Argyll and Bute
Argyll and Bute (Scottish Gaelic: Earra-Ghàidheal agus Bòd, pronounced [ɛrˠəˈɣɛːəlˠ̪ akəs̪ ˈpɔːtʲ]) is one of 32 unitary authority council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area. The administrative centre for the council area is in Lochgilphead.
Argyll and Bute Earra-Ghaidheal agus Bòd' | |
|---|---|
 Kilchurn Castle reflected on Loch Awe | |
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Sovereign State | United Kingdom |
| Constituent Country | Scotland |
| Admin HQ | Lochgilphead |
| Government | |
| • Body | Argyll & Bute Council |
| • Control | Ind + Con + LD (council NOC) |
| • MPs |
|
| • MSPs |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,668 sq mi (6,909 km2) |
| Area rank | Ranked 2nd |
| Population (mid-2018 est.) | |
| • Total | 86,260 |
| • Rank | Ranked 27th |
| • Density | 32/sq mi (12/km2) |
| ONS code | S12000035 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-AGB |
| Website | www |

Description
Argyll and Bute covers the second-largest administrative area of any Scottish council. The council area adjoins those of Highland, Perth and Kinross, Stirling and West Dunbartonshire. Its border runs through Loch Lomond.
The present council area was created in 1996, when it was carved out of the Strathclyde region, which was a two-tier local government region of 19 districts, created in 1975.[1] Argyll and Bute merged the existing Argyll and Bute district and one ward of the Dumbarton district. The Dumbarton ward, called 'Helensburgh and Lomond', included the burgh of Helensburgh and consisted of an area to the west of Loch Lomond, north of the Firth of Clyde and mostly east of Loch Long.
The council area can also be described by reference to divisions of the counties which were abolished in 1975. The council area includes most of the county of Argyll (Argyll minus the Morvern area, north of Mull, which became part of the Highland region in 1975), part of the county of Bute (the Isle of Bute) and part of the county of Dunbartonshire (the Helensburgh and Lomond ward).
Argyll and Bute Council
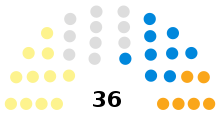
Thirty-six representative members make up the council, elected, since 2007, by single transferable vote and, before that, by the first-past-the-post system. The 2017 election saw the SNP become the largest group. This was the first time since the creation of the modern authority that the representatives of a political party had outnumbered Independents in holding the largest number of seats on the council; nevertheless, it was a coalition of Independents, Conservatives, and Liberal Democrats who would go on to form an administration following the election.
In February 2012, the council was criticised for allegedly setting up "spy" accounts on social media. As a result of the investigation, a council employee was suspended for setting up "fake social media accounts to monitor what was being said about the council".[2] The council's own investigation later confirmed it had "found no evidence of any form of spying or covert surveillance having been carried out by any employee within the council's communication team."[3]
Wards
Eleven multi-member wards were created for the 2007 election, replacing 36 single-member wards which had been in place since 1999 (adjusted up from 33 in the 1990s):
- South Kintyre (3 seats)
- Kintyre and the Islands (3 seats)
- Mid Argyll (3 seats)
- Oban South and the Isles (4 seats)
- Oban North and Lorn (4 seats)
- Cowal (3 seats)
- Dunoon (3 seats)
- Isle of Bute (3 seats)
- Lomond North (3 seats)
- Helensburgh Central (4 seats)
- Helensburgh and Lomond South (3 seats)
Elections
- 1992 Argyll and Bute District Council election (Strathclyde region)
- 1995 Argyll and Bute Council election
- 1999 Argyll and Bute Council election
- 2003 Argyll and Bute Council election
- 2007 Argyll and Bute Council election
- 2012 Argyll and Bute Council election
- 2017 Argyll and Bute Council election
NeverSeconds
In June 2012, the council was heavily criticised[4] for banning a local primary student, Martha Payne (aged 9), from taking photographs of her school dinners for her online blog. The blog, NeverSeconds, had been praised by the celebrity chef, Jamie Oliver,[5] had attracted over two million visits, and at the time of the ban had raised nearly £2,000[6] for a food charity.[7] On the day the story broke, the blog had raised over £40,000.[8] After an initial statement from the council defending the decision,[9] the ban was subsequently overturned by council leader, Roddy McCuish.[10] In November 2012 a book written by David Payne, Martha's father, revealed the background to the council's attempt to censor and bully a 9-year-old girl. The book says: "My anger and frustration at Argyll and Bute Council was not being soothed by time. Thinly veiled attacks on our parenting on national radio and an abusive phonecall stood out as examples of a public body sick to the very top. Complaints via the proper procedures and through elected councillors had brought no visible changes. Far from being contrite they seemed to take a pride in being untouchable."[11]
Transport
Railways
The main railway line in Argyll and Bute is the West Highland Line, which links Oban to Glasgow, passing through much of the eastern and northern parts of the area. From the south the line enters Argyll and Bute just to the west of Dumbarton, continuing north via Helensburgh Upper to the eastern shores of the Gare Loch and Loch Long. The line comes inland at Arrochar and Tarbet to meet the western shore of Loch Lomond. At the northern end of the loch the lines leaves Argyll and Bute to enter Stirling council area. The Oban branch of the West Highland Line re-enters the area just west of Tyndrum, and heads west to Oban: stations on this section of the line include Dalmally and Taynuilt railway station. The majority of services on the line are operated by ScotRail: as of 2019 the summer service has six trains a day to Oban, with four on Sundays. In addition to the ScotRail service is the nightly Caledonian Sleeper, although this does not run on the Oban branch.[12][13]
Helensburgh also has a much more frequent service into Glasgow and beyond via the North Clyde Line, which has its western terminus at the town's central railway station.[14]
Roads
The main trunk roads in Argyll and Bute are:[12][15]
- The A82, which runs along the western shore of Loch Lomond, providing the main route between Glasgow and Fort William.
- The A83, which leaves the A82 at Tarbet, heading west and then south to eventually reach Campbeltown by way of Inveraray and Lochgilphead.
- The A85, which leaves the A82 at Tyndrum (just outside Argyll and Bute) and heads west to Oban via Dalmally.
- The A828, which leaves the A85 at Connel and north through Appin to join the A82 at Ballachulish.
Ferry services
Due to its heavily indented coastline and many islands, ferries form an important part of the council area's tranport system. The main ferry operator in Argyll & Bute is Caledonian MacBrayne (CalMac), which operates services from the mainland to most of the inhabited islands. Several other routes are operated by commercial operators, usually on contract to the council, although the Western Ferries service across the Firth of Clyde is run on a commercial basis.
- Bute is served by a route across the Kyles of Bute between Rhubodach and Colintraive in Cowal, as well as a route between Rothesay to Wemyss Bay in Inverclyde. Both routes are operated by CalMac.[16][17]
- Coll and Tiree are each served from Oban, via a CalMac service that also provides links between the two islands, and a once-weekly link to Barra.[18]
- Gigha is served by a CalMac route from Tayinloan in Kintyre.[19]
- Islay is served by a CalMac route from Kennacraig in Kintyre. The service is timetabled to utilise either one of two ports on the island, with both Port Askaig and Port Ellen having a service to the mainland.[20]
- Feolin on Jura is linked to Port Askaig on Islay via a vehicle ferry run by ASP Ship Management on behalf of Argyll and Bute Council.[21][22] There is also a passenger-only service between the island's main centre, Craighouse, and Tayvallich on the mainland that is operated by Islay Sea Safaris.[23]
- Kerrera is linked to Gallanach (about 3 km (1.9 mi) southwest of Oban) by a passenger-only service operated by CalMac.[24]
- Lismore is served by two ferries, a vehicle and passenger service operated by CalMac that runs from Oban,[25] and a passenger-only service from Port Appin that is operated by ASP Ship Management on behalf of Argyll and Bute Council.[21][26]
- Mull is served by a route between Oban and Craignure on the island's east coast,[27] as well as routes across the Sound of Mull (between Lochaline and Fishnish, and Tobermory and Kilchoan). All three routes are operated by CalMac.[28][29]
- Iona is linked to Mull via a CalMac service from Fionnphort at Mull's southwest tip.[30]
- The island of Seil, which itself is linked to the mainland via the Clachan Bridge, has links to two further islands: Easdale and Luing. Both services are operated by ASP Ship Management on behalf of Argyll and Bute Council.[21][31][32]

There are also routes connecting some mainland locations in Argyll and Bute to other parts of the mainland:
- There is a CalMac service across Loch Fyne which provides a link between Portavadie in Cowal and Tarbert in Kintyre.[33]
- The Cowal peninsula route is a passenger-only service from Dunoon Breakwater to Gourock pier, giving easy access to ScotRail services at Gourock railway station.[34] This route was for a period run by a CalMac subsidiary company, Argyll Ferries, but has since January 2019 been operated directly by CalMac.[35][36]
- CalMac provide a limited (3 ferry each way per week) service between Cambeltown in Kintyre and Ardrosssan in North Aryshire during the summer months.[37]
- Western Ferries, a commercial operator, runs a vehicle and passenger service between Hunters Quay to McInroy's Point that also provides a link between Cowal and Inverclyde in (partial) competition with the subsidised CalMac service.
- A service operated by Clyde Marine Services on behalf of Strathclyde Partnership for Transport runs between Kilcreggan and Gourock pier, providing a link from the Rosneath peninsula to the rail network at Gourock.[35][38]
Argyll and Bute also has ferry services linking it to islands in neighbouring council areas:
- Oban is the mainland terminal for services to Barra in the Outer Hebrides.[39]
- Lochranza on Arran has a year-round service to Kintyre: during the summer the mainland port used is Claonaig, however in winter the service is reduced to a single daily return crossing from Tarbert.[40][41]
Cultural references
The later scenes of the 1963 James Bond film From Russia with Love were filmed around the lochs and hills of Argyll and Bute.[42]
The area has also been indirectly immortalised in popular culture by the 1977 hit song "Mull of Kintyre" by Kintyre resident Paul McCartney's band of the time, Wings.
Towns and villages
- Achahoish; Airdeny; Appin; Ardbeg (Islay); Ardbeg (Bute); Arden; Ardfern; Aldochlay; Ardlui; Ardmay; Ardgartan; Ardpeaton; Ardrishaig; Arduaine; Arrochar; Ardentinny;
- Barcaldine; Bellochantuy; Benderloch; Blairglas; Bonawe; Bowmore; Blairmore;
- Cairndow; Cardross; Carradale; Clachan; Cairnbaan; Campbeltown; Clachan of Glendaruel; Cladich; Clynder; Colgrain; Colintraive; Connel; Coulport; Cove; Craigendoran; Craighouse; Craignure; Craobh Haven; Crarae; Crinan; Clachaig; Carrick Castle;
- Dunoon; Dalavich; Dalmally; Druimdrishaig; Drumlemble; Duchlage; Dunbeg;
- Edentaggart;
- Faslane Port; Ford; Furnace;
- Glenbranter; Garelochhead; Geilston; Glenbarr; Glencoe; Glenmallan; Grogport;
- Helensburgh; Hunters Quay;
- Innellan; Inveraray; Inverbeg; Inveruglas Isle;
- Kames; Keillmore; Kilberry; Kilchenzie; Kilcreggan; Kilmadan; Kilmartin; Kilmore; Kilmun; Kilninver; Kilmelford; Kilfinan; Kirn;
- Lagavulin; Lochawe; Lochgair; Lochgilphead; Lochgoilhead; Luss;
- Machrihanish; Millhouse; Minard; Muasdale;
- Oban; Ormsary; Otter Ferry;
- Peninver; Portavadie; Port Askaig; Port Bannatyne; Port Charlotte; Port Ellen; Portincaple; Portnahaven; Portkil;
- Rahane; Rhu; Rosneath; Rothesay;
- Saddell; Salen; Sandbank; Shandon; Skipness; Southend; Stewarton; Strachur; Succoth; Strone; St Catherines;
- Tarbert (Kintyre); Tarbet (Dunbartonshire); Tayinloan; Taynuilt; Tayvallich; Tighnabruaich; Tobermory; Torinturk; Toward;
- Whistlefield; Whitehouse;
Places of interest

- Ardbeg distillery
- Argyll Forest Park
- Argyll Mountains
- Arrochar Alps
- Avinagillan standing stone
- Beinn Dorain
- Ben Cruachan
- Ben Cruachan, Pump Storage Hydroelectric plant
- Ballochroy standing stones
- Ben Donich
- Benmore Botanic Garden
- Carrick Castle
- Castle Stalker
- Castle Sween
- Crinan Canal
- Dun Skeig – Iron Age forts near Clachan
- Fincharn Castle
- Fingal's Cave
- Gare Loch and Faslane Naval Base
- Gulf of Corryvreckan
- Iona Abbey
- Kilchurn Castle
- Kilmartin Glen
- Loch Goil Mountains
- Loch Goil
- Loch Lomond and the Trossachs National Park
- Loch Melfort
- Mull of Kintyre
- Old Castle Lachlan
- River Orchy
- Saddell Abbey
- Saddell Castle
- Skipness Castle
- Tarbert Castle
- West Highland Way
Islands
- Bute
- Cara Island
- Coll
- Colonsay
- Island Davaar
- Fladda, Slate Islands
- Fladda, Treshnish Isles
- Gigha
- Glunimore Island
- Gometra
- Gunna
- Inchconnachan
- Inchmarnock
- Inchtavannach
- Iona
- Islay
- Jura
- Kerrera
- Lismore
- Luing
- Lunga, Treshnish Isles
- Lunga, Firth of Lorn
- Mull
- Sanda Island
- Scarba
- Seil (not always regarded as an island)
- Sheep Island
- Shuna, Firth of Lorn
- Shuna Island, near Appin
- Staffa
- Texa
- Tiree
- Ulva
See also
- 2012 Argyll and Bute Council election
- Censorship in the United Kingdom
- List of places in Argyll and Bute
References
- Argyll, Undiscovered Scotland
- "Social Media Spying". Bbc.co.uk. 10 February 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Argyll and Bute Council (23 August 2012). "Argyll and Bute Council – Meetings, Agendas, Minutes". Argyll-bute.gov.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Hough, Andrew (15 June 2012). "School Dinner Blog Banned By Council". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- "NeverSeconds blogger Martha Payne school dinner photo ban lifted". Bbc.co.uk. 15 June 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- VEG (14 June 2012). "Goodbye". Neverseconds.blogspot.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- "Mary's Meals and NeverSeconds' Martha Payne". Marysmeals.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Mary's Meals. "Veg from NeverSeconds". Justgiving.com. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- "Statement on school meals from Argyll and Bute Council". Argyll-bute.gov.uk. 15 June 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Peterkin, Tom (16 June 2012). "Food blogger Martha Payne enjoys taste of victory". Scotsman.com. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Neverseconds, The Incredible Story of Martha Payne. Payne, Martha; Payne, David., Cargo Publishing, 2012. ISBN 978-1908885166
- OS Maps online
- "Timetable: Glasgow to Oban, Fort William and Mallaig" (PDF). Abellio ScotRail. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Dunbartonshire - Glasgow, Cumbernauld & Falkirk Grahamston Timetable" (PDF). Abellio ScotRail. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Scottish trunk road network map". Transport Scotland. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Bute: Colintraive - Rhubodach". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Bute: Wemyss Bay - Rothesay". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Coll & Tiree: Oban - Coll - Tiree". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Gigha: Tayinloan - Gigha". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Islay: Kennacraig - Port Ellen/Port Askaig". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ASP Ship Management Ltd
- "Port Askaig - Feolin". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Jura Passenger Ferry". Jura Passenger Ferry. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Kerrera: Gallanach - Kerrera". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Lismore: Oban - Lismore". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Port Appin - Lismore". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Mull: Oban - Craignure". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Ardnamurchan and Mull: Tobermory - Kilchoan". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Mull: Lochaline - Fishnish". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Iona: Fionnphort-Iona". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Cuan - Luing". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Ellenabeich - Easdale". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Cowal & Kintyre: Tarbert Loch Fyne - Portavadie". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Dunoon: Gourock - Dunoon". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Gourock - Kilcreggan". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "CalMac to take over Dunoon to Gourock ferry next month". The Lochside Press. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Kintyre: Ardrossan - Campbeltown". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Kilcreggan Ferry". Strathclyde Partnership for Transport. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Barra: Oban - Castlebay". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Arran: Claonaig - Lochranza". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "Arran: Claonaig/Tarbert - Lochranza". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- "From Russia with Love (1963)".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Argyll and Bute. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Argyll and Bute. |