Saccharum officinarum
Saccharum officinarum is a large, strong-growing species of grass in the genus Saccharum. Its stout stalks are rich in sucrose, a simple sugar which accumulates in the stalk internodes. It originated in New Guinea[1]. It arrived in the New World with the Spanish and is now cultivated in tropical and subtropical countries worldwide for the production of sugar, ethanol and other products.
| Saccharum officinarum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Saccharum officinarum growing in Mozambique | |
| Harvesting sugarcane by hand | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Saccharum |
| Species: | S. officinarum |
| Binomial name | |
| Saccharum officinarum | |
Saccharum officinarum is one of the most productive and most intensively cultivated kinds of sugarcane. It can interbreed with other sugarcane species, such as Saccharum sinense and Saccharum barberi. The major commercial cultivars are complex hybrids.[2] About 70% of the sugar produced worldwide comes from Saccharum officinarum and hybrids using this species.[3]
Origin
There are two centers of domestication for sugarcane: one for Saccharum officinarum by Papuans in New Guinea and another for Saccharum sinense by Austronesians in Taiwan and southern China. Papuans and Austronesians originally primarily used sugarcane as food for domesticated pigs. The spread of both S. officinarum and S. sinense is closely linked to the migrations of the Austronesian peoples. Saccharum barberi was only cultivated in India after the introduction of S. officinarum.[4][5]
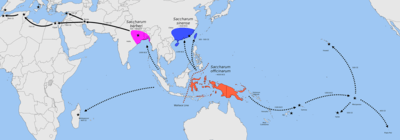
Saccharum officinarum was first domesticated in New Guinea and the islands east of the Wallace Line by Papuans, where it is the modern center of diversity. Beginning at around 6,000 BP it was selectively bred from the native Saccharum robustum. From New Guinea it spread westwards to Island Southeast Asia after contact with Austronesians, where it hybridized with Saccharum spontaneum.[5]
The second domestication center is mainland southern China and Taiwan where S. sinense was a primary cultigen of the Austronesian peoples. Words for sugarcane exist in the Proto-Austronesian languages in Taiwan, reconstructed as *təbuS or **CebuS, which became *tebuh in Proto-Malayo-Polynesian. It was one of the original major crops of the Austronesian peoples from at least 5,500 BP. Introduction of the sweeter S. officinarum may have gradually replaced it throughout its cultivated range in Island Southeast Asia.[7][8][6][9][10]
From Island Southeast Asia, S. officinarum was spread eastward into Polynesia and Micronesia by Austronesian voyagers as a canoe plant by around 3,500 BP. It was also spread westward and northward by around 3,000 BP to China and India by Austronesian traders, where it further hybridized with Saccharum sinense and Saccharum barberi. From there it spread further into western Eurasia and the Mediterranean.[5][6]
Description
Saccharum officinarum, a perennial plant, grows in clumps consisting of a number of strong unbranched stems. A network of rhizomes forms under the soil which sends up secondary shoots near the parent plant. The stems vary in colour, being green, pinkish, or purple and can reach 5 m (16 ft) in height. They are jointed, nodes being present at the bases of the alternate leaves. The internodes contain a fibrous white pith immersed in sugary sap. The elongated, linear, green leaves have thick midribs and saw-toothed edges and grow to a length of about 30 to 60 cm (12 to 24 in) and width of 5 cm (2.0 in). The terminal inflorescence is a panicle up to 60 cm (24 in) long, a pinkish plume that is broadest at the base and tapering towards the top. The spikelets are borne on side branches and are about 3 mm (0.12 in) long and are concealed in tufts of long, silky hair. The fruits are dry and each one contains a single seed.[11][12] Sugarcane harvest typically occurs before the plants flower, as the flowering process causes a reduction in sugar content.[13]
Uses
Portions of the stem of this and several other species of sugarcane have been used from ancient times for chewing to extract the sweet juice. It was cultivated in New Guinea about 8000 years ago for this purpose. Extraction of the juice and boiling to concentrate it was probably first done in India more than 2000 years ago.[11]
Saccharum officinarum and its hybrids are grown for the production of sugar, ethanol, and other industrial uses in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The stems and the byproducts of the sugar industry are used for feeding to livestock. Pigs fed on sugarcane juice and a soy-based protein supplement produced stronger piglets that grew faster than those on a more conventional diet.[14] As its specific name (officinarum, "of dispensaries") implies, it is also used in traditional medicine both internally and externally.[11]
References
- In New Guinea, according to sources cited by Christian Daniels in Joseph Needham, Science and Civilisation in China, Volume 6.3, p. 129ff
- Vilela; Del-Bem; et al. (2017). "Analysis of Three Sugarcane Homo/Homeologous Regions Suggests Independent Polyploidization Events of Saccharum officinarum and Saccharum spontaneum". Genome Biology and Evolution. 9 (2): 266–278. doi:10.1093/gbe/evw293. PMC 5381655. PMID 28082603.
- "Plants & Fungi: Saccharum officinarum (sugar cane)". Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew. Archived from the original on 2012-06-04.
- Daniels, John; Daniels, Christian (April 1993). "Sugarcane in Prehistory". Archaeology in Oceania. 28 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.1993.tb00309.x.
- Paterson, Andrew H.; Moore, Paul H.; Tom L., Tew (2012). "The Gene Pool of Saccharum Species and Their Improvement". In Paterson, Andrew H. (ed.). Genomics of the Saccharinae. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 43–72. ISBN 9781441959478.
- Daniels, Christian; Menzies, Nicholas K. (1996). Needham, Joseph (ed.). Science and Civilisation in China: Volume 6, Biology and Biological Technology, Part 3, Agro-Industries and Forestry. Cambridge University Press. pp. 177–185. ISBN 9780521419994.
- Blust, Robert (1984–1985). "The Austronesian Homeland: A Linguistic Perspective". Asian Perspectives. 26 (1): 44–67.CS1 maint: date format (link)
- Spriggs, Matthew (2 January 2015). "Archaeology and the Austronesian expansion: where are we now?". Antiquity. 85 (328): 510–528. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00067910.
- Aljanabi, Salah M. (1998). "Genetics, phylogenetics, and comparative genetics of Saccharum L., a polysomic polyploid Poales: Andropogoneae". In El-Gewely, M. Raafat (ed.). Biotechnology Annual Review. 4. Elsevier Science B.V. pp. 285–320. ISBN 9780444829719.
- Baldick, Julian (2013). Ancient Religions of the Austronesian World: From Australasia to Taiwan. I.B.Tauris. p. 2. ISBN 9780857733573.
- "Saccharum officinarum". Kew Royal Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 2012-09-21.
- "Saccharum officinarum L." FAO. Retrieved 2012-09-21.
- "The Biology and Ecology of Sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrids) in Australia, Australian Government, Department of Health and Ageing, Office of the Gene Technology Regulator, 2004; p. 10.
- "Sugar cane". Feeding pigs in the tropics. FAO. Retrieved 2012-09-21.