Stockport–Stalybridge line
The Stockport–Stalybridge line is a railway line in Greater Manchester, England, running from Stockport northeast to Stalybridge, via Guide Bridge. The line is today mostly used by freight and empty stock workings, although it once had a frequent passenger service;[1] since 1992, it has been served by a single train run by Northern, now once a week in both directions, usually a Class 142 Pacer.
| Stockport–Stalybridge line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||
| Type | Heavy rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Locale | Greater Manchester | ||
| Termini | Stockport Stalybridge | ||
| Stations | |||
| Operation | |||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Operator(s) | Northern | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 8.14 mi (13.10 km) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| |||
| Stockport– Stalybridge line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This minimal service, termed a parliamentary train for historical reasons, avoids the official procedures of terminating a passenger service. The re-routeing of TransPennine Express services from Leeds to Manchester Piccadilly station and Manchester Victoria in May 1989 removed the main reason for its passenger service, with passengers who formerly used the Stalybridge–Stockport shuttle avoiding the need to change stations in Manchester, travelling via Manchester Piccadilly and changing there instead. The service was initially reduced to five trains per day (three in one direction and two the other) [2] but, by 1992, had been cut to its present minimal level. The northern part of the route (from Guide Bridge to Stalybridge) is now used by the re-routed express services between Leeds and Manchester Piccadilly.
The scarcity of services on the line has led to it becoming popular with rail enthusiasts, as well as real ale connoisseurs visiting the station buffet at Stalybridge.
The line serves the following places:
History
The southern stretch of the line between Stockport and Guide Bridge was built by the Manchester and Birmingham Railway, at around the time of its merger into the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). The contract was let to John Brogden and Sons in October 1845.[3]
The northern section from Guide Bridge to Stalybridge was built by the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway in 1845. This later became part of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR).
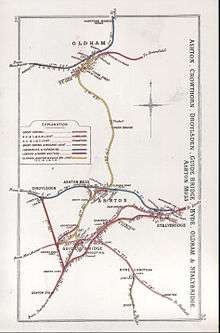
Guide Bridge avoiding line
Congestion around Guide Bridge led to the LNWR building a new line to avoid Guide Bridge station. Known as the Stalybridge Junction Railway, it ran from Denton Junction, then under the MS&LR main line east of Guide Bridge, and then ran parallel to the existing Guide Bridge-Stalybridge line, before joining the main line again just west of Stalybridge station. As well as relieving congestion, it also had the advantage of allowing LNWR trains to bypass MS&LR tracks altogether. The line was completed in 1893, with stations at Hooley Hill and Dukinfield and Ashton. A local Stockport-Stalybridge passenger service ran on this line until 25 September 1950. The line was closed completely in 1968 and was dismantled in the early 1970s. As it ran mostly on brick viaducts, which have since been demolished, little physical trace now remains of the line.[4][5]
Closure proposal
Network Rail, in their Route Utilisation Strategy (RUS) for the North West, proposed closure of Reddish South and Denton stations and withdrawal of the remaining passenger service. The report noted however that the cost of withdrawing the service (closure notices, dealing with objections, etc.) would be greater than the costs of operating the weekly service (Network Rail, in their North Western RUS, noted that the cost of each trip was just £96). The line itself would have remained open for empty stock transfers, freight and diverted passenger workings.[6] The threat was withdrawn in May 2007, possibly temporarily [7], when GMPTE suggested it was to support three trains per hour between Stockport and Manchester Victoria.[8]
In September 2006, Grand Central, an open access train operating company, had proposed using the line for passenger services between London Euston and Bradford Interchange via the West Coast Main Line, using Stockport, Guide Bridge and Stalybridge stations as a stop. These proposals were withdrawn in August 2008.
Metrolink proposal

It has been proposed that the line become a part of the Manchester Metrolink network.[9]
Service
This service previously operated on a Friday morning, leaving Stockport at 09:22 and arriving at Stalybridge at 09:42 (with the train reporting number 2J45[10][11]).
In the 20 May 2018 timetable changes, Northern introduced a second journey on the line, as well as shifting the day of operation to Saturday. The first train departs Stalybridge at 08:46 to arrive into Stockport at 09:09, this train will have the reporting number 2J44.[12] The train then makes a return journey leaving Stockport at 09:45 and arriving into Stalybridge at 10:06, with the original train reporting number, 2J45.[13] These services operate every Saturday from 26 May 2018, instead of Fridays as in previous years, and will call at the intermediate stations on both journeys. This means that Reddish South and Denton are now receiving two passenger services per week in the timetable for the first time since 1992.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stockport to Stalybridge Line. |
- Astley, Conrad (28 May 2004). "Ghost train in reverse gear". Manchester Evening News. Guardian Media Group. Retrieved 11 October 2006.
- Vallantine, Stuart (3 March 2007). "Point of No Return: All Aboard the Ghost Train". East of the M60. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- Directors’ Minutes: Manchester and Birmingham Railway Co, Public Record Office, RAIL 454/3 and the contract 454/11
- "Stalybridge Junction Railway". steamrailways.com. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- Suggitt, Gordon. Lost Railways of Merseyside & Greater Manchester. Countryside Books. pp. 114–115. ISBN 1-85306-869-1.
- Network Rail (10 November 2006). "North West Route Utilisation Strategy (draft)". Retrieved 14 November 2006.
- Rooth, Ben (4 May 2007). "Rail bosses lift axe threat". Manchester Evening News. M.E.N. Media. Retrieved 6 May 2007.
- Devine, Peter (2 May 2007). "Reddish station back on track". Stockport Express. M.E.N. Media. Retrieved 3 March 2008.
- http://www.mcrua.org.uk/chairmansblog/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Stockport-Rail-Strategy-January-2015.pdf
- "Section CL04 Stockport to Guide Bridge & Ashton Moss North Jn" (PDF). Working Timetable Book CL. Network Rail. 10 December 2017. p. 1, col. 3. Retrieved 21 December 2017.
- "Section YG01 Leeds and Wakefield Westgate to Guide Bridge" (PDF). Working Timetable Book YG. Network Rail. 10 December 2017. p. 65, col. 73. Retrieved 21 December 2017.
- 2J44 0846 Stalybridge to Stockport, 26 May 2018Realtime Trains website; Retrieved 7 May 2018
- 2J45 0945 Stockport to Stalybridge, 26 May 2018Realtime Trains website; Retrieved 7 May 2018