Sterile insect technique
The sterile insect technique (SIT)[1][2] is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects are released into the wild. The released insects are preferably male, as this is more cost-effective and the females may in some situations cause damage by laying eggs in the crop, or, in the case of mosquitoes, taking blood from humans. The sterile males compete with wild males to mate with the females. Females that mate with a sterile male produce no offspring, thus reducing the next generation's population. Sterile insects are not self-replicating and, therefore, cannot become established in the environment. Repeated release of sterile males over low population densities can further reduce and in cases of isolation eliminate pest populations, although cost-effective control with dense target populations is subjected to population suppression prior to the release of the sterile males.
.jpg)
The technique has successfully been used to eradicate the screw-worm fly (Cochliomyia hominivorax) from North and Central America. Many successes have been achieved for control of fruit fly pests, most particularly the Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata) and the Mexican fruit fly (Anastrepha ludens). Active research is being conducted to determine this technique's effectiveness in combatting the Queensland Fruit Fly (Bactrocera tyroni).
Sterilization is induced through the effects of irradiation on the reproductive cells of the insects. SIT does not involve the release of insects modified through transgenic (genetic engineering) processes.[3] Moreover, SIT does not introduce non-native species into an ecosystem.
History
The idea of using sterile males was first written about by the Russian geneticist A.S. Serebrovsky in 1940[4] but the English speaking world came up with the idea independently and applied it practically around the 1950s. Raymond Bushland and Edward Knipling developed the SIT to eliminate screw-worms preying on warm-blooded animals, especially cattle. They exploited the fact that female screw-worms mate only once to attack screw-worm reproduction. The larvae of these flies invade open wounds and eat into animal flesh, killing infected cattle within 10 days. In the 1950s, screw-worms caused annual losses to American meat and dairy supplies that were projected at above $200 million. Screw-worm maggots can also parasitize human flesh.

Bushland and Knipling began searching for an alternative to chemical pesticides in the late 1930s when they were working at the United States Department of Agriculture Laboratory in Menard, Texas. At that time, the screw-worm was devastating livestock herds across the American South. Red meat and dairy supplies were affected across Mexico, Central America, and South America.
Knipling developed the theory of autocidal control – breaking the pest's reproductive cycle. Bushland's enthusiasm for Knipling's theory sparked the pair to search for a way to rear flies in a "factory" setting, and to find an effective way to sterilize flies.
Their work was interrupted by World War II, but they resumed their efforts in the early 1950s with successful tests on the screw-worm population of Sanibel Island, Florida. The sterile insect technique worked; near eradication was achieved using X-ray-sterilized flies.
Successes
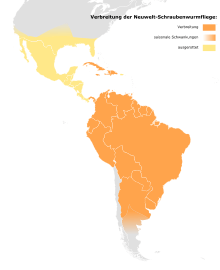
In 1954, the technique was used to eradicate screw-worms from the 176-square-mile (460 km2) island of Curaçao, off the coast of Venezuela. Screw-worms were eliminated in seven weeks, saving the domestic goat herds that were a source of meat and milk.
During the late 1950s to the 1970s, SIT was used to control the screw-worm population in the US. In the 1980s, Mexico and Belize eliminated their screw-worm problems with SIT. Eradication programs progressed across Central America in the 1990s, followed by the establishment of a biological barrier in Panama to prevent reinfestation from the south. The map shows the current and former distribution area and the approximate seasonal spread of the screw-worm fly.
In 1991, Knipling and Bushland's technique halted a serious outbreak of New World screw-worm in northern Africa. Programs against the Mediterranean fruit fly in Mexico, Florida and California use the SIT to maintain their fly-free status. The technique was used to eradicate the melon fly from Okinawa and in the fight against the tsetse fly in Africa.
The technique has suppressed insects threatening livestock, fruit, vegetable, and fiber crops. The technique was lauded for its environmental attributes: it leaves no residues and has no (direct) negative effect on nontarget species.
The technique has been a boon in protecting the agricultural products to feed the world's human population. Both Bushland and Knipling received worldwide recognition for their leadership and scientific achievements, including the 1992 World Food Prize.[5] The technique were hailed by former U.S. Secretary of Agriculture Orville Freeman as "the greatest entomological achievement of the 20th century."
African trypanosomiasis
Sleeping sickness or African trypanosomiasis is a parasitic disease in humans. Caused by protozoa of genus Trypanosoma and transmitted by the tsetse fly, the disease is endemic in regions of sub-Saharan Africa, covering about 36 countries and 60 million people. An estimated 50,000 – 70,000 people are infected and about 40,000 die every year. The three most recent epidemics occurred in 1896 -1906, 1920, and 1970.
Studies of the tsetse fly show that females generally mate only once (occasionally twice). Studies found this process to be effective in preventing the scourge.
Successful programs
- The screw-worm fly (Cochliomyia hominivorax) was eradicated from the United States, Mexico, Central America, Puerto Rico and Libya.[6]
- The Mexican fruit fly (Anastrepha ludens, Loew) was eradicated from most of northern Mexico.
- The tsetse fly was eradicated from Zanzibar.
- The Mediterranean fruit fly (Medfly, Ceratitis capitata, Wiedemann) was eradicated from the northern part of Chile and southern parts of Argentina, Peru and Mexico. It is being suppressed by SIT in fruit-producing areas of Croatia, Israel, South Africa and Spain.
- The codling moth (Cydia pomonella) is being effectively suppressed in parts of British Columbia, Canada,[7]
- The pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) eradicated from southwestern USA and northwestern Mexico.
- The false codling moth (Thaumatotibia leucotreta) is being effectively suppressed in parts of South Africa.
- The cactus moth (Cactoblastis cactorum) was eradicated from an outbreak in Yucatán, Mexico.
- The melon fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae, Coquillett) was eradicated from Okinawa.[8]
- The onion fly (Delia antiqua) managed in onion production areas in the Netherlands[9]
Targets
- Anopheles mosquito – malaria[10] vector, example Anopheles arabiensis.
- Tsetse fly (Glossina spp.) – vector of sleeping sickness in humans and nagana in livestock.
- Painted apple moth in Auckland, New Zealand
- Aedes aegypti [11] and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, vectors for filariasis, dengue, yellow fever, chikungunya, and the Zika virus[12][13]
- Fruit fly species, including Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata), Caribbean fruit fly (Anastrepha suspensa) and Mexican fruit fly (Anastrepha ludens) in Americas, Queensland fruit fly (Bactrocera tryoni) in Australia, the oriental fruit fly (Bactrocera dorsalis) in Hawaii, and several other Bactrocera spp. across Australia, Asia, and Oceania: FAO/IAEA[14] lists 39 different SIT facilities (DIR-SIT)[15] across the globe, aiding the retrieval of information on mass production and on radiation doses (IDIDAS).[16] It includes data on both the radiation dose required for the disinfestation of generic commodity groups and the radiation dose used to induce sterility for pest control through the SIT.
History of transboundary shipment of sterile insects
Transboundary shipment of sterile insects has taken place on a continuous basis for 55 years (since 1963). The total number of sterile insects shipped has been estimated at more than one trillion in thousands of shipments across borders to 23 recipient countries from 50 sterile insect factories in 25 countries. During this long period and many precedents, no problems associated with possible hazards have been identified, and thus the shipment of sterile insects have never been subjected to any regulatory action. The table shows the history of transboundary shipments which started in 1963 with the shipments of sterile Mexican fruit fly (Anastrepha ludens, Loew), from Monterrey, Mexico, to Texas, US.[17]
Drawbacks
- Naturally low population periods or repeated pesticide treatment are sometimes required to suppress populations before the use of sterile insects.
- Sex separation can be difficult,[11] though this can be easily performed on a large scale where genetic sexing systems have been developed as for the Mediterranean fruit fly.
- Radiation, transport and release treatments can reduce male mating fitness.
- The technique is species-specific. For instance, the technique must be implemented separately for each of the 6 economically important tsetse fly species.
- Mass rearing and irradiation[18][19] require precision processes. Failures have occurred when unexpectedly fertile breeding males were released.
- Area-wide approach is more effective, as migration of wild insects from outside the control area could recreate the problem.
- The cost of producing sufficient sterile insects can be prohibitive in some locations [20] but decreases with economies of scale.
Conclusion and perspectives
Biotechnological approaches based on genetically modified organism (transgenic organisms) are still under development. However, since no legal framework exists to authorize the release of such organisms in nature,[21][22] sterilization by irradiation remains the most used technique. A meeting was held at FAO headquarters in Rome, 8 to 12 April 2002 on "Status and Risk Assessment of the Use of Transgenic Arthropods in Plant Protection". The resulting proceedings[23] of the meeting have been used by the North American Plant Protection Organization (NAPPO) to develop NAPPO Regional Standard No. 27[24] on "Guidelines for Importation and Confined Field release of Transgenic Arthropods", which might provide the basis for the rational development of the use of transgenic arthropods.
Economic benefits
Economic benefits have been demonstrated. The direct benefits of screwworm eradication to the North and Central American livestock industries are estimated to be over $1.5 billion/year, compared with an investment over half a century around $1 billion. Mexico protects a fruit and vegetable export market of over $3 billion/year through an annual investment around $25 million. Medfly-free status has been estimated to have opened markets for Chile's fruit exports up to $500 million. Eradication of tsetse has resulted in major socio-economic benefits for Zanzibar.[25] When implemented on an area-wide basis and a scaled rearing process, SIT is cost-competitive with conventional control, in addition to its environmental benefits.[26]
References
- Dyck, V.A.; Hendrichs, J.; Robinson, A.S., eds. (2005). Sterile Insect Technique: Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. ISBN 1-4020-4050-4.
- Vreysen, M. J. B., Robinson, A. S., and Hendrichs, J. (2007). "Area-wide Control of Insect Pests, From Research to Field Implementation." pp. 789 Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
- (in French) Luigi D'Andrea, "Des insectes transgéniques contre la dengue. Sous quel contrôle et avec quels dangers ?", Stop OGM infos, no. 52, 2013.
- Serebrovsky, A.S. (1940). "[On the possibility of a new method for the control of insect pests]". Zool. Zh. 19: 618–630.
- https://www.worldfoodprize.org/en/laureates/19871999_laureates/1992_knipling_and_bushland/
- The Area-Wide Sterile Insect Technique for Screwworm (Diptera: Calliphoridae) Eradication
- Okanagan-Kootenay Sterile Insect Release (SIR) Program
- The Sterile Insect Technique: Example of Application to Melon Fly Bactrocera cucurbitae. (accessed December 13, 2016)
- List of SIT facilities
- Benedict Mark Q, Alan S Robinson and Bart GJ Knols (edts.) 2009. Development of the sterile insect technique for African malaria vectors. Malaria Journal Volume 8 Suppl 2"
- Mamai, Wadaka; Maiga, Hamidou; Somda, Nanwintoum Séverin Bimbilé; Wallner, Thomas; Konczal, Anna; Yamada, Hanano; Bouyer, Jérémy (2020). "Aedes aegypti larval development and pupal production in the FAO/IAEA mass-rearing rack and factors influencing sex sorting efficiency". Parasite. 27: 43. doi:10.1051/parasite/2020041. ISSN 1776-1042.

- A Genetically Engineered Swat
- Chen, Lin H.; Hamer, Davidson H. (2016). "Zika Virus: Rapid Spread in the Western Hemisphere". Annals of Internal Medicine. 164 (9): 613–5. doi:10.7326/M16-0150. ISSN 0003-4819. PMID 26832396.
- IAEA
- World-Wide Directory of SIT Facilities
- International Database on Insect Disinfestation and Sterilization
- Read more information on Packing, Shipping, Holding and Release of sterile insects.
- FAO/IAEA/USDA-2003-Manual for Product Quality Control and Shipping Procedures for Sterile Mass-Reared Tephritid Fruit Flies, Version 5.0. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria. 85pp.
- FAO/IAEA. 2006. FAO/IAEA Standard Operating Procedures for Mass-Rearing Tsetse Flies, Version 1.0. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria. 239pp.
- Mamai, Wadaka; Bimbilé Somda, Nanwintoum Sévérin; Maiga, Hamidou; Konczal, Anna; Wallner, Thomas; Bakhoum, Mame Thierno; Yamada, Hanano; Bouyer, Jérémy (2019). "Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae powder as a larval diet ingredient for mass-rearing Aedes mosquitoes". Parasite. 26: 57. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019059. ISSN 1776-1042.

- Knols BG and Louis C. 2005. Bridging laboratory and fields research for genetic control of disease vectors. In proceedings of the joint WHO/TDR, NIAID, IAEA and Frontis workshop on bridging laboratory and field research for genetic control of disease vectors, Nairobi, Kenya 14–16 July 2004 Wageningen. Frontis
- Scott, TW; Takken, W; Knols, BG; Boete, C (2002). "The ecology of genetically modified mosquitoes". Science. 298 (5591): 117–119. doi:10.1126/science.298.5591.117.
- Status and risk assessment of the use of transgenic arthropods in plant protection (PDF). 2002. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- NAPPO Regional Standard No. 27 Archived 2008-08-20 at the Wayback Machine
- "Tsetse Eradication: Zanzibar" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 19, 2005. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- Hendrichs, Jorge, and Alan Robinson. 2009. Sterile Insect Technique. In Encyclopedia of Insects, ed. Vincent H. Resh and Ring T. Carde. pp. 953–957. Second Edition. London, Oxford, Boston, New York and San Diego: Academic Press, Elsevier Science Publisher.