largest refugee-producing country in the world, a title held for 32 years.[160] Millions have since returned. Afghanistan's healthcare has improved since the turn of the century, causing falls in infant mortality and increases in life expectancy. This, combined with the average Afghan woman having at least 5 children, has led to a rapid population growth that has only started to recently slow down.
The only city with over a million residents is its capital, Kabul. After Kabul, the other five large cities are Kandahar, Herat, Mazar-i-Sharif, Kunduz and Jalalabad.[9]
Ethnic groups

Afghanistan's population is divided into several ethnolinguistic groups, which are represented in the ethnolinguistic map and listed in the chart below. The percentages given are estimates only, as accurate and current statistical data on ethnicity are not available.[8]
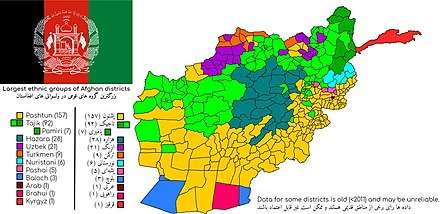
| Ethnic group | Library of Congress 2008 estimate[3] |
|---|---|
| Pashtun | 38% |
| Tajik | 27% |
| Hazara | 11% |
| Uzbek | 9% |
| Aimak | 4% |
| Turkmen | 2% |
| Baloch | 2% |
| others (Pashayi, Nuristani, Pamiri, Arab, etc.) | 4% |
Languages
Dari and Pashto are the official languages of Afghanistan; bilingualism is very common.[1] Dari, which is a variety of and mutually intelligible with Persian (and very often called 'Farsi' by some Afghans like in Iran) functions as the lingua franca in Kabul as well as in much of the northern and northwestern parts of the country.[1] Pashto is the native tongue of the Pashtuns, although many of them are also fluent in Dari while some non-Pashtuns are fluent in Pashto.
There are a number of smaller regional languages, they include Uzbek, Turkmen, Balochi, Pashayi, and Nuristani. Some Afghans are also fluent in Urdu, English, and other foreign languages.[162]
Religion
An estimated 99.7% of the Afghan population is Muslim.[8]
| Source | Sunni Islam | Shia Islam | other | just a Muslim |
Nothing, do not know, or no answer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pew Research Center[164] | 90% | 7% | 0% | 3% | 0% | |
| CIA Factbook (2009 estimate)[8] | 84.7 – 89.7% | 10 – 15% | 0.3% | |||
| Source | Sunni Islam | Imami Shia Islam | Ismaili Shia Islam | other | ||
| Dr Michael Izady[163] | 70% | 25% | 4.5% | 0.5% | ||
Thousands of Afghan Sikhs and Hindus are also found in the major cities.[165][166] There was a small Jewish community in Afghanistan who had emigrated to Israel and the United States by the end of the twentieth century; at least one Jew, Zablon Simintov, remained.[167] Afghan Christians, who number 500–8,000, practice their faith secretly due to intense societal opposition.[168][169]
Governance

Afghanistan is an Islamic republic consisting of three branches, the executive, legislative, and judicial. The nation is led by President Ashraf Ghani with Abdul Rashid Dostum and Sarwar Danish as vice presidents. Abdullah Abdullah serves as the chief executive officer (CEO). The National Assembly is the legislature, a bicameral body having two chambers, the House of the People and the House of Elders. The Supreme Court is led by Chief Justice Said Yusuf Halem, the former Deputy Minister of Justice for Legal Affairs.[170][171]
According to Transparency International, Afghanistan remains in the top most corrupt countries list.[172] A January 2010 report published by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime revealed that bribery consumed an amount equal to 23% of the GDP of the nation.[173]
Elections and parties
.jpg)
One instrument of Afghan governance is the loya jirga (grand assembly), a Pashtun consultative meeting that is mainly organized for choosing a new head of state, adopting a new constitution, or to settle national or regional issue such as war.[174] Loya jirgas have been held since at least 1747,[175] with the most recent one occurring in 2013.[176]
Under the 2004 constitution, both presidential and parliamentary elections are to be held every five years. However, due to the disputed 2014 presidential election, the scheduled 2015 parliamentary elections were delayed until 2018.[177] Presidential elections use the two-round system; if no candidate receives a majority of the vote in the first round, a second round will be held featuring the top two candidates. Parliamentary elections have only one round and are based on the single non-transferable vote system, which allows some candidates to be elected with as little as one percent of the vote.[178]
The 2004 Afghan presidential election was relatively peaceful, in which Hamid Karzai won in the first round with 55.4% of the votes. However, the 2009 presidential election was characterized by lack of security, low voter turnout, and widespread electoral fraud, ending in Karzai's reelection.[179] The 2014 presidential election ended with Ashraf Ghani winning by 56.44% of the votes.[180]
.jpg)
Political parties played a marginal role in post-2001 Afghan politics, in part due to Karzai's opposition to them.[181] In the 2005 parliamentary election, the ballots did not show candidates' party affiliation, so the results were dictated by the personal prestige of the candidates.[181] Among the elected officials were former mujahideen, Islamic fundamentalists, warlords, communists, reformists, and several Taliban associates.[182] In the same period, Afghanistan became the 30th highest nation in terms of female representation in the National Assembly.[183] Parties became more influential after 2009, when a new law established more stringent requirements for party registration.[184] Nearly a hundred new parties were registered after the law came into effect,[185] and party activity increased in the 2014 elections, but party influence remained limited.[186]
Administrative divisions
Afghanistan is administratively divided into 34 provinces (wilayats).[187] Each province is the size of a U.S. county, having a governor and a capital. The country is further divided into nearly 400 provincial districts, each of which normally covers a city or several villages. Each district is represented by a district governor.
The provincial governors are appointed by the President of Afghanistan, and the district governors are selected by the provincial governors.[188] The provincial governors are representatives of the central government in Kabul and are responsible for all administrative and formal issues within their provinces. There are also provincial councils that are elected through direct and general elections for four years.[189] The functions of provincial councils are to take part in provincial development planning and to participate in the monitoring and appraisal of other provincial governance institutions.
According to article 140 of the constitution and the presidential decree on electoral law, mayors of cities should be elected through free and direct elections for a four-year term. In practice however, mayors are appointed by the government.[190]
The following is a list of all the 34 provinces in alphabetical order:
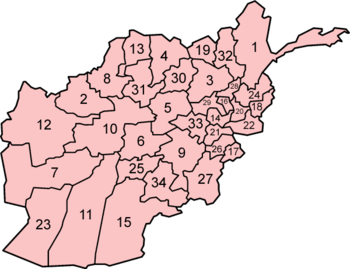
- Badakhshan
- Badghis
- Baghlan
- Balkh
- Bamyan
- Daykundi
- Farah
- Faryab
- Ghazni
- Ghor
- Helmand
- Herat
- Jowzjan
- Kabul
- Kandahar
- Kapisa
- Khost
- Kunar
- Kunduz
- Laghman
- Logar
- Nangarhar
- Nimruz
- Nuristan
- Oruzgan
- Paktia
- Paktika
- Panjshir
- Parwan
- Samangan
- Sar-e Pol
- Takhar
- Wardak
- Zabul
Foreign relations and military

Afghanistan became a member of the United Nations in 1946.[191] It enjoys cordial relations with a number of NATO and allied nations, particularly the United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, and Turkey. In 2012, the United States and Afghanistan signed their Strategic Partnership Agreement in which Afghanistan became a major non-NATO ally.[192] Afghanistan also has friendly diplomatic relations with neighboring China, Iran, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, including with regional states such as Bangladesh, India, Japan, Kazakhstan, Nepal, Russia, South Korea, the UAE, and so forth. The Afghan Ministry of Foreign Affairs continues to develop diplomatic relations with other countries around the world.
The United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) was established in 2002 to help the country recover from decades of war.[193] Today, several NATO member states deploy about 17,000 troops in Afghanistan as part of the Resolute Support Mission.[194] Its main purpose is to train the Afghan National Security Forces. The Afghan Armed Forces are under the Ministry of Defense, which includes the Afghan Air Force (AAF) and the Afghan National Army (ANA). The Afghan Defense University houses various educational establishments for the Afghan Armed Forces, including the National Military Academy of Afghanistan.[195]
Law enforcement

Law enforcement in Afghanistan is the responsibility of the Afghan National Police (ANP), which is part of the Ministry of Interior Affairs. The ANP consists of two primary branches, the Afghan Uniformed Police and the Afghan Border Police. The mission of the Uniformed Police is to ensure security within Afghanistan, prevent crime, and protect property. The Border Police is responsible for securing and maintaining the nation's borders with neighboring states as well as all international airports within the country.[196] Afghanistan's intelligence agency, the National Directorate of Security (NDS), assists the ANP with security matters.[197]
All parts of Afghanistan are considered dangerous due to militant activities and terrorism-related incidents. Kidnapping for ransom and robberies are common in major cities. Every year hundreds of Afghan police are killed in the line of duty.[198] Afghanistan is also the world's leading producer of opium.[199] Afghanistan's opium poppy harvest produces more than 90% of illicit heroin globally, and more than 95% of the European supply.[200][201] The Afghan Ministry of Counter Narcotics is responsible for the monitoring and eradication of the illegal drug business.
Human rights
Journalist in Afghanistan face threat from both the security forces and insurgents.[202] Afghan Journalists Safety Committee (AJSC) in 2017 claim that Afghan government accounted for 46% of the attacks on Afghans journalist, while insurgents were responsible for rest of the attacks.[203]
Homosexuality is illegal and is a capital offense in Afghanistan.[204]
Economy

Afghanistan's nominal GDP was $21.7 billion in 2018, or $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP).[10] Its GDP per capita is $2,024 (PPP).[10] Despite having $1 trillion or more in mineral deposits,[205] it remains one of the world's least developed countries. The country imports over $7 billion worth of goods but exports only $784 million, mainly fruits and nuts. It has $2.8 billion in external debt.[8]
Agricultural production is the backbone of Afghanistan's economy.[206] The country is known for producing pomegranates, grapes, apricots, melons, and several other fresh and dry fruits. It is also known as the world's largest producer of opium. As much as 16% or more of the nation's economy is derived from the cultivation and sale of opium.[207]

While the nation's current account deficit is largely financed with donor money, only a small portion is provided directly to the government budget. The rest is provided to non-budgetary expenditure and donor-designated projects through the United Nations system and non-governmental organizations.[208]
Da Afghanistan Bank serves as the central bank of the nation[209] and the "Afghani" (AFN) is the national currency, with an exchange rate of about 75 Afghanis to 1 US dollar.[210] A number of local and foreign banks operate in the country, including the Afghanistan International Bank, New Kabul Bank, Azizi Bank, Pashtany Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, and the First Micro Finance Bank.
One of the main drivers for the current economic recovery is the return of over 5 million expatriates, who brought with them entrepreneurship and wealth-creating skills as well as much needed funds to start up businesses. Many Afghans are now involved in construction, which is one of the largest industries in the country.[211] Some of the major national construction projects include the $35 billion New Kabul City next to the capital, the Aino Mena project in Kandahar, and the Ghazi Amanullah Khan Town near Jalalabad.[212][213][214] Similar development projects have also begun in Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, and other cities.[215] An estimated 400,000 people enter the labor market each year.[216]

Several small companies and factories began operating in different parts of the country, which not only provide revenues to the government but also create new jobs. Improvements to the business environment have resulted in more than $1.5 billion in telecom investment and created more than 100,000 jobs since 2003.[217] Afghan rugs are becoming popular again, allowing many carpet dealers around the country to hire more workers.
Afghanistan is a member of WTO, SAARC, ECO, and OIC. It holds an observer status in SCO.
Mining

Michael E. O'Hanlon of the Brookings Institution estimated that if Afghanistan generates about $10 billion per year from its mineral deposits, its gross national product would double and provide long-term funding for Afghan security forces and other critical needs.[218] The United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimated in 2006 that northern Afghanistan has an average 460 million m3 (2.9 billion bbl) of crude oil, 440 billion m3 (15.7 trillion cu ft) of natural gas, and 67 billion L (562 million US bbl) of natural gas liquids.[219] In 2011, Afghanistan signed an oil exploration contract with China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) for the development of three oil fields along the Amu Darya river in the north.[220]
The country has significant amounts of lithium, copper, gold, coal, iron ore, and other minerals.[149][150][221] The Khanashin carbonatite in Helmand Province contains 1,000,000 tonnes (980,000 long tons; 1,100,000 short tons) of rare earth elements.[222] In 2007, a 30-year lease was granted for the Aynak copper mine to the China Metallurgical Group for $3 billion,[223] making it the biggest foreign investment and private business venture in Afghanistan's history.[224] The state-run Steel Authority of India won the mining rights to develop the huge Hajigak iron ore deposit in central Afghanistan.[225] Government officials estimate that 30% of the country's untapped mineral deposits are worth at least $1 trillion.[151] One official asserted that "this will become the backbone of the Afghan economy" and a Pentagon memo stated that Afghanistan could become the "Saudi Arabia of lithium".[226] In a 2011 news story, the CSM reported, "The United States and other Western nations that have borne the brunt of the cost of the Afghan war have been conspicuously absent from the bidding process on Afghanistan's mineral deposits, leaving it mostly to regional powers."[227]
Transportation
Air

Air transport in Afghanistan is provided by the national carrier, Ariana Afghan Airlines,[228] and by the private company Kam Air. Airlines from a number of countries also provide flights in and out of the country. These include Air India, Emirates, Gulf Air, Iran Aseman Airlines, Pakistan International Airlines, and Turkish Airlines.
The country has four international airports: Hamid Karzai International Airport (formerly Kabul International Airport), Kandahar International Airport, Herat International Airport, and Mazar-e Sharif International Airport. Including domestic airports, there are 43.[8]
Rail

The country has three rail links: one, a 75-kilometer (47 mi) line from Mazar-i-Sharif to the Uzbekistan border;[229] a 10-kilometer (6.2 mi) long line from Toraghundi to the Turkmenistan border (where it continues as part of Turkmen Railways); and a short link from Aqina across the Turkmen border to Kerki, which is planned to be extended further across Afghanistan.[230] These lines are used for freight only and there is no passenger service. A rail line between Khaf, Iran and Herat, western Afghanistan, intended for both freight and passengers, is under construction as of 2019.[231][232] About 125 kilometers (78 mi) of the line will lie on the Afghan side.[233][234] There are various proposals for the construction of additional rail lines in the country.[235]
Roads
The most important road in Afghanistan is Highway 1, also called the Ring Road, which extends for 2,210 kilometers (1,370 mi) and connects four major cities: Kabul, Ghazni, Kandahar, and Herat.[236] A key portion of Highway 1 is the Salang Tunnel, completed in 1964, which facilitates travel through the Hindu Kush mountain range and connects northern and southern Afghanistan.[237] Traveling by bus in Afghanistan remains dangerous due to militant activities.[238] Serious traffic accidents are common on Afghan roads and highways, particularly on the Kabul–Kandahar and the Kabul–Jalalabad Road.[239]
Health

According to the Human Development Index, Afghanistan is the 15th least developed country in the world. The average life expectancy is estimated to be around 60 years.[240][241] The country's maternal mortality rate is 396 deaths/100,000 live births and its infant mortality rate is 66[241] to 112.8 deaths in every 1,000 live births.[8] The Ministry of Public Health plans to cut the infant mortality rate to 400 for every 100,000 live births before 2020. The country has more than 3,000 midwives, with an additional 300 to 400 being trained each year.[242]
There are over 100 hospitals in Afghanistan,[243] with the most advanced treatments being available in Kabul. The French Medical Institute for Children and Indira Gandhi Children's Hospital in Kabul are the leading children's hospitals in the country. Some of the other leading hospitals in Kabul include the Jamhuriat Hospital and Jinnah Hospital.[244] In spite of all this, many Afghans travel to Pakistan and India for advanced treatment.
It was reported in 2006 that nearly 60% of the Afghan population lives within a two-hour walk of the nearest health facility.[245] Disability rate is also high in Afghanistan due to the decades of war.[246] It was reported recently that about 80,000 people are missing limbs.[247][248] Non-governmental charities such as Save the Children and Mahboba's Promise assist orphans in association with governmental structures.[249] Demographic and Health Surveys is working with the Indian Institute of Health Management Research and others to conduct a survey in Afghanistan focusing on maternal death, among other things.[250]
Education
Education in Afghanistan includes K–12 and higher education, which is overseen by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education. There are over 16,000 schools in the country and roughly 9 million students. Of this, about 60% are males and 40% females. Over 174,000 students are enrolled in different universities around the country. About 21% of these are females.[251] Former Education Minister Ghulam Farooq Wardak had stated that construction of 8,000 schools is required for the remaining children who are deprived of formal learning.[252]
The top universities in Afghanistan are the American University of Afghanistan (AUAF) followed by Kabul University (KU), both of which are located in Kabul. The National Military Academy of Afghanistan, modeled after the United States Military Academy at West Point, is a four-year military development institution dedicated to graduating officers for the Afghan Armed Forces. The Afghan Defense University was constructed near Qargha in Kabul. Major universities outside of Kabul include Kandahar University in the south, Herat University in the northwest, Balkh University and Kunduz University in the north, Nangarhar University and Khost University in the east. The United States is building six faculties of education and five provincial teacher training colleges around the country, two large secondary schools in Kabul, and one school in Jalalabad.[251]
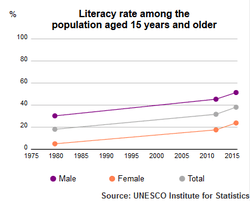
The literacy rate of the population is 38.2% (males 52% and females 24.2%).[8] The Afghan National Security Forces are provided with mandatory literacy courses.[253]
Culture


Afghanistan is a predominantly tribal society, with different regions of the country having their own cultures. In the southern and eastern region, the people live according to the Pashtun culture by following Pashtunwali (the Pashtun way).[254] Key tenets of Pashtunwali include hospitality, the provision of sanctuary to those seeking refuge, and revenge for the shedding of blood.[255] The Pashtuns (and Baloch) are largely connected to the culture of South Asia. The remaining Afghans are culturally Persian and Turkic. Some non-Pashtuns who live in proximity with Pashtuns have adopted Pashtunwali in a process called Pashtunization, while some Pashtuns have been Persianized. Those who have lived in Pakistan and Iran over the last 30 years have been further influenced by the cultures of those neighboring nations.
Afghans, particularly Pashtuns, are noted for their tribal solidarity and high regard for personal honor.[256] One writer considers the tribal system to be the best way of organizing large groups of people in a country that is geographically difficult, and in a society that, from a materialistic point of view, has an uncomplicated lifestyle.[257] There are various Afghan tribes, and an estimated 2–3 million nomads.[258] Afghan culture is deeply Islamic,[259] but pre-Islamic practices persist.[260] One example is bacha bazi, a term for activities involving sexual relations between older men and younger adolescent men, or boys.[261]
The nation has a complex history that has survived either in its current cultures or in the form of various languages and monuments. However, many of its historic monuments have been damaged in modern times.[262] The two famous Buddhas of Bamiyan were destroyed by the Taliban, who regarded them as idolatrous. Despite that, archaeologists are still finding Buddhist relics in different parts of the country, some of them dating back to the 2nd century.[263][264] This indicates that Buddhism was widespread in Afghanistan. Other historical places include the cities of Herat, Kandahar, Ghazni, Mazar-i-Sharif, and Zaranj. The Minaret of Jam in the Hari River valley is a UNESCO World Heritage site. A cloak reputedly worn by Islam's prophet Muhammad is kept inside the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar, a city founded by Alexander and the first capital of Afghanistan. The citadel of Alexander in the western city of Herat has been renovated in recent years and is a popular attraction for tourists. In the north of the country is the Shrine of Ali, believed by many to be the location where Ali was buried.[265] The National Museum of Afghanistan is located in Kabul.
Women
According to Global Rights, almost 90% of women in Afghanistan experience physical abuse, sexual abuse, psychological abuse or forced marriage. The perpetrators of these crimes are the families of the victim.[266] A 2009 proposal for a law against the violence of women could only be passed through a presidential decree.[266]
In 2012, Afghanistan recorded 240 cases of honor killing, but the total number is believed to be much higher. Of the reported honor killings, 21% were committed by the victims' husbands, 7% by their brothers, 4% by their fathers, and the rest by other relatives.[267][268]
Child marriage is prevalent in Afghanistan.[269] The legal age for marriage is 16.[270] The most preferred marriage in Afghan society is to one's parallel cousin, and the groom is often expected to pay a bride price.[271]
Media and entertainment

Afghanistan has around 350 radio stations and over 200 television stations.[272] which includes the state-owned RTA TV and various private channels such as TOLO and Shamshad TV. The first Afghan newspaper was published in 1873,[273] and there are hundreds of print outlets today.[272] By the 1920s, Radio Kabul was broadcasting local radio services.[274] Television programs began airing in the early 1970s. Voice of America, BBC, and Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) broadcast in both of Afghanistan's official languages.[275]
Since 2002, press restrictions have been gradually relaxed and private media diversified. Freedom of expression and the press is promoted in the 2004 constitution, and censorship is banned, although defaming individuals or producing material contrary to the principles of Islam is prohibited. In 2019, Reporters Without Borders listed the media environment of Afghanistan as 121st out of 179 on its Press Freedom Index, with 1st being most free.[276][277]
The city of Kabul has been home to many musicians who were masters of both traditional and modern Afghan music. Traditional music is especially popular during the Nowruz (New Year) and National Independence Day celebrations. Ahmad Zahir, Nashenas, Ustad Sarahang, Sarban, Ubaidullah Jan, Farhad Darya, and Naghma are some of the notable Afghan musicians, but there are many others.[278] Afghans have long been accustomed to watching Indian Bollywood films and listening to its filmi songs. Many Bollywood film stars have roots in Afghanistan, including Salman Khan, Saif Ali Khan, Shah Rukh Khan, Aamir Khan, Feroz Khan, Kader Khan, Naseeruddin Shah, Zarine Khan, Celina Jaitly, and a number of others. Several Bollywood films have been shot inside Afghanistan, including Dharmatma, Khuda Gawah, Escape from Taliban, and Kabul Express.
Communication
Telecommunication services in Afghanistan are provided by Afghan Telecom, Afghan Wireless, Etisalat, MTN Group, and Roshan. The country uses its own space satellite called Afghansat 1, which provides services to millions of phone, internet, and television subscribers. By 2001 following years of civil war, telecommunications was virtually a non-existent sector, but by 2016 it had grown to a $2 billion industry, with 22 million mobile phone subscribers and 5 million internet users. The sector employs at least 120,000 people nationwide.[279]
Cuisine

Afghan cuisine is largely based upon the nation's chief crops, such as wheat, maize, barley and rice. Accompanying these staples are native fruits and vegetables as well as dairy products such as milk, yogurt and whey. Kabuli palaw is the national dish of Afghanistan.[280] The nation's culinary specialties reflect its ethnic and geographic diversity.[281] Afghanistan is known for its high quality pomegranates, grapes, and sweet melons.[282]
Poetry
Classic Persian and Pashto poetry are a cherished part of Afghan culture. Thursdays are traditionally "poetry night" in the city of Herat when men, women and children gather and recite both ancient and modern poems.[283] Poetry has always been one of the major educational pillars in the region, to the level that it has integrated itself into culture. Some notable poets include Rumi, Rabi'a Balkhi, Sanai, Jami, Khushal Khan Khattak, Rahman Baba, Khalilullah Khalili, and Parween Pazhwak.[284]
Sports
_vs_Jeje_Lalpekhlua_(in_blue_uniform).jpg)
.jpg)
Sport in Afghanistan is managed by the Afghan Sports Federation. Cricket and association football are the two most popular sports in the country.[285][286] The Afghan Sports Federation promotes cricket, association football, basketball, volleyball, golf, handball, boxing, taekwondo, weightlifting, bodybuilding, track and field, skating, bowling, snooker, chess, and other sports.
Afghanistan's sports teams are increasingly celebrating titles at international events. Its basketball team won the first team sports title at the 2010 South Asian Games.[287] Later that year, the country's cricket team followed as it won the 2009–10 ICC Intercontinental Cup.[288] In 2012, the country's 3x3 basketball team won the gold medal at the 2012 Asian Beach Games. In 2013, Afghanistan's football team followed as it won the SAFF Championship.[289]
The Afghan national cricket team, which was formed in 2001, participated in the 2009 ICC World Cup Qualifier, 2010 ICC World Cricket League Division One and the 2010 ICC World Twenty20. It won the ACC Twenty20 Cup in 2007, 2009, 2011 and 2013. The team eventually made it and played in the 2015 Cricket World Cup.[290] The Afghanistan Cricket Board (ACB) is the official governing body of the sport and is headquartered in Kabul. The Alokozay Kabul International Cricket Ground serves as the nation's main cricket stadium. There are several other stadiums throughout the country, including the Ghazi Amanullah Khan International Cricket Stadium near Jalalabad. Domestically, cricket is played between teams from different provinces.
The Afghanistan national football team has been competing in international football since 1941.[291] The national team plays its home games at the Ghazi Stadium in Kabul, while football in Afghanistan is governed by the Afghanistan Football Federation. The national team has never competed or qualified for the FIFA World Cup but has recently won an international football trophy in 2013.[289] The country also has a national team in the sport of futsal, a 5-a-side variation of football.
The traditional and the national sport of Afghanistan is buzkashi, mainly popular among the northern Afghans. It is similar to polo, played by horsemen in two teams, each trying to grab and hold a goat carcass.[292] The Afghan Hound (a type of running dog) originated in Afghanistan and was formerly used in wolf hunting. In 2002, traveler Rory Stewart reported that dogs were still used for wolf hunting in remote areas.[293]
See also
- Index of Afghanistan-related articles
- Outline of Afghanistan
Notes
- The phoneme /f/ ف occurs only in loanwords in Pashto, it tends to be replaced with /p/ پ. [b] is also an allophone of /p/ before voiced consonants; [v] is an allophone of /f/ before voiced consonants in loanwords.
- Afghanistan is regarded as a border country also by the Government of India, which considers all of Kashmir to be part of India. However, this is disputed, and the region of Kashmir bordering Afghanistan is administered by Pakistan. Source: "Ministry of Home Affairs (Department of Border Management)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
References
- "Article Sixteen of the 2004 Constitution of Afghanistan". 2004. Archived from the original on 28 October 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
Pashto and Dari are the official languages of the state. Uzbek, Turkmen, Baluchi, Pashai, Nuristani and Pamiri are – in addition to Pashto and Dari – the third official language in areas where the majority speaks them
- "South Asia :: Afghanistan – the World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency".
- "Country Profile: Afghanistan" (PDF). Library of Congress Country Studies on Afghanistan. August 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- Dictionary.com. The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2004. Reference.com (Retrieved 13 November 2007).
- Dictionary.com. WordNet 3.0. Princeton University. Reference.com (Retrieved 13 November 2007). Archived 28 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- "Constitution of Afghanistan". 2004. Archived from the original on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- Afghan | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary. the Cambridge English Dictionary. ISBN 9781107660151.
- "Afghanistan". The World Factbook. cia.gov. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
- "Afghan Population Estimates 1398" (PDF). Central Statistics Organization. 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 June 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- "Afghanistan". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 14 November 2018.
- "Gini Index". World Bank. Archived from the original on 11 May 2014. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- "Human Development Report 2019". United Nations Development Programme. 10 December 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 March 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- Tomsen, Peter (2014), The Wars of Afghanistan, pp. 41–2, ISBN 978-1610392624
- Rashid, Ahmed (2000), Taliban, p. 187, ISBN 1 86064 417 1
- Vogelsang, Willem (2002). The Afghans. Wiley Blackwell. p. 18. ISBN 0-631-19841-5. Archived from the original on 9 July 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- Ch. M. Kieffer (15 December 1983). "Afghan". Encyclopædia Iranica (online ed.). Columbia University. Archived from the original on 16 November 2013.
- Barfield 2012, p. 159.
- Afghanistan – John Ford Shroder, University of Nebraska. Encarta. Archived from the original on 17 July 2004. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- "Afghanistan: A Treasure Trove for Archaeologists". Time. 26 February 2009. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- George Erdosy (1995). The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia: Language, Material Culture and Ethnicity. p. 321. ISBN 3110144476.
- Barfield 2012, p. 255.
- Nordland, Rod (29 August 2017). "The Empire Stopper". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 5 December 2018. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
Afghanistan has long been called the "graveyard of empires" — for so long that it is unclear who coined that disputable term.
- Runion 2007, p. 44-49.
- Rita Wright (2009). The Ancient Indus: Urbanism, Economy, and Society. p. 1. ISBN 978-0521576529. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- Kenoyer, Jonathan Mark (1998). Ancient cities of the Indus Valley Civilisation. pp.96
- Bryant, Edwin F. (2001) The quest for the origins of Vedic culture: the Indo-Aryan migration debate Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-513777-4.
- "Chronological History of Afghanistan – the cradle of Gandharan civilisation". Gandhara.com.au. 15 February 1989. Archived from the original on 9 September 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- Runion 2007, p. 44.
- Wink, André (2002). Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: Early Medieval India and the Expansion of Islam 7Th-11th Centuries. BRILL. p. 125. ISBN 0-391-04173-8. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- "Afghan and Afghanistan". Abdul Hai Habibi. alamahabibi.com. 1969. Archived from the original on 23 October 2008. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- Charles Higham (2014). Encyclopedia of Ancient Asian Civilizations. Infobase Publishing. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-4381-0996-1.
- "A.—The Hindu Kings of Kábul". Sir H. M. Elliot. London: Packard Humanities Institute. 1867–1877. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2010.
- Hamd-Allah Mustawfi of Qazwin (1340). "The Geographical Part of the NUZHAT-AL-QULUB". Translated by Guy Le Strange. Packard Humanities Institute. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 19 August 2011.
- "A.—The Hindu Kings of Kábul (p.3)". Sir H. M. Elliot. London: Packard Humanities Institute. 1867–1877. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 18 September 2010.
- Ewans 2002, p. 22-23.
- Richard F. Strand (31 December 2005). "Richard Strand's Nuristân Site: Peoples and Languages of Nuristan". nuristan.info. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- Richard Nyrop; Donald Seekins, eds. (1986). Afghanistan: A Country Study. Foreign Area Studies, The American University. p. 10.
- Ewans 2002, p. 23.
- "Central Asian world cities". Faculty.washington.edu. 29 September 2007. Archived from the original on 23 July 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- Page, Susan (18 February 2009). "Obama's war: Deploying 17,000 raises stakes in Afghanistan". USA Today. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- Barfield, 2012 & 92–93.
- Dupree 1997, pp. 319, 321.
- "Khurasan". The Encyclopaedia of Islam. Brill. 2009. p. 55.
In pre-Islamic and early Islamic times, the term "Khurassan" frequently had a much wider denotation, covering also parts of what are now Soviet Central Asia and Afghanistan
- Ibn Battuta (2004). Travels in Asia and Africa, 1325–1354 (reprint, illustrated ed.). Routledge. p. 416. ISBN 978-0-415-34473-9. Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah (1560). "Chapter 200: Translation of the Introduction to Firishta's History". The History of India. 6. Sir H. M. Elliot. London: Packard Humanities Institute. p. 8. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- Edward G. Browne. "A Literary History of Persia, Volume 4: Modern Times (1500–1924), Chapter IV. An Outline of the History Of Persia During The Last Two Centuries (A.D. 1722–1922)". Packard Humanities Institute. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 9 September 2010.
- "Ahmad Shah Durrani". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Archived from the original on 4 April 2014. Retrieved 9 September 2010.
- Friedrich Engels (1857). "Afghanistan". Andy Blunden. The New American Cyclopaedia, Vol. I. Archived from the original on 27 April 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- The Oxford Dictionary of Islam by John L. Esposito, p.71
- Tanner, Stephen (2009). Afghanistan: A Military History from Alexander the Great to the War against the Taliban. Da Capo Press. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-306-81826-4.
- Nalwa, Vanit (2009). Hari Singh Nalwa, "champion of the Khalsaji" (1791–1837). p. 198. ISBN 978-81-7304-785-5.
- Chahryar, Adle (2003). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: Development in contrast: from the sixteenth to the mid-nineteenth century. UNESCO. p. 296. ISBN 978-92-3-103876-1.
- Ingram, Edward (1980). "Great Britain's Great Game: An Introduction". The International History Review. 2 (2): 160–171. doi:10.1080/07075332.1980.9640210. JSTOR 40105749. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016.
- In Defence of British India: Great Britain in the Middle East, 1775–1842 Archived 6 January 2017 at the Wayback Machine By Edward Ingram. Frank Cass & Co, London, 1984. ISBN 0714632465. p7-19
- "Afghanistan". Encyclopedia Americana. 25. Americana Corporation. 1976. p. 24.
- Muḥammad, Fayz̤; McChesney, R. D. (1999). Kabul under siege: Fayz Muhammad's account of the 1929 Uprising. Markus Wiener Publishers. pp. 39, 40. ISBN 9781558761544. Archived from the original on 4 April 2019. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- Muḥammad, Fayz̤; McChesney, R. D. (1999). Kabul under siege: Fayz Muhammad's account of the 1929 Uprising. Markus Wiener Publishers. pp. 275, 276. ISBN 9781558761544. Archived from the original on 4 April 2019. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- Hafizullah, Emadi (2005). Culture and customs of Afghanistan. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 35. ISBN 0-313-33089-1. Archived from the original on 25 February 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- Ron Synovitz (18 July 2003). "Afghanistan: History Of 1973 Coup Sheds Light On Relations With Pakistan". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 26 June 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- Eur (2002). The Far East and Australasia 2003. Psychology Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-85743-133-9.
- Anthony Hyman (27 July 2016). Afghanistan under Soviet Domination, 1964–91. Springer. p. 46. ISBN 978-1-349-21948-3.
- Ewans 2002, p. 186-88.
- Hussain, Rizwan (2005). Pakistan and the Emergence of Islamic Militancy in Afghanistan. Ashgate Publishing. pp. 108–109. ISBN 978-0-7546-4434-7.
- Meher, Jagmohan (2004). America's Afghanistan War: The Success that Failed. Gyan Books. pp. 68–69, 94. ISBN 978-81-7835-262-6.
- Rasanayagam, Angelo (2005). Afghanistan: A Modern History. I.B.Tauris. p. 73. ISBN 978-1850438571. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- "Afghanistan: 20 years of bloodshed". BBC. 26 April 1998. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- Barfield 2012, p. 234.
- Kalinovsky, Artemy M. (2011). A Long Goodbye: The Soviet Withdrawal from Afghanistan. Harvard University Press. pp. 25–28. ISBN 978-0-674-05866-8.
- "Story of US, CIA and Taliban". The Brunei Times. 2009. Archived from the original on 5 December 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- "The Cost of an Afghan 'Victory'". The Nation. 1999. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- Lacina, Bethany; Gleditsch, Nils Petter (2005). "Monitoring Trends in Global Combat: A New Dataset of Battle Deaths" (PDF). European Journal of Population. 21 (2–3): 154. doi:10.1007/s10680-005-6851-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- Kakar, Mohammed (3 March 1997). The Soviet Invasion and the Afghan Response, 1979–1982. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520208933. Archived from the original on 6 January 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2017.
The Afghans are among the latest victims of genocide by a superpower. Large numbers of Afghans were killed to suppress resistance to the army of the Soviet Union, which wished to vindicate its client regime and realize its goal in Afghanistan.
- Klass, Rosanne (1994). The Widening Circle of Genocide. Transaction Publishers. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-4128-3965-5.
During the intervening fourteen years of Communist rule, an estimated 1.5 to 2 million Afghan civilians were killed by Soviet forces and their proxies- the four Communist regimes in Kabul, and the East Germans, Bulgarians, Czechs, Cubans, Palestinians, Indians and others who assisted them. These were not battle casualties or the unavoidable civilian victims of warfare. Soviet and local Communist forces seldom attacked the scattered guerilla bands of the Afghan Resistance except, in a few strategic locales like the Panjsher valley. Instead they deliberately targeted the civilian population, primarily in the rural areas.
- Reisman, W. Michael; Norchi, Charles H. "Genocide and the Soviet Occupation of Afghanistan" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 October 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2017.
According to widely reported accounts, substantial programmes of depopulation have been conducted in these Afghan provinces: Ghazni, Nagarhar, Lagham, Qandahar, Zabul, Badakhshan, Lowgar, Paktia, Paktika and Kunar...There is considerable evidence that genocide has been committed against the Afghan people by the combined forces of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and the Soviet Union.
- Goodson, Larry P. (2001). Afghanistan's Endless War: State Failure, Regional Politics, and the Rise of the Taliban. University of Washington Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-295-98050-8.
- "Soldiers of God: Cold War (Part 1/5)". CNN. 1998. Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- UNICEF, Land-mines: A deadly inheritance Archived 5 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Landmines in Afghanistan: A Decades Old Danger". Defenseindustrydaily.com. 1 February 2010. Archived from the original on 11 January 2014. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- "Refugee Admissions Program for Near East and South Asia". Bureau of Population, Refugees, and Migration. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- Haroon, Sana (2008). "The Rise of Deobandi Islam in the North-West Frontier Province and Its Implications in Colonial India and Pakistan 1914–1996". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society. 18 (1): 66–67. doi:10.1017/S1356186307007778. JSTOR 27755911.
- "Afghanistan: History – Columbia Encyclopedia". Infoplease.com. 11 September 2001. Archived from the original on 10 August 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 'Mujahidin vs. Communists: Revisiting the battles of Jalalabad and Khost Archived 2 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. By Anne Stenersen: a Paper presented at the conference COIN in Afghanistan: From Mughals to the Americans, Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO), 12–13 February 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2018.
- Barfield 2012, pp. 239, 244.
- Barfield 2012, p. 241.
- Amin Saikal (13 November 2004). Modern Afghanistan: A History of Struggle and Survival (2006 1st ed.). I.B. Tauris & Co Ltd., London New York. p. 352. ISBN 978-1-85043-437-5.
- "Blood-Stained Hands, Past Atrocities in Kabul and Afghanistan's Legacy of Impunity". Human Rights Watch. 7 July 2005. Archived from the original on 12 December 2009.
- GUTMAN, Roy (2008): How We Missed the Story: Osama Bin Laden, the Taliban and the Hijacking of Afghanistan, Endowment of the United States Institute of Peace, 1st ed., Washington D.C.
- "Afghanistan: The massacre in Mazar-i Sharif. (Chapter II: Background)". Human Rights Watch. November 1998. Archived from the original on 2 November 2008. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- "Casting Shadows: War Crimes and Crimes against Humanity: 1978–2001" (PDF). Afghanistan Justice Project. 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- "Casting Shadows: War Crimes and Crimes against Humanity: 1978–2001" (PDF). Afghanistan Justice Project. 2005. p. 63. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- Matinuddin, Kamal, The Taliban Phenomenon, Afghanistan 1994–1997, Oxford University Press, (1999), pp. 25–26
- 'The Taliban' Archived 11 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Mapping Militant Organizations. Stanford University. Updated 15 July 2016. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
- "Documents Detail Years of Pakistani Support for Taliban, Extremists". George Washington University. 2007. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013.
- Afghanistan: Chronology of Events January 1995 – February 1997 (PDF) (Report). Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada. February 1997. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- Coll, Ghost Wars (New York: Penguin, 2005), 14.
- Country profile: Afghanistan (published August 2008) Archived 25 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine (page 3). Library of Congress. Retrieved 13 February 2018.
- Skain, Rosemarie (2002). The women of Afghanistan under the Taliban. McFarland. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7864-1090-3.
-
- James Gerstenzan; Lisa Getter (18 November 2001). "Laura Bush Addresses State of Afghan Women". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 10 October 2012. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- "Women's Rights in the Taliban and Post-Taliban Eras". A Woman Among Warlords. PBS. 11 September 2007. Archived from the original on 14 January 2013. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- Rashid, Ahmed (2002). Taliban: Islam, Oil and the New Great Game in Central Asia. I.B.Tauris. p. 253. ISBN 978-1-86064-830-4.
- Gargan, Edward A (October 2001). "Taliban massacres outlined for UN". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on 16 September 2011. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- "Confidential UN report details mass killings of civilian villagers". Newsday. newsday.org. 2001. Archived from the original on 18 November 2002. Retrieved 12 October 2001.
- U.N. says Taliban starving hungry people for military agenda, Associated Press, 7 January 1998, archived from the original on 13 September 2018, retrieved 7 July 2019
- Goodson, Larry P. (2002). Afghanistan's Endless War: State Failure, Regional Politics and the Rise of the Taliban. University of Washington Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-295-98111-6.
- "Re-Creating Afghanistan: Returning to Istalif". NPR. 1 August 2002. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013.
- Marcela Grad. Massoud: An Intimate Portrait of the Legendary Afghan Leader (1 March 2009 ed.). Webster University Press. p. 310.
- "Ahmed Shah Massoud". History Commons. 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- Maley, William (2009). The Afghanistan wars. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 288. ISBN 978-0-230-21313-5.
- Rashid, Ahmed (11 September 2001). "Afghanistan resistance leader feared dead in blast". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013.
- "Brigade 055". CNN. Archived from the original on 29 July 2013.
- "Life under Taliban cuts two ways". CSM. 20 September 2001 Archived 30 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Rory McCarthy in Islamabad (17 October 2001). "New offer on Bin Laden". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 28 June 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- 'Trump calls out Pakistan, India as he pledges to 'fight to win' in Afghanistan Archived 1 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. CNN, 24 August 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- "WPO Poll: Afghan Public Overwhelmingly Rejects al-Qaeda, Taliban". 30 January 2006. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2017.
Equally large percentages endorse the US military presence in Afghanistan. Eighty-three percent said they have a favorable view of "the US military forces in our country" (39% very favorable). Just 17% have an unfavorable view.
- "Afghan Futures: A National Public Opinion Survey" (PDF). 29 January 2015. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 March 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2017.
Seventy-seven percent support the presence of U.S. forces; 67 percent say the same of NATO/ISAF forces more generally. Despite the country’s travails, eight in 10 say it was a good thing for the United States to oust the Taliban in 2001. And much more blame either the Taliban or al Qaeda for the country’s violence, 53 percent, than blame the United States, 12 percent. The latter is about half what it was in 2012, coinciding with a sharp reduction in the U.S. deployment.
- Tyler, Patrick (8 October 2001). "A Nation challenged: The attack; U.S. and Britain strike Afghanistan, aiming at bases and terrorist camps; Bush warns 'Taliban will pay a price'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 April 2014. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1386. S/RES/1386(2001) 31 May 2001. Retrieved 21 September 2007. – (UNSCR 1386)
- "United States Mission to Afghanistan". Nato.usmission.gov. Archived from the original on 21 October 2010. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- Fossler, Julie. "USAID Afghanistan". Afghanistan.usaid.gov. Archived from the original on 17 October 2010. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- "Canada's Engagement in Afghanistan: Backgrounder". Afghanistan.gc.ca. 9 July 2010. Archived from the original on 15 December 2010. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- "Pakistan Accused of Helping Taliban". ABC News. 31 July 2008. Archived from the original on 21 December 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- Crilly, Rob; Spillius, Alex (26 July 2010). "Wikileaks: Pakistan accused of helping Taliban in Afghanistan attacks". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 29 January 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- Howard Adelman (15 April 2016). Protracted Displacement in Asia: No Place to Call Home. Taylor & Francis. p. 167. ISBN 978-1-317-07407-6.
- Witte, Griff (8 December 2009). "Taliban shadow officials offer concrete alternative". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 16 May 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- Mirwais Khan (15 July 2015). "Afghan Taliban leader backs peace talks with Kabul officials". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 6 August 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- Note: It later came to light that Mullah Omar died in 2013.
- See also: Mullah Omar: Taliban leader 'died in Pakistan in 2013' Archived 3 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- See also: Afghanistan says Taliban leader Mullah Omar died 2 years ago Archived 2 August 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- "Huge security as Afghan presidential election looms". BBC. 4 April 2014. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 21 October 2018.
- "Afghanistan votes in historic presidential election". BBC. 5 April 2014. Archived from the original on 21 October 2018. Retrieved 21 October 2018.
- Shalizi and Harooni, Hamid and Mirwais (4 April 2014). "Landmark Afghanistan Presidential Election Held Under Shadow of Violence". HuffPost. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2018.
- "Afghanistan's Future: Who's Who in Pivotal Presidential Election". NBC News. Archived from the original on 30 September 2019. Retrieved 7 October 2019.
- "Afghan president Ashraf Ghani inaugurated after bitter campaign". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 21 April 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "U.S. formally ends the war in Afghanistan" (online). CBA News. Associated Press. 28 December 2014. Archived from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- Sune Engel Rasmussen in Kabul (28 December 2014). "Nato ends combat operations in Afghanistan". The Guardian. Kabul. Archived from the original on 2 January 2015. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- "U.S. formally ends the war in Afghanistan". CBS News. Archived from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "TSG IntelBrief: Afghanistan 16.0". The Soufan Group. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- "Afghan Civilians". Brown University. 2015. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
-
- "Body Count – Casualty Figures after 10 Years of the 'War on Terror' – Iraq Afghanistan Pakistan" Archived 30 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine (PDF), by IPPNW, PGS and PSR, First international edition (March 2015)
- Gabriela Motroc (7 April 2015). "U.S. War on Terror has reportedly killed 1.3 million people in a decade". Australian National Review. Archived from the original on 5 May 2015.
- "220,000 killed in US war in Afghanistan 80,000 in Pakistan: report". Daily Times. 30 March 2015. Archived from the original on 5 May 2015.
- Beck, Hylke E.; Zimmermann, Niklaus E.; McVicar, Tim R.; Vergopolan, Noemi; Berg, Alexis; Wood, Eric F. (30 October 2018). "Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution". Scientific Data. 5: 180214. Bibcode:2018NatSD...580214B. doi:10.1038/sdata.2018.214. PMC 6207062. PMID 30375988.
-
- "U.S. maps". Pubs.usgs.gov. Archived from the original on 25 December 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- "South Asia: Data, Projects, and Research". Archived from the original on 1 March 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- "MAPS SHOWING GEOLOGY, OIL AND GAS FIELDS AND GEOLOGICAL PROVINCES OF SOUTH ASIA (Includes Afghanistan)". Archived from the original on 25 December 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- "University of Washington Jackson School of International Studies: The South Asia Center". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- "Syracruse University: The South Asia Center". 26 March 2013. Archived from the original on 26 March 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- "Center for South Asian studies". Archived from the original on 11 December 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings". UNdata. 26 April 2011. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- "Afghanistan". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 25 February 2010. Retrieved 17 March 2010.
- Tan, Anjelica (18 February 2020). "A new strategy for Central Asia". TheHill.
, as Afghan President Ashraf Ghani has noted, Afghanistan is itself a Central Asian country.
- Afghanistan | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary. Cambridge University. ISBN 9781107619500.
- "History of Environmental Change in the Sistan Basin 1976–2005" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 20 July 2007.
- "Snow in Afghanistan: Natural Hazards". NASA. 3 February 2006. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- "Snow may end Afghan drought, but bitter winter looms". Reuters. 18 January 2012. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013.
- "Afghanistan's woeful water management delights neighbors". The Christian Science Monitor. 15 June 2010. Archived from the original on 14 November 2010. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- Crone, Anthony J. (April 2007). Earthquakes Pose a Serious Hazard in Afghanistan (PDF) (Technical report). US Geological Survey. Fact Sheet FS 2007–3027. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "Earthquake Hazards". USGS Projects in Afghanistan. US Geological Survey. 1 August 2011. Archived from the original on 4 October 2011. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "'Seven dead' as earthquake rocks Afghanistan". BBC News. 19 April 2010. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- Peters, Steven G. (October 2007). Preliminary Assessment of Non-Fuel Mineral Resources of Afghanistan, 2007 (PDF) (Technical report). USGS Afghanistan Project/US Geological Survey/Afghanistan Geological Survey. Fact Sheet 2007–3063. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "Minerals in Afghanistan" (PDF). British Geological Survey. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2010.
- "Afghans say US team found huge potential mineral wealth". BBC News. 14 June 2010. Archived from the original on 9 August 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "Land area (sq. km)". World Development Indicators. World Bank. 2011. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "CIA Factbook – Area: 41". CIA. 26 November 1991. Archived from the original on 31 January 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- Cary Gladstone (2001). Afghanistan Revisited. Nova Publishers. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-59033-421-8.
- "STATE OF AFGHAN CITIES -2015 VOLUME ONE" (PDF). samuelhall.org. Ministry of Urban Development Affairs.
- ""World Population prospects – Population division"". population.un.org. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ""Overall total population" – World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision" (xslx). population.un.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- "Afghanistan – Population Reference Bureau". Population Reference Bureau. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2009.
- Wickramasekara, P., Sehgal, J., Mehran, F., Noroozi, L., Eisazadeh (2006). Afghan Households in Iran: Profile and Impact. UNHCR-ILO Cooperation. http://www.unhcr.org/455835d92.pdf
- "Afghan Population Estimates 1398" (PDF). Central Statistics Organization. 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- The Asia Foundation. Afghanistan in 2018: A Survey of the Afghan People. Archived 7 August 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- Izady, Michael (2002–2017). "Chapter 1: Religious Composition of Afghanistan". Gulf2000.columbia.edu. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
- "Chapter 1: Religious Affiliation". The World's Muslims: Unity and Diversity. Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 9 August 2012. Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
- Lavina Melwani. "Hindus Abandon Afghanistan". Hinduism Today. Archived from the original on 11 January 2007. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- Majumder, Sanjoy (25 September 2003). "Sikhs struggle in Afghanistan". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 February 2009. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- N.C. Aizenman (27 January 2005). "Afghan Jew Becomes Country's One and Only". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 16 May 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- USSD Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (2009). "International Religious Freedom Report 2009". Archived from the original on 30 November 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2010.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Christians in Afghanistan: A Community of Faith and Fear". Der Spiegel. 20 March 2006. Archived from the original on 27 January 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- "The Supreme Court Chief Justice Biography". supremecourt.gov.af. Archived from the original on 3 October 2015.
- "Database". afghan-bios.info. Archived from the original on 2 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- "Corruption Perceptions Index 2016 Results". Transparency International. Archived from the original on 25 January 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- "Corruption widespread in Afghanistan, UNODC survey says". UNODC.org. 19 January 2010. Archived from the original on 16 April 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- "Q&A: What is a loya jirga?". BBC News. 1 July 2002. Archived from the original on 23 May 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- Barfield 2012, p. 295.
- "Loya jirga approves U.S.-Afghan security deal; asks Karzai to sign". CNN. 17 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2 June 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- "Afghans defy deadly poll violence". BBC News. 21 October 2018. Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 16 November 2018.
- "Afghanistan's "Lottery Effect"". Afghan 2010. Archived from the original on 10 January 2015. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- Cooper, Helene (2 November 2009). "Karzai Gets New Term as Afghan Runoff is Scrapped". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- "2014 Afghanistan Election Results". Independent Election Commission of Afghanistan. Archived from the original on 6 June 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- Barfield 2012, p. 301.
- "RAWA Photo Gallery: They are Responsible for Afghanistan's Tragedy". RAWA. Archived from the original on 19 October 2010. Retrieved 11 October 2010.
- "Women in Parliaments: World Classification". Ipu.org. 30 November 2009. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2009.
- "Political Parties in Afghanistan". British Embassy Kabul. Archived from the original on 3 July 2011. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- Zia Ur Rehman. "Afghanistan sees new political parties form". Central Asia Online. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
- Anna Larson. "Political Parties in Afghanistan" (PDF). United States Institute of Peace. pp. 1–3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- "Afghanistan Provinces". Ariana News. Archived from the original on 4 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- Ahmed, Azam (8 December 2012). "For Afghan Officials, Prospect of Death Comes With Territory". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- "Explaining Elections, Independent Election Commission of Afghanistan". Iec.org.af. 9 October 2004. Archived from the original on 27 August 2010. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- Jamie Boex; Grace Buencamino; Deborah Kimble. "An Assessment of Afghanistan's Municipal Governance Framework" (PDF). Urban Institute Center on International Development and Governance. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- Dupree 1997, p. 642.
- "Hillary Clinton says Afghanistan 'major non-Nato ally'". BBC News. 7 July 2012. Archived from the original on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- "Security Council endorses establishment of UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan for initial 12-month period". United Nations. 28 March 2002. Archived from the original on 21 July 2006. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- "Resolute Support Mission: Key Facts and Figures" (PDF). NATO. June 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- Glasch, Mike. "USACE TAA employee named top engineer". Army.mil. US Army. Archived from the original on 22 November 2016. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- CJ Radin (November 2008). "Afghan National Security Forces Order of Battle" (PDF). The Long War Journal. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- "Afghanistan's dysfunctional security agencies". BBC. 14 August 2011. Archived from the original on 25 September 2019. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- "Staggering Afghan death toll revealed". 25 January 2019. Archived from the original on 25 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- "UNODC 2010 world drug report, page 43" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 December 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- Vanda Felbab-Brown (1 December 2009). Shooting Up: Counterinsurgency and the War on Drugs. Brookings Institution Press. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-8157-0450-8. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- David Greene (host, Morning Edition), Hayatullah Hayat (Governor of Helmand Province, Afghanistan), Tom Bowman (reporter), Dianne Feinstein (U.S. Senator, Chair of the Caucus on International Narcotics Control) (6 July 2016). Afghan Governor Wants Government To Control Poppy Crop (Radio broadcast). NPR. Event occurs at 0:10. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
Afghanistan's poppy production… accounts for more than 91 percent of the world's heroin.
- "Afghan journalists 'face increasing attacks and threats' – report". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 25 March 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- "Violence Against Journalists Surges in Afghanistan in 2017". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 25 July 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- "LGBT relationships are illegal in 74 countries, research finds". The Independent. 17 May 2016. Archived from the original on 14 June 2019. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- Mehrotra, Kartikay. "Karzai Woos India Inc. as Delay on U.S. Pact Deters Billions". Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- "Agriculture". USAID. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- "AAN Q&A: An established industry – Basic facts about Afghanistan's opium-driven economy". Afghanistan Analysts Network. 11 July 2017. Archived from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- "The Taliban Is Capturing Afghanistan's $1 Trillion in Mining Wealth". Bloomberg L.P. 20 October 2015. Archived from the original on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- "Interest Rate Cut in Place, Says Central Bank". TOLOnews. Archived from the original on 4 July 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- "Afghani Falls Against Dollar By 3% In A Month". TOLOnews. 18 April 2019. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- Gall, Carlotta (7 July 2010). "Afghan Companies Say U.S. Did Not Pay Them". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 April 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- "the Kabul New City Official Website". DCDA. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- "Ghazi Amanullah Khan City". najeebzarab.af. 2009. Archived from the original on 29 April 2013. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- "Case study: Aino Mina". Designmena.com. Archived from the original on 6 January 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- A Humane Afghan City? by Ann Marlowe in Forbes 2 September 2009. Archived 31 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Michael Sprague. "AFGHANISTAN COUNTRY PROFILE" (PDF). usaid.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- "Economic Growth". USAID. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- O'Hanlon, Michael E. "Deposits Could Aid Ailing Afghanistan" Archived 23 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine, The Brookings Institution Archived 26 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine, 16 June 2010.
- Klett, T.R. (March 2006). Assessment of Undiscovered Petroleum Resources of Northern Afghanistan, 2006 (PDF) (Technical report). USGS-Afghanistan Ministry of Mines & Industry Joint Oil & Gas Resource Assessment Team. Fact Sheet 2006–3031. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "Afghanistan signs '$7 bn' oil deal with China". 28 December 2011. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- "Afghanistan's Mineral Fortune". Institute for Environmental Diplomacy and Security Report. 2011. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- Tucker, Ronald D. (2011). Rare Earth Element Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Preliminary Resource Assessment of the Khanneshin Carbonatite Complex, Helmand Province, Afghanistan (PDF) (Technical report). USGS. Open-File Report 2011–1207. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "China, Not U.S., Likely to Benefit from Afghanistan's Mineral Riches". Daily Finance. 14 June 2010 Archived 31 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "China Willing to Spend Big on Afghan Commerce". The New York Times. 29 December 2009. Archived from the original on 31 July 2011.
- "Indian Group Wins Rights to Mine in Afghanistan's Hajigak Archived 10 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine". Businessweek. 6 December 2011
- Risen, James (17 June 2010). "U.S. Identifies Vast Riches of Minerals in Afghanistan". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 17 June 2010. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- "China wins $700 million Afghan oil and gas deal. Why didn't the US bid?". The Christian Science Monitor. 28 December 2011 Archived 31 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "EU To Impose Ban on Afghan Planes". Airwise News. 22 November 2010. Archived from the original on 24 May 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
Kabul-based Safi is the country's No. 2 airline after national carrier Ariana Afghan Airlines
- "Hairatan to Mazar-i-Sharif railway – Railways of Afghanistan". andrewgrantham.co.uk. Archived from the original on 24 December 2017. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- "Afghan-Turkmenistan railroad inaugurated". pajhwok.com. Archived from the original on 12 May 2017. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- "Khaf-Herat railroad to be launched in Iran soon". Archived from the original on 28 September 2018. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
"Iran-Afghanistan railway networks through Khaf-Herat Railroad will be completed in the next few months," Yazdani said, according to Mehr news agency on August 3
- "Iran Strongly Condemns Herat Railway Mine Blast". Iran Front Page. 20 May 2019. Archived from the original on 21 May 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Rail Linkup With Afghanistan by March 2018". 25 February 2017. Archived from the original on 22 September 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- "Khaf-Herat railway". RaillyNews | Dailly Railway News in English. 10 December 2013. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- "Railways of Afghanistan -Afghan railroads, past, present and future". andrewgrantham.co.uk. Archived from the original on 8 December 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- Qayoom Suroush (16 January 2015). "Going in Circles: The never-ending story of Afghanistan's unfinished Ring Road". Afghanistan Analysts Network. Archived from the original on 7 July 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Cary Gladstone (2001). Afghanistan Revisited. Nova Publishers. p. 122. ISBN 978-1-59033-421-8.
- "Driving in Afghanistan". Caravanistan. Caravanistan. Archived from the original on 4 September 2016. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- "Afghan bus crash kills 45". The Guardian. 26 April 2013. Archived from the original on 5 November 2014. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- "Afghanistan" (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 July 2017. Retrieved 17 May 2017.
- UNESCO, Country profile, https://uis.unesco.org/en/country/af Archived 23 June 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Peter, Tom A. (17 December 2011). "Childbirth and maternal health improve in Afghanistan". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- "Afghanistan National Hospital Survey" (PDF). Afghan Ministry of Health. August 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- Gul, Ayaz (20 April 2019). "Pakistan-funded Afghan Hospital Begins Operations". VOA News. Archived from the original on 23 April 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
It opens a new chapter in the friendship of the two countries... This is the second-largest hospital [in Afghanistan] built with your support that will serve the needy," Feroz told the gathering.
- "Health". United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- Anne-Marie DiNardo, LPA/PIPOS (31 March 2006). "Empowering Afghanistan's Disabled Population – 31 March 2006". Usaid.gov. Archived from the original on 8 May 2004. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- Richard Norton-Taylor (13 February 2008). "Afghanistan's refugee crisis 'ignored'". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 15 December 2010. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- "Afghanistan: People living with disabilities call for integration Archived 20 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Virginia Haussegger Mahooba's Promise ABC TV 7.30 Report. 2009. ABC.net.au. Retrieved 15 July 2009. Archived 26 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Afghanistan". Measuredhs.com. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- "Education". USAID. Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2017.
- "Wardak seeks $3b in aid for school buildings". Pajhwok Afghan News. 18 May 2013. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- "Rising literacy in Afghanistan ensures transition". Army.mil. Archived from the original on 9 December 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- US Library of Congress: Afghanistan – Ethnic Groups (Pashtun) Archived 14 July 2012 at Archive.today
- Dupree 1997, p. 126.
- Barfield 2012, p. 59.
- Heathcote, Tony (1980, 2003) "The Afghan Wars 1839–1919", Sellmount Staplehurst.
- "Afghanistan: Kuchi nomads seek a better deal". IRIN Asia. 18 February 2008. Archived 10 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Barfield 2012, p. 40–41.
- Dupree 1997, p. 104.
- Qobil, Rustam (7 September 2010). "The sexually abused dancing boys of Afghanistan". BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 August 2019. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
- G.V. Brandolini. Afghanistan cultural heritage. Orizzonte terra, Bergamo. 2007. p. 64.
- "Afghan archaeologists find Buddhist site as war rages". Sayed Salahuddin. 17 August 2010. Archived from the original on 18 August 2010. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- "Buddhist remains found in Afghanistan". Press TV. 17 August 2010. Archived from the original on 20 August 2010. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- Dupree 1997, p. 115.
- "Afghanistan: No Country for Women | International Women's Day | Al Jazeera". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 5 January 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- "240 cases of honor killing recorded in Afghanistan". khaama.com. 9 June 2013. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- "AIHRC: 400 rape, honor killings registered in Afghanistan in 2 years". latinbusinesstoday.com. 10 June 2013. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- Bahgam, S; Mukhatari (2004). "Study on Child Marriage in Afghanistan" (PDF). Medica Mondiale: 1–20. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 May 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- "Afghanistan Has a Tougher Law on Child Marriage than Florida". Human Rights Watch. 20 October 2017. Archived from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2019.
In Afghanistan girls can marry at 16, or at 15 with permission from their father or a judge.
- Dupree 1997, p. 122, 198.
- "Suspects Sentenced To Death For Killing Journalist in Kandahar". TOLOnews. 16 April 2019. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- Dupree 1997, p. 405.
- Monica Whitlock (24 October 2003). Land Beyond the River: The Untold Story of Central Asia. St. Martin's Press. p. 127. ISBN 978-0-312-27727-7.
- "Freedom of the Press 2016: Afghanistan". Freedom House. 2016. Archived from the original on 5 February 2017. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- "Afghanistan". Reporters Without Borders. Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- "Afghanistan Descends 3 Points on Press Freedom Index". TOLOnews. 19 April 2019. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- "Artist Biographies". Afghanland.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2013. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- "Connecting Afghanistan: The rise of technology in governance and society – The Embassy of Afghanistan in London". afghanistanembassy.org.uk. Archived from the original on 21 January 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- Ali, Tanveer (31 July 2012). "Everything You Need To Know About Afghan Food". foodrepublic. Archived from the original on 13 February 2013.
- Brittin, Helen (2011). The Food and Culture Around the World Handbook. Boston: Prentice Hall. pp. 20–21.
- "Rare Heirloom Seeds – Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds". Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- "Afghanistan: 10 facts you may not know". 6 July 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018 – via BBC.
- "Classical Dari and Pashto Poets". Afghan-web.com. Archived from the original on 12 April 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- Uthra Ganesan (11 January 2016). "Cricket is now the biggest sport in Afghanistan". The Hindu. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- "Sport in Afghanistan". Top End Sports. Archived from the original on 11 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- "South Asian Games: Shooters, swimmers shine as India consolidate dominance". The Times of India. 5 February 2010. Archived from the original on 13 June 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- "2009–10 Intercontinental Cup". CricketEurope. Archived from the original on 24 February 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- Lyse, Doucet (12 September 2013). "Precious moments of unity touch Afghans after football triumph". BBC News. Archived from the original on 25 September 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- "Afghanistan Makes History in Cricket World Cup, Despite Debut Loss to Bangladesh". Archived from the original on 28 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- "Statistics: Iran". Team Melli. Archived from the original on 3 November 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- Abi-Habib, Maria; Fazly, Walid (13 April 2011). "In Afghanistan's National Pastime, It's Better to Be a Hero Than a Goat". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2011.
- Stewart, Rory (2007). The Places in Between. HMH Books. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-15-603593-4.
Bibliography
Books
- Barfield, Thomas (2012). Afghanistan: A Cultural and Political History. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15441-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bleaney, C. H; Gallego, María Ángeles (2006). Afghanistan: a bibliography. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-14532-0.
- Clements, Frank (2003). Conflict in Afghanistan: a Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-85109-402-8.
- Dupree, Louis (1997). Afghanistan (2nd ed.). Oxford Pakistan Paperbacks. ISBN 978-0-19-577634-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ewans, Martin (2002). Afghanistan: A Short History of Its People and Politics. Curzon Press. ISBN 0060505087.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fowler, Corinne (2007). Chasing Tales: Travel Writing, Journalism and the History of British Ideas About Afghanistan. Rodopi. ISBN 978-90-420-2262-1.
- Griffiths, John C (2001). Afghanistan: a History of Conflict. Carlton Books. ISBN 978-1-84222-597-4.
- Habibi, Abdul Hai (2003). Afghanistan: an Abridged History. Fenestra Books. ISBN 978-1-58736-169-2.
- Hopkins, B.D. (2008). The Making of Modern Afghanistan. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-55421-4.
- Johnson, Robert (2011). The Afghan Way of War: How and Why They Fight. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-979856-8.
- Levi, Peter (1972). The Light Garden of the Angel King: Journeys in Afghanistan. Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-211042-6.
- Malleson, George Bruce (2005). History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878 (Elibron Classic Replica ed.). Adamant Media Corporation. ISBN 978-1-4021-7278-6.
- Olson, Gillia M (2005). Afghanistan. Capstone Press. ISBN 978-0-7368-2685-3.
- Omrani, Bijan; Leeming, Matthew (2011). Afghanistan: A Companion and Guide (2nd ed.). Odyssey Publications. ISBN 978-962-217-816-8.
- Reddy, L.R. (2002). Inside Afghanistan: End of the Taliban Era?. APH Publishing. ISBN 978-81-7648-319-3.
- Runion, Meredith L. (2007). The History of Afghanistan. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-33798-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Afghanistan. |
- Office of the President
- "Afghanistan". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Afghanistan web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Afghanistan at Curlie

- Research Guide to Afghanistan