Alligator snapping turtle
The alligator snapping turtle (Macrochelys temminckii) is a species of turtle in the family Chelydridae. The species is native to freshwater habitats in the United States. M. temminckii is one of the heaviest freshwater turtles in the world.[3] It is often associated with, but not closely related to, the common snapping turtle, which is in the genus Chelydra. The specific epithet temminckii is in honor of Dutch zoologist Coenraad Jacob Temminck.[4][5]
| Alligator snapping turtle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Family: | Chelydridae |
| Genus: | Macrochelys |
| Species: | M. temminckii |
| Binomial name | |
| Macrochelys temminckii (Troost, 1835)[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Species synonymy[2]
| |
Taxonomy
Although it was once believed that only one extant species exists in the genus Macrochelys, recent studies have shown that there are two species, the other being the Suwannee snapping turtle (M. suwanniensis) of the Suwannee River[6][7] (a third species, the Apalachicola snapping turtle (M. apalachicolae), has been proposed,[8] but is generally not recognized).[6][7][9]
Common name
The alligator snapping turtle is given its common name because of its immensely powerful jaws and distinct ridges on its shell that are similar in appearance to the rough, ridged skin of an alligator. It is also slightly less commonly known as "the loggerhead snapper" (not to be confused with the loggerhead sea turtle or loggerhead musk turtle).
Distribution and habitat
The alligator snapping turtle is found primarily in southeastern United States waters. They are found from the Florida Panhandle west to East Texas, north to southeastern Kansas, Missouri, southeastern Iowa, western Illinois, southern Indiana, western Kentucky, and western Tennessee. They are found on the Missouri River at least as far north as the Gavins Point Dam, the southernmost dam on the Missouri River at Yankton, South Dakota, and are featured in the Gavins Point Dam Aquarium.[10] Typically, only nesting females venture onto open land.
There are non-native established invasive populations of alligator snapping turtles in South Africa.[11]
Description
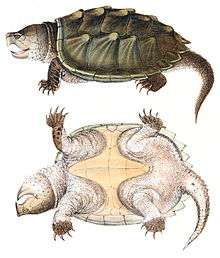
The alligator snapping turtle is characterized by a large, heavy head, and a long, thick shell with three dorsal ridges of large scales (osteoderms), giving it a primitive appearance reminiscent of some of the plated dinosaurs, most notably Ankylosaurus. They can be immediately distinguished from the common snapping turtle by the three distinct rows of spikes and raised plates on the carapace, whereas the common snapping turtle has a smoother carapace. They are a solid gray, brown, black, or olive-green in color, and often covered with algae. They have radiating yellow patterns around their eyes, serving to break up the outline of the eyes to keep the turtle camouflaged. Their eyes are also surrounded by a star-shaped arrangement of fleshy, filamentous "eyelashes".

Though not verified, a 183 kg (403 lb) alligator snapping turtle was found in Kansas in 1937,[12] but the largest verifiable one is debatable. One weighed at the Shedd Aquarium in Chicago was a 16-year resident giant alligator snapper weighing 113 kg (249 lb), sent to the Tennessee Aquarium as part of a breeding loan in 1999, where it subsequently died. Another weighing 107 kg (236 lb) was housed at the Brookfield Zoo in suburban Chicago. Another large turtle reportedly weighed 135 kg (298 lb).[13] They generally do not grow quite that large. Breeding maturity is attained around 8 kg (18 lb), when the length is around 33 cm (13 in), but then they continue to grow throughout life.[14] Excluding exceptionally large specimens, adult alligator snapping turtles generally range in carapace length from 35 to 80.8 cm (13.8 to 31.8 in) and weigh from 8.4 to 80 kg (19 to 176 lb).[12][15][16][17] Males are typically larger than females.[18] 88 adult alligator snapping turtles averaged 21.05 kg (46.4 lb), 92 averaged 19.72 kg (43.5 lb), and 249 averaged 13.5 kg (30 lb). Usually very old males comprise the specimens that weigh in excess of 45 kg (99 lb) per most population studies.[16][17][19] Among extant freshwater turtles, only the little-known giant softshell turtles of the genera Chitra, Rafetus, and Pelochelys, native to Asia, reach comparable sizes.


In "mature" specimens (carapace length over 30 cm (12 in)), males and females can be differentiated by the position of the cloaca from the carapace and the thickness of the tail's base. A mature male's cloaca extends beyond the carapace edge, a female's is placed exactly on the edge if not nearer to the plastron. The base of the tail of the male is also thicker as compared to females because of the hidden reproductive organs.
The inside of the turtle's mouth is camouflaged, and it possesses a vermiform (i.e., "worm-shaped") appendage on the tip of its tongue used to lure fish, a form of aggressive mimicry. The turtle hunts by lying motionless in the water with its mouth wide open. The vermiform tongue imitates the movements of a worm, luring prey to the turtle's mouth. The mouth is then closed with tremendous speed and force, completing the ambush.
These turtles must be handled with extreme care and considered potentially dangerous.[18] This species can bite through the handle of a broom and rare cases have been reported where human fingers have been cleanly bitten off by the species.[20] No human deaths have been reported to have been caused by alligator snapping turtles.[20]
Diet
Alligator snapping turtles are opportunistic feeders that are almost entirely carnivorous. They rely on both live food caught by themselves and dead organisms which they scavenge. In general, they will eat almost anything they can catch. Fishermen have glorified the species' ability to catch fish and to deplete fish populations, whereas in fact they largely target any abundant and easily caught prey, and rarely have any extensive deleterious effect on fish populations.[21] Their natural diets consist primarily of fish and fish carcasses, molluscs, carrion, and amphibians, but they are also known to eat snakes, crayfish, worms, water birds, aquatic plants, other turtles and sometimes even small alligators.[20][21] In one study conducted in Louisiana, 79.8% of the stomach contents of adult alligator snapping turtles was found to be composed of other turtles, although the resistance of shell and reptile-bone fragments to digestion may have led these fragments to remain longer in the digestive tract than other items.[22] This species may also, on occasion, prey on aquatic rodents, including nutrias and muskrats or even snatch small to mid-sized other mammals, including squirrels, mice, opossums, raccoons, and armadillos when they attempt to swim or come near the water's edge.[20]
Alligator snapping turtles seemingly most often hunt at night. They may also hunt diurnally, however. By day, they may try to attract fish and other prey by sitting quietly at the bottom of murky water and let their jaws hang open to reveal their tongues, which look like small, pink, worm-like lures in the back of their gray mouths, and lure the prey into striking distance.[21] Small fish, such as minnows, are often caught in this way by younger alligator snapping turtles, whereas adults must eat a greater quantity per day and must forage more actively.[20] Though not a regular food source for them, adult alligator snappers have even been known to kill and eat small American alligators.[23]
In captivity, they may consume almost any kind of meat provided, including beef, chicken, and pork. They will refuse to eat if exposed to extremes in temperature.
Reproduction and lifespan
Maturity is reached around 12 years of age.[24] Mating takes place yearly, in early spring in the southern part of their total range, and later spring in the north. The female builds a nest and lays a clutch of 10–50 eggs[15] about two months later. The sex of the young depends on the temperature at which the eggs are incubated. Nests are typically excavated at least 50 yards from the water's edge to prevent them from being flooded and drowned. Incubation takes from 100 to 140 days, and hatchlings emerge in the early fall.[25]
Though their potential lifespans in the wild are unknown, alligator snapping turtles are believed to be capable of living to 200 years of age, but 80 to 120 is more likely.[26] In captivity, they typically live between 20 and 70 years.[27]
Under human care

Alligator snapping turtles are sometimes captive-bred as pets and are readily available in the exotic animal trade. Due to their potential size and specific needs, they do not make particularly good pets for any but the most experienced aquatic turtle keepers.[28]
They prefer to feed on live fish which they catch with their special technique, but will readily feed on other types of meat or leafy vegetables if offered. Hand feeding is dangerous. Extreme temperatures are known to affect the turtle's appetite and would result in the turtle refusing to feed until it has been remedied.
Due to their sheer size, handling adult specimens can pose significant problems. Small turtles can be held by the sides of the shell with relative safety, but large individuals must be held by grasping the turtle's shell just behind the head and in front of the tail.
Despite their reputation, alligator snapping turtles are typically not prone to biting. However, if provoked they are quite capable of delivering a powerful bite which can easily amputate fingers or cause other significant injuries.[29] Some U.S. states where alligator snapping turtles do not naturally occur (such as California) prohibit them from being kept as pets by residents.
Invasive species
Some alligator snapping turtles were released or escaped into waters of the Czech Republic, Germany and Hungary. In Bavaria, one turtle caused injury to a child, but was not caught.[30] In Bohemia, four turtles of this species have been caught.[31][32] In Hungary, one turtle was caught on the middle of a street near a lake.[33] These countries have strong laws against keeping alligator snapping turtles without permission. They are member states of the EU, which has laws against invasive species.[34]
Conservation status
Because of collection for the exotic pet trade, overharvesting for their meat, and habitat destruction, some states have imposed bans on collecting alligator snapping turtles from the wild.[35] The IUCN lists it as a threatened species, and as of June 14, 2006, it was afforded some international protection by being listed as a CITES III species (which will put limits on exportation from the United States and all international trade in this species).[36]
The alligator snapping turtle is now endangered in several states, including Kentucky, Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri, where they are protected by state law.[37][38] They are designated as "in need of conservation" in Kansas.[39]
In October 2013, one was found in the Prineville Reservoir in Oregon. It was captured and euthanized by the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, which considers alligator snapping turtles to be an invasive species.[40] This one was the first found in the state.
References
- Tortoise & Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group (1996). "Macrochelys temminckii". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 1996: e.T12589A97272309. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T12589A3362355.en.
- Fritz, Uwe; Havaš, Peter (2007). "Checklist of Chelonians of the World" (PDF). Vertebrate Zoology. 57 (2): 149–368. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 1, 2011.
- Carwardine, Mark (2008). Animal Records. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. p. 174. ISBN 9781402756238.
- "Biographies of People Honored in the Herpetological Nomenclature North America". Archived from the original on July 10, 2006. Retrieved July 9, 2006.
- Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Macrochelys temminckii, p. 263).
- Uetz, P. & J. Hallermann. "Macrochelys". Reptile Database. Retrieved September 26, 2017. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Rhodin, A.G.J.; Iverson, J.B.; Bour, R. Fritz; U., Georges; A., Shaffer, H.B. & van Dijk, P.P. (Turtle Taxonomy Working Group) (2017). Rhodin, A.G.J.; Iverson, J.B.; van Dijk, P.P.; Saumure, R.A.; Buhlmann, K.A.; Pritchard, P.C.H. & Mittermeier, R.A. (eds.). Turtles of the World: Annotated Checklist and Atlas of Taxonomy, Synonymy, Distribution, and Conservation Status. Chelonian Research Monographs. Conservation Biology of Freshwater Turtles and Tortoises: A Compilation Project of the IUCN/SSC Tortoise and Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group. 7 (8th ed.). pp. 1–292. doi:10.3854/crm.7.checklist.atlas.v8.2017. ISBN 9781532350269.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Thomas, Travis M.; Granatosky, Michael C.; Bourque, Jason R.; Krysko, Kenneth L.; Moler, Paul E.; Gamble, Tony; Suarez, Eric; Leone, Erin; Roman, Joe (2014). "Taxonomic assessment of Alligator Snapping Turtles (Chelydridae: Macrochelys), with the description of two new species from the southeastern United States". Zootaxa. 3786 (2): 141–165. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3786.2.4. PMID 24869532.
- Folt, B. & C. Guyer (2015). "Evaluating recent taxonomic changes for alligator snapping turtles (Testudines: Chelydridae)". Zootaxa. 3947 (3): 447–450. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3947.3.11. PMID 25947748.
- Conant, Roger; Collins, Joseph T. (1991). A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians: Eastern and Central North America (third ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 978-0395904527.
- http://www.invasives.org.za/component/k2/item/852-alligator-snapping-turtle-macrochelys-temmincki Invasive Species South Africa - Protecting Biodiversity from Invasion - Alligator snapping turtle | Macrochelys temminckii
- "Smithsonian National Zoological Park: Alligator Snapping Turtle". Archived from the original on March 7, 2006. Retrieved March 26, 2006.
- Telford Jr, S. R.; Norton, T. M.; Moler, P. E.; Jensen, J. B. (2009). "A New Haemogregarina Species of the Alligator Snapping Turtle, Macrochelys temminckii (Testudines: Chelydridae), in Georgia and Florida that Produces Macromeronts in Circulating Erythrocytes". Journal of Parasitology. 95 (1): 208–214. doi:10.1645/ge-1696.1.
- Alligator Snapping Turtle. People.wcsu.edu. Retrieved on August 22, 2012.
- Kindersley, Dorling (2005). Animal. New York City: DK Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7566-1634-2.
- Chaffin, K.; Norton, T. M.; Gilardi, K.; Poppenga, R.; Jensen, J. B.; Moler, P.; Cray, C.; Dierenfeld, E.S.; Chen, T. Oliva; Origgi, F.C.; Gibbs, F.; Mazzaro, L.; Mazet, J. (2008). "Health assessment of free-ranging alligator snapping turtles (Macrochelys temminckii) in Georgia and Florida". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 44 (3): 670–686. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-44.3.670.
- Moore, D. B., LIGON, D., Fillmore, B. M., & Fox, S. F. (2013). GROWTH AND VIABILITY OF A TRANSLOCATED POPULATION OF ALLIGATOR SNAPPING TURTLES (MACROCHELYS TEMMINCKII). Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 8(1), 141-148.
- "Alligator Snapping Turtle: Giant of the Southeastern States". Archived from the original on April 8, 2006. Retrieved March 26, 2006.
- Elsey, R. M. (2006). "Food habits of Macrochelys temminckii (alligator snapping turtle) from Arkansas and Louisiana". Southeastern Naturalist. 5 (3): 443–452. doi:10.1656/1528-7092(2006)5[443:fhomta]2.0.co;2.
- Pritchard, P. (1979). Encyclopedia of Turtles. Neptune, New Jersey: T.F.H. Publications, Inc. ISBN 0876669186.
- Ernst, C., R. Barbour, J. Lovich. (1994). Turtles of the United States and Canada. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 1560988231.
- Elsey, R. M. (2006). "Food Habits of Macrochelys temminckii (Alligator Snapping Turtle) from Arkansas and Louisiana". Southeastern Naturalist. 5 (3): 443–452. doi:10.1656/1528-7092(2006)5[443:FHOMTA]2.0.CO;2.
- Alligator Snapping Turtle. Bronx Zoo
- "Animal Diversity Web: Macrochelys temminickii". Retrieved September 12, 2008.
- "Nashville Zoo: Alligator Snapping Turtle". Archived from the original on February 21, 2006. Retrieved March 26, 2006.
- Gibbons, J. Whitfield (January 1, 1987). "Why Do Turtles Live So Long?". BioScience. 37 (4): 262–269. doi:10.2307/1310589. JSTOR 1310589.
- "WhoZoo: Alligator Snapping Turtle". Archived from the original on April 28, 2006. Retrieved March 26, 2006.
- AST Care Sheet. Austinsturtlepage.com. Retrieved on August 22, 2012.
- "NAS — Species FactSheet". Retrieved March 26, 2006.
- The Bavarian village of Irsee is ramping up efforts to find alligator snapping turtle "Lotti". Spiegel.de (August 15, 2013). Retrieved on 2014-05-15.
- Výskyt a historie vodních želv u nás. Cs.petclub.eu. Retrieved on May 15, 2014.
- Po hlavní silnici na Rokycansku si vykračovala dvanáctikilová želva – iDNES.cz. Plzen.idnes.cz. Retrieved on May 15, 2014.
- Agresszív aligátorteknős lófrált egy zalai faluban. 444.hu (June 20, 2019). Retrieved on 2019-06-20.
- Legislativa. Invaznidruhy.nature.cz (March 28, 2013). Retrieved on 2014-05-15.
- "Alligator Snapping Turtle – National Wildlife Federation". Nwf.org. Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- "Alligator Snapping Turtle and Map Turtles Gain International Protection". US Fish and Wildlife Service. December 2005. Archived from the original on October 29, 2006.
- Recommendation for preliminary adoption of amendments to the list of endangered reptiles and amphibians in 312 IAC 9-5-4; Administrative Cause No. 10-170D. in.gov
- "Conservation". Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on January 6, 2013. Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- Kan. Admin. Reg. § 115-15-2(a)(7).
- Thomas, Pete (October 23, 2013). "Prehistoric-looking alligator snapping turtle is not wanted in Oregon". GrindTV.com. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Macrochelys temminckii |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Macrochelys temminckii. |
- Alligator vs. common snapping turtle – Chelydra.org
- "Care Sheet - Alligator Snapping Turtle".
- "CRUNCH History". Crunch, the alligator snapping turtle
- Dohnal, Martin (August 12, 2013). "Kajmanka supí zaútočila v Bavorsku na dítě. Městečko je na nohou". Deník.cz.
Further reading
- Behler JL, King FW (1979). The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Reptiles and Amphibians. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. 743 pp. ISBN 0-394-50824-6. (Macroclemys temmincki, pp. 436–437 + Plates 325, 326, 327).
- Goin CJ, Goin OB, Zug GR (1978). Introduction to Herpetology, Third Edition. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. xi + 378 pp. ISBN 0-7167-0020-4. (Macroclemys temmincki, pp. 77, 124, 256-257).
- Smith HM, Brodie ED Jr (1982). Reptiles of North America: A Guide to Field Identification. New York: Golden Press. 240 pp. ISBN 0307136663. (Macroclemys temmincki, pp. 38–39).
- Troost G (1835). In: Harlan R (1835). Medical and Physical Researches: or Original Memoirs in Medicine, Surgery, Physiology, Geology, Zoology, and Comparative Anatomy. Philadelphia: L.R. Bailey. xxxix + 653 pp. (Chelonura temminckii, new species, p. 158).
- Zim HS, Smith HM (1956). Reptiles and Amphibians: A Guide to Familiar American Species. Golden Nature Guides. New York: Simon and Schuster. 160 pp. (Macroclemys temmincki, pp. 25, 155).